Effective Nuclear charge
... •Effective nuclear charge (Zeff): actual charge _________________________ •Main concept of Ch. 7 ...
... •Effective nuclear charge (Zeff): actual charge _________________________ •Main concept of Ch. 7 ...
Lecture 1.
... Due to the nucleus exists and the nucleus stays in one volume, there must be a force which stick the protons together. Definition (force inside nucleus = nuclear force): The force which acts in between nucleons (inside nucleus) use to call as nuclear force. It is a very intense force but it has a ve ...
... Due to the nucleus exists and the nucleus stays in one volume, there must be a force which stick the protons together. Definition (force inside nucleus = nuclear force): The force which acts in between nucleons (inside nucleus) use to call as nuclear force. It is a very intense force but it has a ve ...
S1-2-04 - Element Builder
... of Elements which can be used to identify patterns of differences and similarities between elements. This simulation will enhance the knowledge of atoms, molecules, fundamental properties of the atom and the periodic table of elements. Students will have the opportunity to predict, manipulate, const ...
... of Elements which can be used to identify patterns of differences and similarities between elements. This simulation will enhance the knowledge of atoms, molecules, fundamental properties of the atom and the periodic table of elements. Students will have the opportunity to predict, manipulate, const ...
Standard Model
... in quantum mechanics and all of physics and chemistry • Brought quantum theory from real to imaginary numbers! 1926 – The Schrodinger Equation • In classical mechanics, Fnet = ma predicts all future behaviour • In quantum mechanics, Schrodinger’s equation predicts all future behaviour Published his ...
... in quantum mechanics and all of physics and chemistry • Brought quantum theory from real to imaginary numbers! 1926 – The Schrodinger Equation • In classical mechanics, Fnet = ma predicts all future behaviour • In quantum mechanics, Schrodinger’s equation predicts all future behaviour Published his ...
Mineralogy and the Development of Modern Chemistry
... It was recognized in about 1870 that if elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight, there is a periodic repetition of chemical properties ...
... It was recognized in about 1870 that if elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight, there is a periodic repetition of chemical properties ...
Test on Newton`s Laws and Momentum - science
... This question is about an alpha particle making a head on collision with a gold nucleus. (a) (i) When the alpha particle is at a large distance from the gold nucleus it has a kinetic energy of 7.6 10–13 J. Show that its speed is about 1.5 107 m s–1. mass of alpha = 6.6 x 10–27 kg. ...
... This question is about an alpha particle making a head on collision with a gold nucleus. (a) (i) When the alpha particle is at a large distance from the gold nucleus it has a kinetic energy of 7.6 10–13 J. Show that its speed is about 1.5 107 m s–1. mass of alpha = 6.6 x 10–27 kg. ...
Recitation 3
... Problem 20. In 1911, Ernest Rutherford and his assistants Hans Geiger and Ernest Mardsen conducted an experiment in which they scattered alpha particles from thin sheets of gold. An alpha particle, having a charge of qα = +2e and a mass of m = 6.64 · 10−27 kg is a product of certain radioactive deca ...
... Problem 20. In 1911, Ernest Rutherford and his assistants Hans Geiger and Ernest Mardsen conducted an experiment in which they scattered alpha particles from thin sheets of gold. An alpha particle, having a charge of qα = +2e and a mass of m = 6.64 · 10−27 kg is a product of certain radioactive deca ...
Electrons in Atoms - Brunswick City Schools / Homepage
... • Electrons are thought of waves confined to the space around the atomic nucleus. The frequency of the electrons is based on the type of element. ...
... • Electrons are thought of waves confined to the space around the atomic nucleus. The frequency of the electrons is based on the type of element. ...
1st Term Review
... 14. Based on the gold foil experiment, what did Rutherford conclude about the atom? 15. An atom of chromium-60 contains how many protons, neutron and electrons? 16. What is the difference between a compound and an element? 17. What is the electron configuration of a neutral calcium atom? 18. Atomic ...
... 14. Based on the gold foil experiment, what did Rutherford conclude about the atom? 15. An atom of chromium-60 contains how many protons, neutron and electrons? 16. What is the difference between a compound and an element? 17. What is the electron configuration of a neutral calcium atom? 18. Atomic ...
introduction to chemistry
... an element that retains all the properties of that element. Properties of atoms determine the structure and properties of the matter they compose Our understanding of the structure of atoms based on scientific models, not observation ...
... an element that retains all the properties of that element. Properties of atoms determine the structure and properties of the matter they compose Our understanding of the structure of atoms based on scientific models, not observation ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Ector County ISD.
... during, and simultaneous to, α or β radioactive decay. X-rays, emitted during the beta decay of cobalt-60, are a common example of gamma radiation. ...
... during, and simultaneous to, α or β radioactive decay. X-rays, emitted during the beta decay of cobalt-60, are a common example of gamma radiation. ...
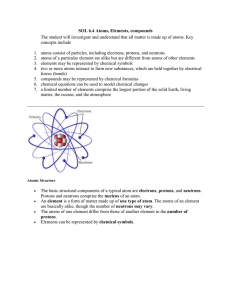
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
... atoms of a particular element are alike but are different from atoms of other elements elements may be represented by chemical symbols two or more atoms interact to form new substances, which are held together by electrical forces (bonds) 5. compounds may be represented by chemical formulas 6. chemi ...
... atoms of a particular element are alike but are different from atoms of other elements elements may be represented by chemical symbols two or more atoms interact to form new substances, which are held together by electrical forces (bonds) 5. compounds may be represented by chemical formulas 6. chemi ...
ChLM Final Review Name: Period: Base Knowledge 1. Classify the
... 25. What kind of particles did Rutherford shoot at the thin gold foil? _________________ ...
... 25. What kind of particles did Rutherford shoot at the thin gold foil? _________________ ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.