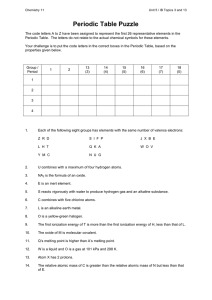
PPT
... the nucleus of the elements. The number of protons is called the atomic number. (In the periodic table, the elements are arranged by their atomic number) ...
... the nucleus of the elements. The number of protons is called the atomic number. (In the periodic table, the elements are arranged by their atomic number) ...
Atomic Radius
... Why? The nuclear attraction is less for an increased number of electrons. Extra electrons repel each other and ...
... Why? The nuclear attraction is less for an increased number of electrons. Extra electrons repel each other and ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... 23. What are the electronegativity difference ranges for nonpolar bonds? For polar bonds? For ionic bonds? ...
... 23. What are the electronegativity difference ranges for nonpolar bonds? For polar bonds? For ionic bonds? ...
Name: Date: Performances of Understanding:
... A. The core, valence, radius (CVR) model separates the ___________ level electrons from the _________ level electrons. 1. To determine the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) on an electron, subtract the number of ___________ shell electrons from the number of _______ in the nucleus. a. Effective nuclea ...
... A. The core, valence, radius (CVR) model separates the ___________ level electrons from the _________ level electrons. 1. To determine the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) on an electron, subtract the number of ___________ shell electrons from the number of _______ in the nucleus. a. Effective nuclea ...
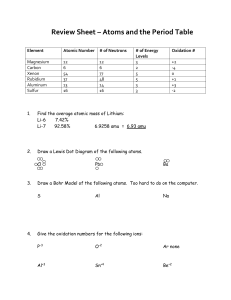
Objective 2 Average Atomic Mass
... The discovery of the (11) ___________________ in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen opened a whole new field of research. Among those who worked in this new field were Pierre and Marie Curie. The Curies discovered that some forms of matter give off (12) ________________, a combination of particles and energy. ...
... The discovery of the (11) ___________________ in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen opened a whole new field of research. Among those who worked in this new field were Pierre and Marie Curie. The Curies discovered that some forms of matter give off (12) ________________, a combination of particles and energy. ...
Nuclear force
... force (nuclear force), but a neutron exerts only strong force and does not feel any electrostatic interaction, because it is not carrying charge. The nuclear force is a force far stronger than electromagnetic forces, but it has a very short range of action. In fact, it acts only on distances of the ...
... force (nuclear force), but a neutron exerts only strong force and does not feel any electrostatic interaction, because it is not carrying charge. The nuclear force is a force far stronger than electromagnetic forces, but it has a very short range of action. In fact, it acts only on distances of the ...
study guide first semester chemistry
... 1. Write the balanced equation for the following: (include the state of each reactant and product) a. magnesium reacts with nitrogen to produce magnesium nitride. (3Mg(s) + N2(g) Mg3N2(s) b. silver nitrate reacts with copper to form copper(II) nitrate and silver. ...
... 1. Write the balanced equation for the following: (include the state of each reactant and product) a. magnesium reacts with nitrogen to produce magnesium nitride. (3Mg(s) + N2(g) Mg3N2(s) b. silver nitrate reacts with copper to form copper(II) nitrate and silver. ...
Glowing Tubes for Signs, Television Sets, and Computers
... passes between the electrodes. The fast-moving particles excite the gas in the tube, causing a glow between the plates. ...
... passes between the electrodes. The fast-moving particles excite the gas in the tube, causing a glow between the plates. ...
biol 1406 chapter 3: water
... 5. Trace elements, such as iron and magnesium, are present in living things in very large amounts. _____________________________ 6. The properties of elements are determined by the structures of their atoms. ________________________ ...
... 5. Trace elements, such as iron and magnesium, are present in living things in very large amounts. _____________________________ 6. The properties of elements are determined by the structures of their atoms. ________________________ ...
Atomic number
... element. Everything is made of atoms Proton: positive particle in the nucleus Neutron: neutral particle in the nucleus Electron: tiny negative charge outside the nucleus Atoms are mostly…. … empty space! Element: a substance made of only one kind of atom, cannot be chemically or physically separated ...
... element. Everything is made of atoms Proton: positive particle in the nucleus Neutron: neutral particle in the nucleus Electron: tiny negative charge outside the nucleus Atoms are mostly…. … empty space! Element: a substance made of only one kind of atom, cannot be chemically or physically separated ...
On the Discovery of the Atomic Nucleus
... nucleus was discovered. In the early 20th century two different models were proposed to describe an atom. One was the watermelon model (alternatively known as the “plum pudding” model), which was proposed by J. J. Thomson. This model posited that small, negatively charged “plums” (now called electro ...
... nucleus was discovered. In the early 20th century two different models were proposed to describe an atom. One was the watermelon model (alternatively known as the “plum pudding” model), which was proposed by J. J. Thomson. This model posited that small, negatively charged “plums” (now called electro ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.