3rd Quarter Test
... 16) The percent by mass of oxygen in MgO (gram formula mass = 40) is closest to a) 16 % b) 24 % c) 40 % d) 60 % 17) What is the mass in grams of 2.00 moles of CaCl2? a) 1.00 b) 2.00 c) 111 ...
... 16) The percent by mass of oxygen in MgO (gram formula mass = 40) is closest to a) 16 % b) 24 % c) 40 % d) 60 % 17) What is the mass in grams of 2.00 moles of CaCl2? a) 1.00 b) 2.00 c) 111 ...
Rutherford`s Atomic Model
... (1) White light produces a continuous spectrum. (2) Accelerating charges release energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. (3) α particles can be scattered at large angles when directing onto a thin gold foil. A. (2) only B. (3) only C. (1) and (2) only D. (1) and (3) only Answer: A ...
... (1) White light produces a continuous spectrum. (2) Accelerating charges release energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. (3) α particles can be scattered at large angles when directing onto a thin gold foil. A. (2) only B. (3) only C. (1) and (2) only D. (1) and (3) only Answer: A ...
Year End P1 IB1 HL Physics 2013
... 1. When a force F moves its point of application through a displacement s in the direction of the force, the work W done by the force is given by W = Fs. How many vector quantities and scalar quantities does this equation contain? A one scalar quantity and two vector quantities B one vector quanti ...
... 1. When a force F moves its point of application through a displacement s in the direction of the force, the work W done by the force is given by W = Fs. How many vector quantities and scalar quantities does this equation contain? A one scalar quantity and two vector quantities B one vector quanti ...
Chapter Two Review
... What is the basic unit of matter? --atom What three particles make up an atom? --proton, neutron, electron What particle(s) is/are located in the nucleus of an atom? -protons, neutrons Atomic number is the number of what? --protons What does atomic mass mean? --number of protons and neutro ...
... What is the basic unit of matter? --atom What three particles make up an atom? --proton, neutron, electron What particle(s) is/are located in the nucleus of an atom? -protons, neutrons Atomic number is the number of what? --protons What does atomic mass mean? --number of protons and neutro ...
atomic number
... All matter is made of tiny particles, called atoms. Atoms are neither subdivided, created nor destroyed. (Dalton based this hypothesis on the law of conservation of mass) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratios, to form chemical compounds with more than one ratio being poss ...
... All matter is made of tiny particles, called atoms. Atoms are neither subdivided, created nor destroyed. (Dalton based this hypothesis on the law of conservation of mass) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratios, to form chemical compounds with more than one ratio being poss ...
Elements Compounds Mixtures
... salad, BLT; PB&J HOMOGENEOUS • Two or more substances evenly mixed. • You can NOT see the different substances, even with a microscope! • Examples: gatorade, salt water, brass, air ...
... salad, BLT; PB&J HOMOGENEOUS • Two or more substances evenly mixed. • You can NOT see the different substances, even with a microscope! • Examples: gatorade, salt water, brass, air ...
AP Chemistry
... 3. Alpha (Â) particles - nuclear particle with a 2+ charge D. The Nuclear Atom - Rutherford's Metal Foil Experiment 1. Most alpha particles pass straight through thin metal foil 2. Some particles were greatly deflected ("like a howitzer shell bouncing off of a piece of paper") a. Could not have been ...
... 3. Alpha (Â) particles - nuclear particle with a 2+ charge D. The Nuclear Atom - Rutherford's Metal Foil Experiment 1. Most alpha particles pass straight through thin metal foil 2. Some particles were greatly deflected ("like a howitzer shell bouncing off of a piece of paper") a. Could not have been ...
UQ3
... 2. Cesium-137 radioactively decays via beta particle decay. Write the nuclear equation for this beta particle decay process and identify the nuclide produced. ...
... 2. Cesium-137 radioactively decays via beta particle decay. Write the nuclear equation for this beta particle decay process and identify the nuclide produced. ...
Snímek 1
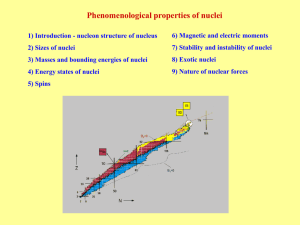
... Nuclei far away from stability curve: 1) with large excess of neutrons 2) with large deficit of neutrons (excess of protons) Effort to study all isotopes between boundaries of proton and neutron stability. Double magic nuclei: 100Sn is such nucleus with maximal numbers of neutrons and protons Firstl ...
... Nuclei far away from stability curve: 1) with large excess of neutrons 2) with large deficit of neutrons (excess of protons) Effort to study all isotopes between boundaries of proton and neutron stability. Double magic nuclei: 100Sn is such nucleus with maximal numbers of neutrons and protons Firstl ...
Lecture notes chapter 4
... Element: is a substance that consists of identical atoms (hydrogen, oxygen, and Iron). 116 elements are known (88 occur in nature and chemist have made the others in the lab). Symbols of elements: often an element’s name is derived from a Greek, Latin, or German word that describes some property of ...
... Element: is a substance that consists of identical atoms (hydrogen, oxygen, and Iron). 116 elements are known (88 occur in nature and chemist have made the others in the lab). Symbols of elements: often an element’s name is derived from a Greek, Latin, or German word that describes some property of ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.