final poster
... protons and neutrons that are surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The nucleus is the center of the atom. An atom is an extremely small particle of matter that retains its identity during chemical reactions. ...
... protons and neutrons that are surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The nucleus is the center of the atom. An atom is an extremely small particle of matter that retains its identity during chemical reactions. ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... table. Other isotopes of krypton are known, but they do not appear in natural samples because they are unstable (radioactive). ...
... table. Other isotopes of krypton are known, but they do not appear in natural samples because they are unstable (radioactive). ...
Effects of atomic electrons on nuclear stability and radioactive decay
... nuclei, which are stable in neutral atoms, become -active when atoms are completely ionized. This means that by affecting electron shells one can alter conditions of nuclear -stability and thus initiate nuclear transmutations by means of weak interactions. 3. We have developed a phenomenological m ...
... nuclei, which are stable in neutral atoms, become -active when atoms are completely ionized. This means that by affecting electron shells one can alter conditions of nuclear -stability and thus initiate nuclear transmutations by means of weak interactions. 3. We have developed a phenomenological m ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... Chemistry Study Guide Atoms and Subatomic Particles Atom. Al matter is made up of unique particles called atoms. An atom contains: o Protons- Positively charged; have atomic mass of one; Located in the nucleus of the atom. o Neutrons- Neutral in charge; the same mass as the proton; also located in ...
... Chemistry Study Guide Atoms and Subatomic Particles Atom. Al matter is made up of unique particles called atoms. An atom contains: o Protons- Positively charged; have atomic mass of one; Located in the nucleus of the atom. o Neutrons- Neutral in charge; the same mass as the proton; also located in ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... Chemistry Study Guide Atoms and Subatomic Particles Atom. Al matter is made up of unique particles called atoms. An atom contains: o Protons- Positively charged; have atomic mass of one; Located in the nucleus of the atom. o Neutrons- Neutral in charge; the same mass as the proton; also located in ...
... Chemistry Study Guide Atoms and Subatomic Particles Atom. Al matter is made up of unique particles called atoms. An atom contains: o Protons- Positively charged; have atomic mass of one; Located in the nucleus of the atom. o Neutrons- Neutral in charge; the same mass as the proton; also located in ...
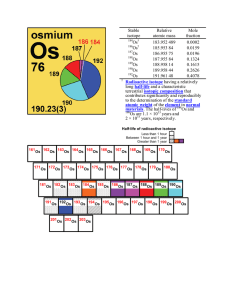
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... either positive or negative charge (an electron or positron). [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric charge and a rest mass of about 9.109 × 10–31 kg. element (chemical element) – a species of atoms; all atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus. ...
... either positive or negative charge (an electron or positron). [return] electron – elementary particle of matter with a negative electric charge and a rest mass of about 9.109 × 10–31 kg. element (chemical element) – a species of atoms; all atoms with the same number of protons in the atomic nucleus. ...
Sep 2
... Atomic theory: John Dalton, 1808 1. Atoms = indestructible, smallest unit of element to retain identity 2. An element has all the same type of atoms 3. A compound contains atoms of 2 or more elements in a fixed ratio ...
... Atomic theory: John Dalton, 1808 1. Atoms = indestructible, smallest unit of element to retain identity 2. An element has all the same type of atoms 3. A compound contains atoms of 2 or more elements in a fixed ratio ...
Topic 7: Atomic and nuclear physics 7.1 The atom
... with a specific number of protons and neutrons) but only about 300 of them are stable, the rest are unstable. • As the number of protons in the nucleus increases the electrostatic repulsion between them grows, but the strong nuclear force does not grow proportionally since it is a short range force. ...
... with a specific number of protons and neutrons) but only about 300 of them are stable, the rest are unstable. • As the number of protons in the nucleus increases the electrostatic repulsion between them grows, but the strong nuclear force does not grow proportionally since it is a short range force. ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... Nuclear fission is a process by which a large atomic nucleus breaks up to form smaller ones. This process is accompanied by the production of a great deal of energy. This process is currently utilized in nuclear reactors and atomic bombs. Nuclear fusion is a process by which small nuclei combine ...
... Nuclear fission is a process by which a large atomic nucleus breaks up to form smaller ones. This process is accompanied by the production of a great deal of energy. This process is currently utilized in nuclear reactors and atomic bombs. Nuclear fusion is a process by which small nuclei combine ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... 2. An electron carries one unit of negative charge and its mass is about 1/1840 the mass of a hydrogen atom or 9.11 x 10-28g (more precisely, 9.10939 × 10–28 g); charge and mass of electron determined by Robert Millikan in 1916 B. Protons and Neutrons 1. Protons have a positive charge, cathode ray t ...
... 2. An electron carries one unit of negative charge and its mass is about 1/1840 the mass of a hydrogen atom or 9.11 x 10-28g (more precisely, 9.10939 × 10–28 g); charge and mass of electron determined by Robert Millikan in 1916 B. Protons and Neutrons 1. Protons have a positive charge, cathode ray t ...
PHET Lab Build an Atom
... 5) Based on what you’ve observed, which two particles appear to determine the mass of the overall atom? Where in the atom are these two particles located? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ...
... 5) Based on what you’ve observed, which two particles appear to determine the mass of the overall atom? Where in the atom are these two particles located? _______________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ...
Syllabus overview
... rate of decay decreases exponentially with time. Exponential decay need not be treated analytically. It is sufficient to know that any quantity that reduces to half its initial value in a constant time decays exponentially. The nature of the decay is independent of the initial amount. 7.2.7 Define t ...
... rate of decay decreases exponentially with time. Exponential decay need not be treated analytically. It is sufficient to know that any quantity that reduces to half its initial value in a constant time decays exponentially. The nature of the decay is independent of the initial amount. 7.2.7 Define t ...
Applications of gamma spectrometry
... A) Neutron – sample is irradiated by neutrons from reactor → production of radioactive nuclei → study of characteristic radiation known neutron flux → activity is proportional to amount of studied element very sensitive – search of trace amounts of elements Sensitivity depends on element (range up t ...
... A) Neutron – sample is irradiated by neutrons from reactor → production of radioactive nuclei → study of characteristic radiation known neutron flux → activity is proportional to amount of studied element very sensitive – search of trace amounts of elements Sensitivity depends on element (range up t ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.