Answers to practice questions
... *Draw lewis structure: _____ 49. The geometry of the phosphorous trichloride molecule can best be described as A) tetrahedral B) bent C) trigonal pyramidal D) trigonal planar *Draw lewis structure Standard 1.3 Understand the physical and chemical properties of atoms based on their position on the Pe ...
... *Draw lewis structure: _____ 49. The geometry of the phosphorous trichloride molecule can best be described as A) tetrahedral B) bent C) trigonal pyramidal D) trigonal planar *Draw lewis structure Standard 1.3 Understand the physical and chemical properties of atoms based on their position on the Pe ...
Chapter 2 - sample definitions and questions
... In the process of decay a radioactive isotope often transforms into a different element half life = the time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample of a specific isotope to decay into a more stable form atomic mass unit (dalton) = the standard unit for measuring the mass of atoms and ...
... In the process of decay a radioactive isotope often transforms into a different element half life = the time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample of a specific isotope to decay into a more stable form atomic mass unit (dalton) = the standard unit for measuring the mass of atoms and ...
Atoms : The Building Blocks of Matter
... Because all kinds of elements produced the same cathode rays, he concluded that electrons were fundamental to all atoms. Because atoms are neutral, if there is a negative charge, there must also be a positive one. There must be other particles that help account for mass of the atom. ...
... Because all kinds of elements produced the same cathode rays, he concluded that electrons were fundamental to all atoms. Because atoms are neutral, if there is a negative charge, there must also be a positive one. There must be other particles that help account for mass of the atom. ...
The Chemical Context of Life Chapter 2 Notes
... required in only minute quantities -ex. Iron, iodine ...
... required in only minute quantities -ex. Iron, iodine ...
Chapter 3 - Chemguide
... • The nuclei of atoms of different elements differ in their number of protons and therefore in the amount of positive charge they possess. • Thus, the number of protons determines that atom’s identity. ...
... • The nuclei of atoms of different elements differ in their number of protons and therefore in the amount of positive charge they possess. • Thus, the number of protons determines that atom’s identity. ...
Classification – 3 main groups
... Boyle’s Law (theoretical) inverse relationship between pressure and volume, as one increases the other decreases Charles Law (theoretical) direct relationship between volume and temperature, if one increases so does the other Chapter 9 Lessons 1-2 Atom smallest piece of an element that still represe ...
... Boyle’s Law (theoretical) inverse relationship between pressure and volume, as one increases the other decreases Charles Law (theoretical) direct relationship between volume and temperature, if one increases so does the other Chapter 9 Lessons 1-2 Atom smallest piece of an element that still represe ...
Ch. 21.1 Nuclear Radiation
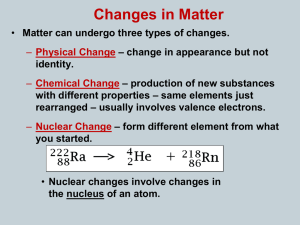
... – The process continues until unstable isotopes of one element are changed, or transformed, into stable isotopes of a different element. – These stable isotopes are not radioactive. – Nuclear radiation is emitted during radioactive decay. – There are three main types of nuclear radiation: alpha rad ...
... – The process continues until unstable isotopes of one element are changed, or transformed, into stable isotopes of a different element. – These stable isotopes are not radioactive. – Nuclear radiation is emitted during radioactive decay. – There are three main types of nuclear radiation: alpha rad ...
Basic chemistry lesson
... Plasma is by far the most common form of matter. Plasma in the stars and in the tenuous space between them makes up over 99% of the visible universe and perhaps most of that which is not visible. ...
... Plasma is by far the most common form of matter. Plasma in the stars and in the tenuous space between them makes up over 99% of the visible universe and perhaps most of that which is not visible. ...
Alpha Beta Fission Fusion
... electrons around an atom's nucleus. In 1896, Henri Becquerel expanded the field of chemistry to include nuclear changes when he discovered that uranium emitted radiation. Soon after Becquerel's discovery, Marie Sklodowska Curie began studying radioactivity and completed much of the pioneering work o ...
... electrons around an atom's nucleus. In 1896, Henri Becquerel expanded the field of chemistry to include nuclear changes when he discovered that uranium emitted radiation. Soon after Becquerel's discovery, Marie Sklodowska Curie began studying radioactivity and completed much of the pioneering work o ...
Chapter 4 Section 1
... electron moved in certain regions depending on its energy level, or specific amount of energy. 11. To this model was later added the neutron, a particle having no charge and found in the nucleus. 12. The modern model describes an atom as consisting of a nucleus that contains protons and neutrons, su ...
... electron moved in certain regions depending on its energy level, or specific amount of energy. 11. To this model was later added the neutron, a particle having no charge and found in the nucleus. 12. The modern model describes an atom as consisting of a nucleus that contains protons and neutrons, su ...
Chapter 22 Clicker questions.
... Unlike Newton’s law of gravity, Coulomb’s law involves a. b. c. d. ...
... Unlike Newton’s law of gravity, Coulomb’s law involves a. b. c. d. ...
Document
... Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are the smallest form of elements. About 100 elements • Hydrogen is an element that accounts for about 90% of total mass of the universe. • Hydrogen makes up about 1% of Earth’s crust and most of that is in wate ...
... Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are the smallest form of elements. About 100 elements • Hydrogen is an element that accounts for about 90% of total mass of the universe. • Hydrogen makes up about 1% of Earth’s crust and most of that is in wate ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.