Chapter 37
... Henri Becquerel in 1896. – The work involved uranium salts which lead to the conclusion that the minerals gave off some sort of radiation. – This radiation was later shown to be separable by electric (and magnetic) fields into three types; alpha (a), beta (b), and gamma (g) rays. ...
... Henri Becquerel in 1896. – The work involved uranium salts which lead to the conclusion that the minerals gave off some sort of radiation. – This radiation was later shown to be separable by electric (and magnetic) fields into three types; alpha (a), beta (b), and gamma (g) rays. ...
ChemFinalgeocities
... Listed below are some imaginary data for a series of compounds. Based on what you have learned, predict whether each compound is probably ionic (I) or covalent (C). If the information given might apply to either kind of compound, put a question mark (?). 91. Is highly soluble in water. Write the fo ...
... Listed below are some imaginary data for a series of compounds. Based on what you have learned, predict whether each compound is probably ionic (I) or covalent (C). If the information given might apply to either kind of compound, put a question mark (?). 91. Is highly soluble in water. Write the fo ...
Scientific Method - Virtual Medical Academy
... *Located to the right of the heavy line. * Dull and brittle. * Poor conductors. ...
... *Located to the right of the heavy line. * Dull and brittle. * Poor conductors. ...
A. Das and T. Ferbel - Ritter Illustration
... the only popular model of the atom was due to Joseph Thomson, who visualized the electrically neutral atom as a "plum pudding" where negatively charged electrons were embedded, like raisins, within a uniform distribution of positive charge. If this model were correct, one would expect only small dev ...
... the only popular model of the atom was due to Joseph Thomson, who visualized the electrically neutral atom as a "plum pudding" where negatively charged electrons were embedded, like raisins, within a uniform distribution of positive charge. If this model were correct, one would expect only small dev ...
review of the review
... a) electric fields b) magnetic fields c) hitting the nucleus d) all three 2) Rutherford fired fast moving alpha particles at gold foil. The alpha particles were accelerated by a) a cyclotron b) an electron gun c) nuclear decay d) parallel plates 3) What does the -particle scattering pattern indicat ...
... a) electric fields b) magnetic fields c) hitting the nucleus d) all three 2) Rutherford fired fast moving alpha particles at gold foil. The alpha particles were accelerated by a) a cyclotron b) an electron gun c) nuclear decay d) parallel plates 3) What does the -particle scattering pattern indicat ...
Notes on Atomic Structure
... are very small An atom has 3 kinds of particles: Protons (positive charge), neutrons (neutral), electrons (negative charge) Protons and neutrons are located in the atomic nucleus (center of atom) Electrons are located around the nucleus in an electron cloud and occupies almost all of the vol ...
... are very small An atom has 3 kinds of particles: Protons (positive charge), neutrons (neutral), electrons (negative charge) Protons and neutrons are located in the atomic nucleus (center of atom) Electrons are located around the nucleus in an electron cloud and occupies almost all of the vol ...
Modern Physics
... of incoming particles that collided with electrons in the metal. If the photon had enough energy, it could knock the electron free of the metal and send it across the cell to the collector. If photon was too small, it couldn’t hit ...
... of incoming particles that collided with electrons in the metal. If the photon had enough energy, it could knock the electron free of the metal and send it across the cell to the collector. If photon was too small, it couldn’t hit ...
Chemistry (B) HW Chapter 25
... c. It increases the rate of heat absorption. d. It recycles the fuel. ____ 42. Control rods made of ____. a. carbon c. plutonium b. liquid sodium d. cadmium ____ 43. What substances are used as moderators in a nuclear reactor? a. carbon and water c. plutonium and neptunium b. liquid sodium and water ...
... c. It increases the rate of heat absorption. d. It recycles the fuel. ____ 42. Control rods made of ____. a. carbon c. plutonium b. liquid sodium d. cadmium ____ 43. What substances are used as moderators in a nuclear reactor? a. carbon and water c. plutonium and neptunium b. liquid sodium and water ...
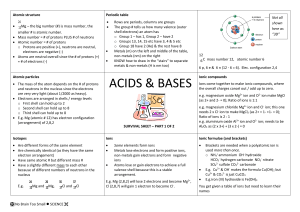
acids and bases - No Brain Too Small
... KNOW how to draw in the “stairs” to separate metals & non-metals (H is nm too) ...
... KNOW how to draw in the “stairs” to separate metals & non-metals (H is nm too) ...
Power Point - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... •Believed universe made of 4 elements: earth, air, fire, and water ...
... •Believed universe made of 4 elements: earth, air, fire, and water ...
4. - period2chem
... 8.7 hours slope = (mass) (volume) = density always record one estimate digit 1200 m 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emissi ...
... 8.7 hours slope = (mass) (volume) = density always record one estimate digit 1200 m 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emissi ...
Unit 2
... 45. The atomic radius generally increases with atomic number in a particular group of elements. The dominant factor that determines this variation is the _____ A. addition of energy levels. B. increase in the number of neutrons. C. formation of anew octet. D. increase in nuclear charge. 46. One-half ...
... 45. The atomic radius generally increases with atomic number in a particular group of elements. The dominant factor that determines this variation is the _____ A. addition of energy levels. B. increase in the number of neutrons. C. formation of anew octet. D. increase in nuclear charge. 46. One-half ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.