Exam 1 Review Sheet Honors Biology This is to be used for
... you think we completely ignore gravity on the atomic level? (Hint: why do we ignore electrons when calculating mass?) 13. The nucleus of elements larger than hydrogen obviously has more than one proton in close proximity. How can this be if the electromagnetic force is pushing these like charges ap ...
... you think we completely ignore gravity on the atomic level? (Hint: why do we ignore electrons when calculating mass?) 13. The nucleus of elements larger than hydrogen obviously has more than one proton in close proximity. How can this be if the electromagnetic force is pushing these like charges ap ...
Branches of Chemistry
... Biochemists study the compounds and chemical reactions in living organisms. Electrochemists investigate the relationship between the flow of electricity and chemical reactions. Environmental chemists study how changes in the natural environment affect living organisms. Geochemists analyze the chemic ...
... Biochemists study the compounds and chemical reactions in living organisms. Electrochemists investigate the relationship between the flow of electricity and chemical reactions. Environmental chemists study how changes in the natural environment affect living organisms. Geochemists analyze the chemic ...
Overview - RI
... atomic level because of atomic attractions stems from an understanding of atomic structure. This activity is not directly supported by any other SAM activities because it is so fundamental. However, it supports many other SAM activities. First, to understand Electrostatics — the attraction and repul ...
... atomic level because of atomic attractions stems from an understanding of atomic structure. This activity is not directly supported by any other SAM activities because it is so fundamental. However, it supports many other SAM activities. First, to understand Electrostatics — the attraction and repul ...
Unit 2: Biochem Notes
... Element - A pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom. ...
... Element - A pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom. ...
atomic nuclei without neutrons
... As singular particles, electrons only occur in the electron shells around the atomic nucleus and do not occur inside the atomic nucleus. Free neutrons are unstable and decay into one proton, one electron and one antineutrino/energy. -) Strong and weak nuclear force: In order to keep together the str ...
... As singular particles, electrons only occur in the electron shells around the atomic nucleus and do not occur inside the atomic nucleus. Free neutrons are unstable and decay into one proton, one electron and one antineutrino/energy. -) Strong and weak nuclear force: In order to keep together the str ...
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... 13. A sphere of gold has a radius of 1.5 inches. The volume of a sphere is 4.19r3. Given that the mass of this sphere is 4469 g, calculate the density of gold in g/cm3 to the correct number of significant figures. V = 4.19(1.5 in)3 =113.13 in3 x (2.54 cm/ in)3 = 231.73 cm3 ρ = 4469 g/ 231.73 cm3 = 1 ...
... 13. A sphere of gold has a radius of 1.5 inches. The volume of a sphere is 4.19r3. Given that the mass of this sphere is 4469 g, calculate the density of gold in g/cm3 to the correct number of significant figures. V = 4.19(1.5 in)3 =113.13 in3 x (2.54 cm/ in)3 = 231.73 cm3 ρ = 4469 g/ 231.73 cm3 = 1 ...
Notetakers
... 1. __________________________________: if the sample is not already as gas, the sample is heated to this point. 2. __________________________________: sample is bombarded with a stream of high energy electons. In practice, the instrument is set so that only ions with a single positive charge are for ...
... 1. __________________________________: if the sample is not already as gas, the sample is heated to this point. 2. __________________________________: sample is bombarded with a stream of high energy electons. In practice, the instrument is set so that only ions with a single positive charge are for ...
vibrations and waves
... ____________________ 3. Both Democritus and Dalton suggested that matter is made up of atoms. ____________________ 4. Dalton’s atomic theory stated that atoms separate, combine, or rearrange in chemical reactions. ____________________ 5. Dalton’s atomic theory stated that matter is mostly empty spac ...
... ____________________ 3. Both Democritus and Dalton suggested that matter is made up of atoms. ____________________ 4. Dalton’s atomic theory stated that atoms separate, combine, or rearrange in chemical reactions. ____________________ 5. Dalton’s atomic theory stated that matter is mostly empty spac ...
AP Chemistry
... iv) Going down a column, Zeff increases slowly (compared to the L to R change) (1) This is because larger electron cores are less effective at screening (a) More electron-electron repulsions (b) Electrons are placed in energy levels intrinsically farther from nucleus (2) Period L R change in Zeff ...
... iv) Going down a column, Zeff increases slowly (compared to the L to R change) (1) This is because larger electron cores are less effective at screening (a) More electron-electron repulsions (b) Electrons are placed in energy levels intrinsically farther from nucleus (2) Period L R change in Zeff ...
"Strange nuclear materials"()
... to speculate that there was an exception to the rule. Despite this, Niels Bohr did just that – and turned out to be wrong. Another proposal, made by Wolfgang Pauli in 1930, was that a second, virtually undetectable particle was emitted at the same time as the electron. This new particle, later calle ...
... to speculate that there was an exception to the rule. Despite this, Niels Bohr did just that – and turned out to be wrong. Another proposal, made by Wolfgang Pauli in 1930, was that a second, virtually undetectable particle was emitted at the same time as the electron. This new particle, later calle ...
Chapter 24: The Nucleus
... the mass number (total number of nucleons) of nuclei changes during gamma decay, although mass does change because energy is released. Gamma decay usually follows all the other radioactive decays, because the residual nuclei are almost always left in an excited condition. ...
... the mass number (total number of nucleons) of nuclei changes during gamma decay, although mass does change because energy is released. Gamma decay usually follows all the other radioactive decays, because the residual nuclei are almost always left in an excited condition. ...
What 3 ways can things become charged?
... In solid conductors, the electrons carry the charge through the circuit because they are loosely held. In fluids, like those in a car battery, positive and negative ions and electrons may compose the flow of electric charge. ...
... In solid conductors, the electrons carry the charge through the circuit because they are loosely held. In fluids, like those in a car battery, positive and negative ions and electrons may compose the flow of electric charge. ...
Unit 2 note
... 5.1 Models of the Atom p. 127-130 Rutherford’s orbital atomic model could not explain the chemical properties of elements. For example, why do metal elements, or compounds that contain metals, give off characteristic colours when heated in a flame? Explaining what leads to the chemical properties of ...
... 5.1 Models of the Atom p. 127-130 Rutherford’s orbital atomic model could not explain the chemical properties of elements. For example, why do metal elements, or compounds that contain metals, give off characteristic colours when heated in a flame? Explaining what leads to the chemical properties of ...
File
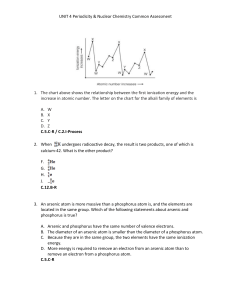
... 4. Iodine-131 is a radioactive isotope with a half-life of 8 days. How many grams of a 64 g sample of iodine-131 will remain at the end of 24 days? F. 56 g G. 48 g H. 32 g J. 8 g C.12.B-R / C.2.G-Process 5. What element in the second period has the largest atomic radius? A. Carbon B. Lithium C. Pota ...
... 4. Iodine-131 is a radioactive isotope with a half-life of 8 days. How many grams of a 64 g sample of iodine-131 will remain at the end of 24 days? F. 56 g G. 48 g H. 32 g J. 8 g C.12.B-R / C.2.G-Process 5. What element in the second period has the largest atomic radius? A. Carbon B. Lithium C. Pota ...
_____ Name _____ _ Date ______ Mrs. G
... What is the symbol for each subatomic particle? Which 2 subatomic particles make up most of the mass of atoms? Which subatomic particle has negligible mass? o Why do atoms found in their neutral state have no charge? o What would happen if an atom gained an electron? o What would happen if an ...
... What is the symbol for each subatomic particle? Which 2 subatomic particles make up most of the mass of atoms? Which subatomic particle has negligible mass? o Why do atoms found in their neutral state have no charge? o What would happen if an atom gained an electron? o What would happen if an ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.