Unit 2 Part I PowerPoint
... Typically found in heavier nuclei and the means to achieve stability is to reduce mass Nuclei shed mass in the form of a helium nucleus to become more stable Helium nucleus that is released is ionized and called and Alpha Particle ...
... Typically found in heavier nuclei and the means to achieve stability is to reduce mass Nuclei shed mass in the form of a helium nucleus to become more stable Helium nucleus that is released is ionized and called and Alpha Particle ...
KEY Midterm Exam 1 Sept.14, 1999 Chemistry 211 PAGE 1 0f 5
... 12.What is the correct representation for an entity containing 14 neutrons, 13 protons, and 14 electrons? (a) 1 4Si (b) 4 1Nb(c) 27Co (d) 1 3Si+ (e) 2 7Al13.Which of the following is the best description of an atom? (a) the smallest unit of a chemical compound (b) a small positively charged nucleus ...
... 12.What is the correct representation for an entity containing 14 neutrons, 13 protons, and 14 electrons? (a) 1 4Si (b) 4 1Nb(c) 27Co (d) 1 3Si+ (e) 2 7Al13.Which of the following is the best description of an atom? (a) the smallest unit of a chemical compound (b) a small positively charged nucleus ...
HW-1-Ch1-Atomic-structure-W16
... 4. Calculate the binding energy per nucleon (MeV) of 56Fe isotope of mass 55.952918 amu. ( P= 1.007277 amu,; N= 1.008665 amu; e- = 5.486 x10-4 amu) ...
... 4. Calculate the binding energy per nucleon (MeV) of 56Fe isotope of mass 55.952918 amu. ( P= 1.007277 amu,; N= 1.008665 amu; e- = 5.486 x10-4 amu) ...
My 1st introduction to fresh students
... Electromagnetic Interaction • Force (r) ~ 1/r2 • Two charges can be broken apart and set free ...
... Electromagnetic Interaction • Force (r) ~ 1/r2 • Two charges can be broken apart and set free ...
introduction [Kompatibilitätsmodus]
... Millikan‘s experiment (1911, Nobel Price in 1923): Oil droplets are sprayed in a chamber between two electrodes and charged by ionizing radiation. Their motion is observed by a microscope. ...
... Millikan‘s experiment (1911, Nobel Price in 1923): Oil droplets are sprayed in a chamber between two electrodes and charged by ionizing radiation. Their motion is observed by a microscope. ...
Activity 17 Follow-up
... all the known isotopes of the element •The element which appears on the periodic table is the isotope which is most abundant ...
... all the known isotopes of the element •The element which appears on the periodic table is the isotope which is most abundant ...
link to power point lesson 1
... Every 4 seconds, 4 C-14 atoms in a trillion turn into Nitrogen because one of the neutrons decomposes into a proton and an electron (beta particle) which leaves the nucleus and begins to orbit. Isotopes that release beta or other particles are radioisotopes. ...
... Every 4 seconds, 4 C-14 atoms in a trillion turn into Nitrogen because one of the neutrons decomposes into a proton and an electron (beta particle) which leaves the nucleus and begins to orbit. Isotopes that release beta or other particles are radioisotopes. ...
Particle physics
... • Real world is not done by single quarks • Quarks exist only in groups, to form the so-called hadrons (protons and neutrons are hadrons) • Example: a proton is made of two quarks of up type and one quark of type down. • The matter around, and even each of us, is made of quarks up and down and of el ...
... • Real world is not done by single quarks • Quarks exist only in groups, to form the so-called hadrons (protons and neutrons are hadrons) • Example: a proton is made of two quarks of up type and one quark of type down. • The matter around, and even each of us, is made of quarks up and down and of el ...
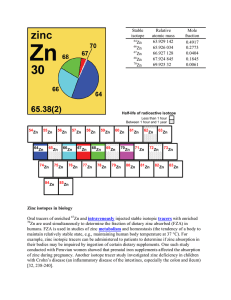
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... anthropogenic – resulting from human activity. [return] atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight (relative mean atomic mass) – the sum of the products of the relative atomic mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that ...
... anthropogenic – resulting from human activity. [return] atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight (relative mean atomic mass) – the sum of the products of the relative atomic mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that ...
Radioactive decay of nucleus
... Have same chemical properties but different physical properties. one isotope of an element may be highly radioactive, while another is stable. Atomic Mass Units- instead of kg for the mass 1 amu or u = 1.66 x 10-27 kg See formula sheet ...
... Have same chemical properties but different physical properties. one isotope of an element may be highly radioactive, while another is stable. Atomic Mass Units- instead of kg for the mass 1 amu or u = 1.66 x 10-27 kg See formula sheet ...
student worksheet
... 12) There are two main types of radioactive decay: beta decay and alpha decay. Alpha is simpler to understand. The nucleus spits out an alpha particle, which is just a helium nucleus. For example, polonium-218 will emit an alpha particle and decay to lead-214. This just involves rearranging existing ...
... 12) There are two main types of radioactive decay: beta decay and alpha decay. Alpha is simpler to understand. The nucleus spits out an alpha particle, which is just a helium nucleus. For example, polonium-218 will emit an alpha particle and decay to lead-214. This just involves rearranging existing ...
Classification of the Elementary Particles
... interact strongly within the range of the kaon and pion forces whilst leptons have only weak interaction. ...
... interact strongly within the range of the kaon and pion forces whilst leptons have only weak interaction. ...
Real-World Applications: C
... • Differentiate between fission and fusion reactions. • Identify examples of how radioisotopes are used in everyday life. ...
... • Differentiate between fission and fusion reactions. • Identify examples of how radioisotopes are used in everyday life. ...
nuclear fission
... nuclear power stations have been built around the world. The neutrons produced in a chain reaction are moving too fast to cause further fission in U235 nuclei and they have to be slowed down. This is done by graphite or heavy water and these materials are called moderators. As the neutrons collide w ...
... nuclear power stations have been built around the world. The neutrons produced in a chain reaction are moving too fast to cause further fission in U235 nuclei and they have to be slowed down. This is done by graphite or heavy water and these materials are called moderators. As the neutrons collide w ...
Basics of Chemistry
... Why are we studying chemistry? Biology has chemistry at its foundation ...
... Why are we studying chemistry? Biology has chemistry at its foundation ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.





![introduction [Kompatibilitätsmodus]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017596641_1-03cad833ad630350a78c42d7d7aa10e3-300x300.png)