What You Need to Know to Pass the Chemistry
... 1. The placement of an element on the Periodic Table gives an indication of the chemical and physical properties of that element. 2. Elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. 3. The number of protons in an atom (atomic number) identifies the element. The number of protons in an a ...
... 1. The placement of an element on the Periodic Table gives an indication of the chemical and physical properties of that element. 2. Elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. 3. The number of protons in an atom (atomic number) identifies the element. The number of protons in an a ...
CHM 101
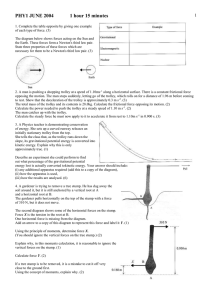
... The reactants in a chemical change have 487 kJ of energy. The change they undergo has a H = -157 kJ. The activation energy for the reaction is 570 kJ. a. Draw the energy vs reaction progress graph on the axes above paying attention to all values. Label a point that represents all products and one t ...
... The reactants in a chemical change have 487 kJ of energy. The change they undergo has a H = -157 kJ. The activation energy for the reaction is 570 kJ. a. Draw the energy vs reaction progress graph on the axes above paying attention to all values. Label a point that represents all products and one t ...
2 - The Student Room
... 5. A model truck A of mass 1.2 kg is travelling due west with a speed of 0.90 m s -1. A second truck B of mass 4.0 kg is travelling due east towards A with a speed of 0.35 m s -1. Calculate the magnitude of the total momentum of the trucks. (2) The trucks collide and stick together. Determine their ...
... 5. A model truck A of mass 1.2 kg is travelling due west with a speed of 0.90 m s -1. A second truck B of mass 4.0 kg is travelling due east towards A with a speed of 0.35 m s -1. Calculate the magnitude of the total momentum of the trucks. (2) The trucks collide and stick together. Determine their ...
Structure of Atoms
... Make up of the atom We covered three key experiments. Thompson’s experiment Use a cathode ray tube to show electrons were negatively charged and measured their mass to charge ratio. How? Used a beam of electrons (cathod rays) and deflected them with an electric field. However, this could not be used ...
... Make up of the atom We covered three key experiments. Thompson’s experiment Use a cathode ray tube to show electrons were negatively charged and measured their mass to charge ratio. How? Used a beam of electrons (cathod rays) and deflected them with an electric field. However, this could not be used ...
SLE133 – “Chemistry in Our World” Summary Notes Week 1
... All the elements in the periodic table are categorized as Metals (good conductors of heat and electricity), Nonmetals (poor conductors of heat and electricity), and Metalloids (have both metallic and non-metallic characteristics). ...
... All the elements in the periodic table are categorized as Metals (good conductors of heat and electricity), Nonmetals (poor conductors of heat and electricity), and Metalloids (have both metallic and non-metallic characteristics). ...
Heisenburg uncertainty principle
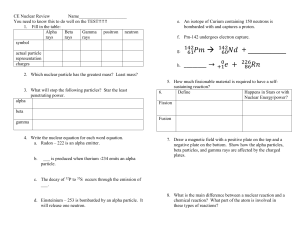
... forces both have infinite range but gravity is 1036 times weaker at a given distance The strong and weak forces are both short range forces (<10-14 m) The weak force is 108 times weaker than the strong force within a nucleus ...
... forces both have infinite range but gravity is 1036 times weaker at a given distance The strong and weak forces are both short range forces (<10-14 m) The weak force is 108 times weaker than the strong force within a nucleus ...
Small Business Success on the Web
... Elements & their valence shells Elements in the same column have the same valence & similar chemical properties ...
... Elements & their valence shells Elements in the same column have the same valence & similar chemical properties ...
File
... in sign. Electrons carry a negative charge while protons carry positive charge. The objects around us contain billions and billions of atoms, and each atom contains many protons and electrons. The protons are located in the center of the atom, concentrated in a small area called the nucleus. The ele ...
... in sign. Electrons carry a negative charge while protons carry positive charge. The objects around us contain billions and billions of atoms, and each atom contains many protons and electrons. The protons are located in the center of the atom, concentrated in a small area called the nucleus. The ele ...
A Conceptual Introduction to Chemistry, First Edition
... 2. The cell can absorb the radiation and be damaged, but it can subsequently repair the damage and resume normal functioning. 3. The cell can be damaged so severely that it cannot repair itself. New cells formed from this cell will be abnormal. This mutant cell can ultimately cause cancer if it cont ...
... 2. The cell can absorb the radiation and be damaged, but it can subsequently repair the damage and resume normal functioning. 3. The cell can be damaged so severely that it cannot repair itself. New cells formed from this cell will be abnormal. This mutant cell can ultimately cause cancer if it cont ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.