Radioactive Decay
... Note that a neutron consists of two down quarks and one up quark (↑↓↓), and a proton consists of two “up quarks” and one “down quark” (↑↑↓). When β− decay occurs, one of the quarks changes its spin from down to up, which changes the neutron into a proton. Because a proton was gained, the atomic numb ...
... Note that a neutron consists of two down quarks and one up quark (↑↓↓), and a proton consists of two “up quarks” and one “down quark” (↑↑↓). When β− decay occurs, one of the quarks changes its spin from down to up, which changes the neutron into a proton. Because a proton was gained, the atomic numb ...
Chapter 32 and 33 Review
... charges are strongest when the charges are a. far apart. b. close together. c. The electrical force is constant everywhere. ...
... charges are strongest when the charges are a. far apart. b. close together. c. The electrical force is constant everywhere. ...
Static Electricity Notes
... Let’s Start from the Beginning Atoms- smallest particle that makes up all matter. Electrons-Negative charged particles that make up an ...
... Let’s Start from the Beginning Atoms- smallest particle that makes up all matter. Electrons-Negative charged particles that make up an ...
d. all of the above
... charges are strongest when the charges are a. far apart. b. close together. c. The electrical force is constant everywhere. ...
... charges are strongest when the charges are a. far apart. b. close together. c. The electrical force is constant everywhere. ...
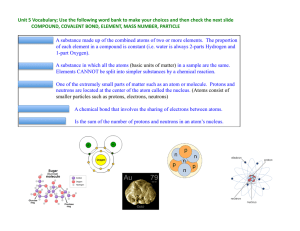
Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. A shared
... Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. A shared pair of electrons between two nuclei, where the electrons are attracted to each nucleus. A shared pair of electrons between two atoms where one atom contributes both electrons to the bond. The electrostatic attraction between a regul ...
... Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. A shared pair of electrons between two nuclei, where the electrons are attracted to each nucleus. A shared pair of electrons between two atoms where one atom contributes both electrons to the bond. The electrostatic attraction between a regul ...
RES9_phys_flash_card..
... Specific heat capacity and latent heat The heating of a body leads to an increase in internal energy and to either an increase in temperature or a change of state. The specific heat capacity of a substance is the energy provided by heating to raise the temperature of unit mass by 1 °C or 1 K. ...
... Specific heat capacity and latent heat The heating of a body leads to an increase in internal energy and to either an increase in temperature or a change of state. The specific heat capacity of a substance is the energy provided by heating to raise the temperature of unit mass by 1 °C or 1 K. ...
Document
... 52) What are the four pieces of information that a coefficient gives you and give conditions, if necessary. Ratio of moles, molecules, atoms or formula units 53) Which of the following represents 4 moles of chlorine a) 4 Cl b) Cl4 c) Cl4 d) 4 Cl2 54) What is the empirical formula for C4H6O4? C2H3O2 ...
... 52) What are the four pieces of information that a coefficient gives you and give conditions, if necessary. Ratio of moles, molecules, atoms or formula units 53) Which of the following represents 4 moles of chlorine a) 4 Cl b) Cl4 c) Cl4 d) 4 Cl2 54) What is the empirical formula for C4H6O4? C2H3O2 ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.