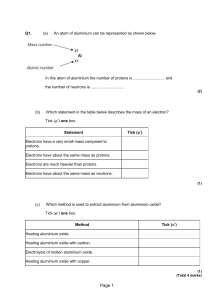
Reactions I Can..
... 8. Trace the changes in atomic theory starting with Dalton and ending with the modern quantum mechanical model. 9. Describe the basic properties of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. 10. Explain why some atomic nuclei are unstable 11. Predict the type of nuclear decay that will occur given the compos ...
... 8. Trace the changes in atomic theory starting with Dalton and ending with the modern quantum mechanical model. 9. Describe the basic properties of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. 10. Explain why some atomic nuclei are unstable 11. Predict the type of nuclear decay that will occur given the compos ...
Atoms
... 8. Trace the changes in atomic theory starting with Dalton and ending with the modern quantum mechanical model. 9. Describe the basic properties of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. 10. Explain why some atomic nuclei are unstable 11. Predict the type of nuclear decay that will occur given the compos ...
... 8. Trace the changes in atomic theory starting with Dalton and ending with the modern quantum mechanical model. 9. Describe the basic properties of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. 10. Explain why some atomic nuclei are unstable 11. Predict the type of nuclear decay that will occur given the compos ...
Ch. 2 - Ltcconline.net
... D Atoms consist of protons, neutrons and electrons 1. atom is the smallest unit of matter 2. subatomic particles make up the atom. 3. Differences in elements 4. isotopes - different numbers of neutrons so mass changes E. Electron arrangement determines chemical properties of atom 1. electrons determ ...
... D Atoms consist of protons, neutrons and electrons 1. atom is the smallest unit of matter 2. subatomic particles make up the atom. 3. Differences in elements 4. isotopes - different numbers of neutrons so mass changes E. Electron arrangement determines chemical properties of atom 1. electrons determ ...
Document
... B. Because our skin shields us from electrical forces C. Because we have just as many positive charges as negative D. Because gravity involves the entire earth, but earth has no charges ...
... B. Because our skin shields us from electrical forces C. Because we have just as many positive charges as negative D. Because gravity involves the entire earth, but earth has no charges ...
Chemistry Notes with Blanks
... The combination of carbon and water contains the same _________ as sugar. Elements: can’t be broken into _________ substances (atoms.) (Carbon is an element) Sugar + water…would you drink this? Ash + water…would you drink this? Why? They contain the same elements don’t they? Why don’t you get sugar ...
... The combination of carbon and water contains the same _________ as sugar. Elements: can’t be broken into _________ substances (atoms.) (Carbon is an element) Sugar + water…would you drink this? Ash + water…would you drink this? Why? They contain the same elements don’t they? Why don’t you get sugar ...
Chapter 8 Physics 205 Solution of Home Work Problems
... ~ originates with the orbiting electron. To estimate B, ~ we adopt the The magnetic field B equivalent viewpoint of the atomic nucleus (proton) circling the electron, and borrow a result ~ field at the center or a circular current loop with from classical electromagnetism for the B radius r: 2km µ r ...
... ~ originates with the orbiting electron. To estimate B, ~ we adopt the The magnetic field B equivalent viewpoint of the atomic nucleus (proton) circling the electron, and borrow a result ~ field at the center or a circular current loop with from classical electromagnetism for the B radius r: 2km µ r ...
Additional Problems - AppServ Open Project 2.4.9
... This equation is the law of successive radioactive decays. (c) 218Po decays into 214Pb with a half-life of 3.10 min, and 214Pb decays into 214Bi with a half-life of 26.8 min. On the same axes, plot graphs of N1(t) for 218Po and N2(t) for 214Pb. Let N10 = 1 000 nuclei, and choose values of t from 0 t ...
... This equation is the law of successive radioactive decays. (c) 218Po decays into 214Pb with a half-life of 3.10 min, and 214Pb decays into 214Bi with a half-life of 26.8 min. On the same axes, plot graphs of N1(t) for 218Po and N2(t) for 214Pb. Let N10 = 1 000 nuclei, and choose values of t from 0 t ...
eq04
... bombarded by particles was a new type of neutral particle – the neutron (originally proposed by Rutherford). He then applied the conservation of energy and momentum laws to his experimental results and showed that the particles emitted from the Be had to be neutral with about the same mass as the ...
... bombarded by particles was a new type of neutral particle – the neutron (originally proposed by Rutherford). He then applied the conservation of energy and momentum laws to his experimental results and showed that the particles emitted from the Be had to be neutral with about the same mass as the ...
Exam Review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... a) alpha particles are the nuclei of helium atoms. b) the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus. c) cathode rays are streams of negatively charged ions. d) the charge-to-mass (e/m) ratio is the same for all cathode ray particles ...
... a) alpha particles are the nuclei of helium atoms. b) the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus. c) cathode rays are streams of negatively charged ions. d) the charge-to-mass (e/m) ratio is the same for all cathode ray particles ...
Section 12.6: The Standard Model of Elementary Particles
... lambda.” Because the charm quark has the same charge as the up quark, the charmed lambda has a charge of +1. It is unstable, with a lifetime of about 2.00 × 10–13 s, and it is more than twice as heavy as the proton, at 2286.46 MeV/c2. 4. Bosons have an important role in the standard model because th ...
... lambda.” Because the charm quark has the same charge as the up quark, the charmed lambda has a charge of +1. It is unstable, with a lifetime of about 2.00 × 10–13 s, and it is more than twice as heavy as the proton, at 2286.46 MeV/c2. 4. Bosons have an important role in the standard model because th ...
Chapter4 Nuclear atom - UCF College of Sciences
... Never express yourself more clearly than you are able to think. Prediction is very difficult, especially about the future. ...
... Never express yourself more clearly than you are able to think. Prediction is very difficult, especially about the future. ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.