electricity and electronics
... 6. EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 6.3 ELECTROMAGNETISM When there is current flowing in an electric circuit, it creates a magnetic field. This effect is called ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION and it is used in electric motors and relays. ...
... 6. EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 6.3 ELECTROMAGNETISM When there is current flowing in an electric circuit, it creates a magnetic field. This effect is called ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION and it is used in electric motors and relays. ...
A box is sitting on the floor
... creating gravitational potential energy. 3) The cable pulling up the elevator does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 4) The normal force must be larger than MAg in order to overcome gravity and create the upward energy. 5) The box has constant speed so its total mechanical en ...
... creating gravitational potential energy. 3) The cable pulling up the elevator does work on the box, creating gravitational potential energy. 4) The normal force must be larger than MAg in order to overcome gravity and create the upward energy. 5) The box has constant speed so its total mechanical en ...
Physics 8 - Dallas ISD
... for the ACP. Teachers may use this set of items along with the test blueprint as guides to prepare students for the ACP. On the last page, the correct answer and content SE is listed. The specific part of an SE that an Example Item measures is NOT necessarily the only part of the SE that is assessed ...
... for the ACP. Teachers may use this set of items along with the test blueprint as guides to prepare students for the ACP. On the last page, the correct answer and content SE is listed. The specific part of an SE that an Example Item measures is NOT necessarily the only part of the SE that is assessed ...
Moderne Methoden der Materialcharakterisierung
... Cathode material determines emission current density ...
... Cathode material determines emission current density ...
Unit 3: Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table
... Atomic Models: Chemical properties of atoms, ions, and molecules are related to the arrangement of the electrons within them. John Dalton: 1st atomic model & considered the atom as a solid indivisible mass. ...
... Atomic Models: Chemical properties of atoms, ions, and molecules are related to the arrangement of the electrons within them. John Dalton: 1st atomic model & considered the atom as a solid indivisible mass. ...
Electromagnetic Spectrum
... A variety of images can be captured by looking at radiation that is given off from a planet or star in different areas of the electromagnetic spectrum outside the visible light range. ...
... A variety of images can be captured by looking at radiation that is given off from a planet or star in different areas of the electromagnetic spectrum outside the visible light range. ...
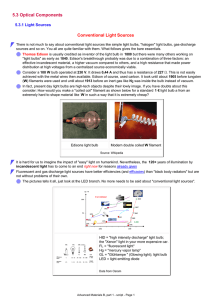
5.3 Optical Components Conventional Light Sources 5.3.1 Light Sources
... electrons up to the higher energy level - just as fast as they come down by "pumping" the Laser. In fact, we need to have more elctrons sitting at the high energy level all the times than at the lower level. This is a very unusual state for electrons called inversion. Pumping requires that we put pl ...
... electrons up to the higher energy level - just as fast as they come down by "pumping" the Laser. In fact, we need to have more elctrons sitting at the high energy level all the times than at the lower level. This is a very unusual state for electrons called inversion. Pumping requires that we put pl ...
Free Electrons in a Metal - in a typical metal each atom contributes
... ionization energy and high electron affinity, - electron affinity is the energy released by an atom when an electron is added to form a negatively charged ion - in the ionic crystal sodium chloride (NaCl, see figure) one electron is transferred from Na (ionization energy 5.14 eV) to Cl (electron aff ...
... ionization energy and high electron affinity, - electron affinity is the energy released by an atom when an electron is added to form a negatively charged ion - in the ionic crystal sodium chloride (NaCl, see figure) one electron is transferred from Na (ionization energy 5.14 eV) to Cl (electron aff ...
IBM-finalrev - Madison Public Schools
... e. KBr _____________________ f. difficult to separate ________________ g. properties are different from the substances that form it ________________ h. formula stands for it ____________________ i. can be separated by hand _______________ ...
... e. KBr _____________________ f. difficult to separate ________________ g. properties are different from the substances that form it ________________ h. formula stands for it ____________________ i. can be separated by hand _______________ ...
The Atom & the Electron Configurtation
... Sublevels have specific numbers of orbitals The maximum number of electrons that can occupy a principle energy level is given by the formula 2n2, where (n) is the principle quantum number. − EX. Energy level n=3: 2(32) = 2(9) = 18 electrons ...
... Sublevels have specific numbers of orbitals The maximum number of electrons that can occupy a principle energy level is given by the formula 2n2, where (n) is the principle quantum number. − EX. Energy level n=3: 2(32) = 2(9) = 18 electrons ...
Revision topic 1-3
... An absorption spectrum is produced where some colours are missing ( those that are absorbed by hydrogen). A corresponding emission line spectrum has only certain wavelegths or frequencies of visible light.The lines correspond to the light of particular wavelengths given off (=emitted) by the element ...
... An absorption spectrum is produced where some colours are missing ( those that are absorbed by hydrogen). A corresponding emission line spectrum has only certain wavelegths or frequencies of visible light.The lines correspond to the light of particular wavelengths given off (=emitted) by the element ...
08_lecture_ppt - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... 1. Electrons only exist in certain allowed orbits 2. Within an orbit, the electron does not radiate 3. Radiation is emitted or absorbed when changing orbits ...
... 1. Electrons only exist in certain allowed orbits 2. Within an orbit, the electron does not radiate 3. Radiation is emitted or absorbed when changing orbits ...
Honors Chemistry Unit 1 Outline – 2012-2013
... Chm 1.1.3 Chapter 4 a. Understand that energy exists in discrete units called quanta b. Describe the concepts of excited and ground state electrons in the atom c. Articulate that electromagnetic radiation is made up of photons d. Understand the relationship between wavelength and frequency e. Use th ...
... Chm 1.1.3 Chapter 4 a. Understand that energy exists in discrete units called quanta b. Describe the concepts of excited and ground state electrons in the atom c. Articulate that electromagnetic radiation is made up of photons d. Understand the relationship between wavelength and frequency e. Use th ...