* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download electricity and electronics
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
General Electric wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
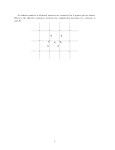
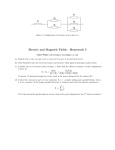
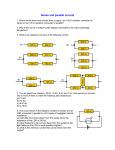
UNIT 1: ELECTRICITY AND ELECTRONICS (PART 3) TECHNOLOGIES ESO 3 ELECTRICITY AND ELECTRONICS 6. EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 6.1 HEAT 6.2 LIGHT 6.3 ELECTROMAGNETISM 7. ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS 7.1 RESISTORS: FIXED AND VARIABLES 7.2 CAPACITORS 7.3 DIODES 6. EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 6.1 HEAT The movement of electrons in a wire causes collisions and the increase of temperature of the wire. The heat produced by an electric current is called JOULE EFFECT. An example of application of this effect are RADIATORS and TOASTERS. 6. EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 6.2 LIGHT There are two ways of producing light using electricity: 1) Light bulbs: Based on the phenomenon of INCANDESCENCE: inside light bulbs there is a filament that produces light when heated by an electric current. 2) Fluorescent tubes: Inside the tube there is a metallic filament, an inert gas, a small quantity of mercury and a phosphorous layer that covers the inner part of the tube. RS. 6. EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT 6.3 ELECTROMAGNETISM When there is current flowing in an electric circuit, it creates a magnetic field. This effect is called ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION and it is used in electric motors and relays. 7. ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS 7.1 RESISTORS There are two types of resistors: fixed and variable: a) FIXED RESISTORS The resistor value is color-coded with stripes. 7. ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS b) VARIABLE RESISTORS - POTENTIOMETERS: These are resistors whose value can be adjusted, with a minimum value of 0 up to the maximum specified by the manufacturer. - RESISTORS THAT DEPEND UPON A PHYSICAL PARAMETER: LDR (LIGHT DEPENDENT RESISTOR): The resistance decreases as the luminous intensity increases. THERMISTORS (TEMPERATURE DEPENDANT RESISTOR): resistance decreases or increases as the temperature changes. 7. ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS 7.2 CAPACITORS A capacitor is a component that can store an electrical charge. 7.3 DIODES A diode is a component that allows current to flow in only one direction. When the anode is connected to higher voltage than the cathode, the diode conducts. LED are special diodes that shine when conducting.