* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Series and parallel circuits
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Charlieplexing wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
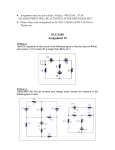
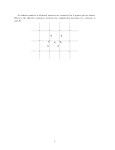
Series and parallel circuits 1. Which would draw more current from a supply, two 100 resistors connected in series or two 100 resistors connected in parallel? 2. Why is the use of a multiple outlet adaptor connected to the mains potentially dangerous? 3. What is the resistance of each of the following circuits: 400 (a) 200 400 (b) 200 500 500 250 (c) (d) 500 300 150 500 (e) 100 200 200 150 400 250 (f) 800 400 4. You are given four resistors, 20 k, 10 k, 5 k and 1 k. How would you connect two or more of them to make the following total resistances: (a) 15 k (b) 14 k (c) 6.67 k (d) 4.33 k 5. The circuit shown in the diagram contains a resistor and an 100 k LDR connected in parallel to a 6V supply of negligible internal resistance. (a) calculate the current drawn from the supply when the resistance of the LDR is 250 k. (b) what happens to the current drawn from the supply as the light falling on the LDR is made steadily brighter? (c) what is the minimum current that can be drawn from the supply?