* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electromagnetic Spectrum
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Doctor Light (Arthur Light) wikipedia , lookup
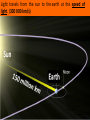
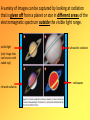
Electromagnetic Spectrum & The Speed of Light Light allows us to have a meaningful interaction with our world. We can see our surroundings when visible light reflects off objects and into our eyes. Light travels from the sun to the earth at the speed of light. (300 000 km/s) There is nothing faster than the speed of light. (except for spacecrafts in science fiction movies) Light is made up of different types of waves or radiation. visible light - needed to see and for photosynthesis infrared radiation - needed to heat the earth UV radiation - can cause cancer Radiowaves have a longest wavelength, visible light has a medium wavelength and gamma rays have the shortest wavelength. All types of light waves from the sun are arranged by size and displayed on the electromagnetic spectrum. It is impossible to see other forms of outside of visible light range of the electromagnetic spectrum with the naked eye. For example, special goggles are needed to see infrared radiation or “heat”. Advances in space technology (non-optical telescopes and observatories) allow us to see light from regions of the EM spectrum that would otherwise be invisible to the human eye. A variety of images can be captured by looking at radiation that is given off from a planet or star in different areas of the electromagnetic spectrum outside the visible light range. visible light ultraviolet radiation [only image that can be seen with naked eye] infrared radiation radiowaves This information has lead us to support theories such as The Big Bang & Expanding Universe. What can we see from our vantage point in the solar system? We can see all objects whose light has had time to reach us. The sun’s energy does not travel to the earth immediately. The farther away an object is, the longer the light takes. It takes about 8 minutes for the sun’s solar radiation to reach the earth’s surface after leaving the sun. When we see the light either from a very distant star or galaxy, we see the object as it appeared a very long ago. Therefore, looking far out in space is like looking back in time. How do we know what the universe looked like 5 billion years ago? We look back 5 billion light years! But what does this mean? The speed of light is 300,000,000 m/s and has the symbol c. Since speed (v) means distance (d) divided by time( t), the equation for speed is v = d/t. This means that in one second light travels 300,000,000 m. Therefore, light travels 9.46 x 10 km in one light year. It can range from energy waves in the x-ray region all the way to the gamma ray region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Our human eye can only see the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. However new technologies (observatories and telescopes) detect energy emitted from the universe within wavelengths of the entire spectrum. These advances allow humans to ‘see’ the unseen!