Don`t Let Granny Break A Nail!
... The Machine This machine is designed to open a tea jar with a paint can lid. ...
... The Machine This machine is designed to open a tea jar with a paint can lid. ...
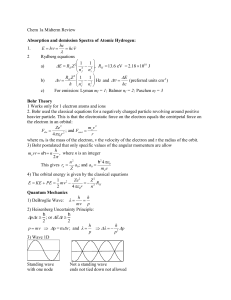
Define:
... 50. Where are the electrons and the protons in the Bohr model? 51. The principal quantum number indicates the _____ _____ of an electron. 52. What is the shape of the following orbitals: s, p 53. How are frequency and wavelength related? 54. What causes the emission of light from an atom? 55. All at ...
... 50. Where are the electrons and the protons in the Bohr model? 51. The principal quantum number indicates the _____ _____ of an electron. 52. What is the shape of the following orbitals: s, p 53. How are frequency and wavelength related? 54. What causes the emission of light from an atom? 55. All at ...
Electrons exhibit both wave
... Of particular interest was the growing field of quantum mechanics, which completely altered the fundamental precepts of physics. By the mid-1960's, physicists realized that their previous understanding, where all matter is composed of the fundamental protons, neutrons, and electron, was insufficient ...
... Of particular interest was the growing field of quantum mechanics, which completely altered the fundamental precepts of physics. By the mid-1960's, physicists realized that their previous understanding, where all matter is composed of the fundamental protons, neutrons, and electron, was insufficient ...
Electricity & Magnetism
... atoms…they can be moved. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. ...
... atoms…they can be moved. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. ...
Chapter 4 Chapter Review Question Answers A. Radio waves (long
... 51. a. An orbital is a 3-D space around the nucleus where there is a high probability that an electron is likely to be located. b. Orbitals are like clouds that show the region of probable electron locations. The sizes and shapes of electron clouds depend on the energies of the electrons that occupy ...
... 51. a. An orbital is a 3-D space around the nucleus where there is a high probability that an electron is likely to be located. b. Orbitals are like clouds that show the region of probable electron locations. The sizes and shapes of electron clouds depend on the energies of the electrons that occupy ...
Review-Semester Final (Part I)
... 16. List 3 elements with a large atomic radius 17. List 3 elements with a small atomic radius 18. Which holds its electrons more tightly- metals or nonmetals? How does this affect the properties of each? ...
... 16. List 3 elements with a large atomic radius 17. List 3 elements with a small atomic radius 18. Which holds its electrons more tightly- metals or nonmetals? How does this affect the properties of each? ...
File
... Electricity is related to charges, and both electrons and protons carry a charge. The amount of the charge is the same for each particle, but opposite in sign. Electrons carry a negative charge while protons carry positive charge. The objects around us contain billions and billions of atoms, and eac ...
... Electricity is related to charges, and both electrons and protons carry a charge. The amount of the charge is the same for each particle, but opposite in sign. Electrons carry a negative charge while protons carry positive charge. The objects around us contain billions and billions of atoms, and eac ...
Chapter 7, 8, and 9 Exam 2014 Name I. 50% of your grade will come
... 15. In the periodic table, as the atomic number increases from 11 to 17, what happens to the atomic radius? (A) It remains constant. (B) It increases only. (C) It increases, then decreases. (D) It decreases only. (E) It decreases, then increases. 16. In a molecule in which the central atom exhibits ...
... 15. In the periodic table, as the atomic number increases from 11 to 17, what happens to the atomic radius? (A) It remains constant. (B) It increases only. (C) It increases, then decreases. (D) It decreases only. (E) It decreases, then increases. 16. In a molecule in which the central atom exhibits ...
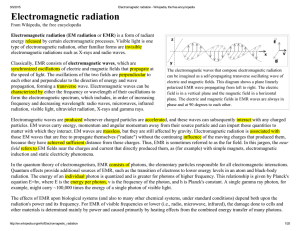
Electromagnetic radiation
... because they have achieved sufficient distance from those charges. Thus, EMR is sometimes referred to as the far field. In this jargon, the near field refers to EM fields near the charges and current that directly produced them, as (for example) with simple magnets, electromagnetic induction and sta ...
... because they have achieved sufficient distance from those charges. Thus, EMR is sometimes referred to as the far field. In this jargon, the near field refers to EM fields near the charges and current that directly produced them, as (for example) with simple magnets, electromagnetic induction and sta ...
Physics IV - Final Exam - SS 2007 Please note:
... before and after the scattering in terms of incident X-ray wavelength λ and the wavelength shift ∆λ. Assuming that the free electron was stationary before the scattering, write down an expression for the kinetic energy of the scattered electron as a function of λ and ∆λ. [4] (c) The Compton shift ∆λ ...
... before and after the scattering in terms of incident X-ray wavelength λ and the wavelength shift ∆λ. Assuming that the free electron was stationary before the scattering, write down an expression for the kinetic energy of the scattered electron as a function of λ and ∆λ. [4] (c) The Compton shift ∆λ ...
Energy - Gyanpedia
... If two equally and oppositely charged bodies are connected by a metallic conductor such as a wire, the charges neutralize each other. This neutralization is accomplished by means of a flow of electrons through the conductor from the negatively charged body to the positively charged one.. In any co ...
... If two equally and oppositely charged bodies are connected by a metallic conductor such as a wire, the charges neutralize each other. This neutralization is accomplished by means of a flow of electrons through the conductor from the negatively charged body to the positively charged one.. In any co ...
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 - Lawndale High School
... Each discrete line in an emission spectrum corresponds to one exact frequency of light emitted by the atom Ground State – lowest possible energy of the electron in the Bohr model The light emitted by an electron moving from higher to a lower energy level has a frequency directly proportional to the ...
... Each discrete line in an emission spectrum corresponds to one exact frequency of light emitted by the atom Ground State – lowest possible energy of the electron in the Bohr model The light emitted by an electron moving from higher to a lower energy level has a frequency directly proportional to the ...