light
... • Both electric and magnetic fields can transport energy – Electric field energy used in electrical circuits, e.g., released in lightning – Magnetic field carries energy through transformer, for example ...
... • Both electric and magnetic fields can transport energy – Electric field energy used in electrical circuits, e.g., released in lightning – Magnetic field carries energy through transformer, for example ...
Unit 3: Electron Configurations
... The Quantum Mechanical Model of electrons within an atom says we cannot pinpoint where an electron is, but we can get the probability of where the electron is. Electron configurations show how electrons are distributed within an atom. ...
... The Quantum Mechanical Model of electrons within an atom says we cannot pinpoint where an electron is, but we can get the probability of where the electron is. Electron configurations show how electrons are distributed within an atom. ...
B1987
... 1987B6. In a photoelectric experiment, light is incident on a metal surface. Electrons are ejected from the surface, producing a current in a circuit. A reverse potential is applied in the circuit and adjusted until the current drops to zero. That potential at which the current drops to zero is cal ...
... 1987B6. In a photoelectric experiment, light is incident on a metal surface. Electrons are ejected from the surface, producing a current in a circuit. A reverse potential is applied in the circuit and adjusted until the current drops to zero. That potential at which the current drops to zero is cal ...
Quiz 1 - sample quiz
... 9. Which one of the following statements is false? a) An electron jumps from a high energy orbital to a lower energy orbital when a photon of energy is emitted by an atom. b) The energy of light is directly proportional to its wavelength. c) The atomic emission spectrum consists of a series of discr ...
... 9. Which one of the following statements is false? a) An electron jumps from a high energy orbital to a lower energy orbital when a photon of energy is emitted by an atom. b) The energy of light is directly proportional to its wavelength. c) The atomic emission spectrum consists of a series of discr ...
63. (a) We use conservation of mechanical energy to find the speed
... For this to be zero, m = M/3. With M = 0.63 kg, we have m = 0.21 kg. (b) We use the same equation to find the velocity of the ball of mass m after the collision: vmf = − ...
... For this to be zero, m = M/3. With M = 0.63 kg, we have m = 0.21 kg. (b) We use the same equation to find the velocity of the ball of mass m after the collision: vmf = − ...
class1_BK - Center for Detectors
... too low in frequency to be visible—it emits infrared waves, which aren’t seen with the eye. You emit waves as well. Even in a completely dark room your waves are there. Your friends may not be able to see you, but a rattlesnake can! ...
... too low in frequency to be visible—it emits infrared waves, which aren’t seen with the eye. You emit waves as well. Even in a completely dark room your waves are there. Your friends may not be able to see you, but a rattlesnake can! ...
T3_Static_Potentials_And_Eigenstates
... – Found by accident (“faulty” nickel target) – “ruined” Germer’s second honeymoon ...
... – Found by accident (“faulty” nickel target) – “ruined” Germer’s second honeymoon ...
Lecture7
... • What are stars and interstellar gas made of? – The same elements we see on Earth, mostly Hydrogen, He, Oxygen, ...
... • What are stars and interstellar gas made of? – The same elements we see on Earth, mostly Hydrogen, He, Oxygen, ...
AS Revision Flash Cards File
... Constructive interference occurs when two wave trains arrive at a point in phase and reinforce. Path difference from the sources = nλ Destructive interference occurs when two wave trains arrive at a point with phase difference 180 and cancel. Path difference = (n + ½)λ For light of wavelength ...
... Constructive interference occurs when two wave trains arrive at a point in phase and reinforce. Path difference from the sources = nλ Destructive interference occurs when two wave trains arrive at a point with phase difference 180 and cancel. Path difference = (n + ½)λ For light of wavelength ...
Unit 1
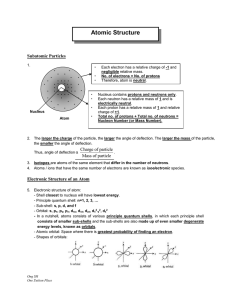
... • The number of protons (atomic number) in a nucleus determines what element a substance is. • Each element has a number of electrons equal to the number of protons • The electron orbitals are different for each element, and the energy differences between the orbitals are unique as well. • This mean ...
... • The number of protons (atomic number) in a nucleus determines what element a substance is. • Each element has a number of electrons equal to the number of protons • The electron orbitals are different for each element, and the energy differences between the orbitals are unique as well. • This mean ...
3.1 - cmpascience
... associated with its location. In Bohr’s model of the atom, electrons were thought to orbit the nucleus in set paths, much like planets orbiting the sun. In the modern atomic theory, the region in an atom where electrons are likely to be found is called an orbital. But, the exact location of an elect ...
... associated with its location. In Bohr’s model of the atom, electrons were thought to orbit the nucleus in set paths, much like planets orbiting the sun. In the modern atomic theory, the region in an atom where electrons are likely to be found is called an orbital. But, the exact location of an elect ...
Atomic-absorption (AA) spectroscopy
... The electric potential ionizes rare gas atoms and accelerates them into the cathode where they sputter metal atoms into the gas phase Collisions with gas atoms or electrons excite the metal atoms On decay the metal atoms emit light ...
... The electric potential ionizes rare gas atoms and accelerates them into the cathode where they sputter metal atoms into the gas phase Collisions with gas atoms or electrons excite the metal atoms On decay the metal atoms emit light ...