Kinetic Energy
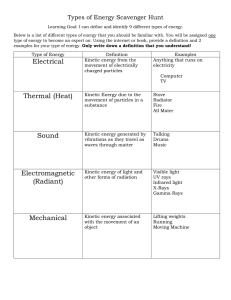
... Learning Goal: I can define and identify 9 different types of energy. Below is a list of different types of energy that you should be familiar with. You will be assigned one type of energy to become an expert on. Using the internet or book, provide a definition and 2 examples for your type of energy ...
... Learning Goal: I can define and identify 9 different types of energy. Below is a list of different types of energy that you should be familiar with. You will be assigned one type of energy to become an expert on. Using the internet or book, provide a definition and 2 examples for your type of energy ...
The Development of a New Atomic Model
... electromagnetic radiation include x-rays, ultraviolet and infrared light, microwaves, and radio waves. Together, all the forms of electromagnetic radiation form the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is represented in Figure 1.1 on the next page. All forms of electromagnetic radi ...
... electromagnetic radiation include x-rays, ultraviolet and infrared light, microwaves, and radio waves. Together, all the forms of electromagnetic radiation form the electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is represented in Figure 1.1 on the next page. All forms of electromagnetic radi ...
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... • Speed is equal to the frequency times the wavelength c = v • Frequency (v) is the number of waves passing a given point in one second • Wavelength () is the distance between peaks of adjacent waves • Speed of light is a constant, so v is also a constant; v and must be inversely proportional ...
... • Speed is equal to the frequency times the wavelength c = v • Frequency (v) is the number of waves passing a given point in one second • Wavelength () is the distance between peaks of adjacent waves • Speed of light is a constant, so v is also a constant; v and must be inversely proportional ...
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... • Speed is equal to the frequency times the wavelength c = v • Frequency (v) is the number of waves passing a given point in one second • Wavelength () is the distance between peaks of adjacent waves • Speed of light is a constant, so v is also a constant; v and must be inversely proportional ...
... • Speed is equal to the frequency times the wavelength c = v • Frequency (v) is the number of waves passing a given point in one second • Wavelength () is the distance between peaks of adjacent waves • Speed of light is a constant, so v is also a constant; v and must be inversely proportional ...
Phys 221 Lecture 36 April 19 , 2004 1 Exam 4 Review Chapter 24
... of the following statements is that best explanation for this observation? a. Each atom has a dense central nucleus. b. The electrons in atoms orbit the nucleus c. Each atom has a unique set of energy levels d. The electrons in atoms are in constant motion e. Each atom is composed of positive and ne ...
... of the following statements is that best explanation for this observation? a. Each atom has a dense central nucleus. b. The electrons in atoms orbit the nucleus c. Each atom has a unique set of energy levels d. The electrons in atoms are in constant motion e. Each atom is composed of positive and ne ...
Chapter 2 Study Guide
... 3. The atomic number of an element whose atoms have 12 protons and 11 neutrons is _____. 4. The mass number of an element whose atoms have 15 protons and 17 neutrons is _________. 5. One isotope of carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. The number of protons and neutrons of a second isotope of carbon ...
... 3. The atomic number of an element whose atoms have 12 protons and 11 neutrons is _____. 4. The mass number of an element whose atoms have 15 protons and 17 neutrons is _________. 5. One isotope of carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. The number of protons and neutrons of a second isotope of carbon ...
$doc.title
... During a solar eclipse, the sun – a small but extended source – casts a shadow of the moon on the earth. The moon’s shadow had a dark center surrounded by a region of increasing brightness as shown in (b). ...
... During a solar eclipse, the sun – a small but extended source – casts a shadow of the moon on the earth. The moon’s shadow had a dark center surrounded by a region of increasing brightness as shown in (b). ...
collective states of 2d electron-hole system under the influence of
... This influence on the chemical potential of the Bose–Einstein condensed magnetoexcitons and on the ground state energy of the metallic-type electron–hole liquid is investigated in the Hartree–Fock approximation. We have established that chemical potential is monotonic function versus the value of th ...
... This influence on the chemical potential of the Bose–Einstein condensed magnetoexcitons and on the ground state energy of the metallic-type electron–hole liquid is investigated in the Hartree–Fock approximation. We have established that chemical potential is monotonic function versus the value of th ...
Atomic Terminology Atomic Terminology What
... the _____ of a glowing black body. – The hotter object emits more ____ light than ____, and thus looks ____. – The cooler object emits more ____ than ____, and consequently looks ____. ...
... the _____ of a glowing black body. – The hotter object emits more ____ light than ____, and thus looks ____. – The cooler object emits more ____ than ____, and consequently looks ____. ...























