Worksheet - Velocity & Speed
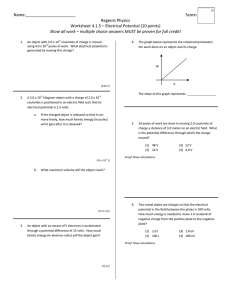
... A proton moving parallel to a negative plate. An electron and proton moving closer together ...
... A proton moving parallel to a negative plate. An electron and proton moving closer together ...
Chapter 4 Exam Review Democritus named tiny pieces of matter
... 19. What do scientists use to predict the locations of electrons in atoms? _______________________________ 20. What does the electron cloud model describe? _________________________________________________________ 21. How many electrons can one orbital contain? ________________________ 22. An electr ...
... 19. What do scientists use to predict the locations of electrons in atoms? _______________________________ 20. What does the electron cloud model describe? _________________________________________________________ 21. How many electrons can one orbital contain? ________________________ 22. An electr ...
Word
... In the 18th and 19th centuries it was believed that light was a ________. Many experiments provided evidence for the wave model of light since they showed that light could refract, ________ and interfere. However, there were other experiments that couldn’t be explained by the wave model of light. In ...
... In the 18th and 19th centuries it was believed that light was a ________. Many experiments provided evidence for the wave model of light since they showed that light could refract, ________ and interfere. However, there were other experiments that couldn’t be explained by the wave model of light. In ...
Light and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
... believed light consisted of particles • By 1900 most scientists believed that light behaved as a wave. ...
... believed light consisted of particles • By 1900 most scientists believed that light behaved as a wave. ...
EP-07 Precision Photoelectric Effect
... provided convincing experimental verification of quantum theory. The actual phenomenon of photoemission of electrons from metals was observed by Hertz in 1887. However, Hertz's experimental data proved to be incompatible with the wave theory of light. Einstein postulated that not only is light emitt ...
... provided convincing experimental verification of quantum theory. The actual phenomenon of photoemission of electrons from metals was observed by Hertz in 1887. However, Hertz's experimental data proved to be incompatible with the wave theory of light. Einstein postulated that not only is light emitt ...
Lecture 15
... PHYSICS 244 NOTES Lecture 15 All atoms besides hydrogen Ionization of atoms What if an H atom has light in the far UV shone on it such that the energy of a photon is greater than 13.6 eV? Then the atom can be ionized – this simply corresponds to a transition from a bound state to an unbound state. T ...
... PHYSICS 244 NOTES Lecture 15 All atoms besides hydrogen Ionization of atoms What if an H atom has light in the far UV shone on it such that the energy of a photon is greater than 13.6 eV? Then the atom can be ionized – this simply corresponds to a transition from a bound state to an unbound state. T ...
what is light? - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... from one place to another. They do this by a series of total internal reflections. Optical fibers are useful for getting light to inaccessible places. Mechanics and machinists use them to look at the interiors of engines, and physicians use them to look inside a patient’s body. ...
... from one place to another. They do this by a series of total internal reflections. Optical fibers are useful for getting light to inaccessible places. Mechanics and machinists use them to look at the interiors of engines, and physicians use them to look inside a patient’s body. ...
Periodic Table Notes Unit 3 – Notes
... energy required to remove an electron from the ground state of an atom. – The first ionization energy is that energy required to remove first electron. – The second ionization energy is that energy required to remove second electron, etc. – Measured in J or kJ ...
... energy required to remove an electron from the ground state of an atom. – The first ionization energy is that energy required to remove first electron. – The second ionization energy is that energy required to remove second electron, etc. – Measured in J or kJ ...
ICP Final Exam Study Guide
... Nuclear energy = converting mass into energy via nuclear fusion (meld) or fission (division) ** Mechanical energy = potential energy + kinetic energy ** Mechanical energy is constant. Sources of energy: fossil fuel, nuclear fission, solar, wind, water, geothermal, alternative fuels Work = transfer o ...
... Nuclear energy = converting mass into energy via nuclear fusion (meld) or fission (division) ** Mechanical energy = potential energy + kinetic energy ** Mechanical energy is constant. Sources of energy: fossil fuel, nuclear fission, solar, wind, water, geothermal, alternative fuels Work = transfer o ...
1 - WordPress.com
... Electron flow is a flow of electrons from negative to positive. Conventional current is an imaginary flow of positive charges from positive to negative. 20. Explain the difference between static electricity and current electricity. Static electricity is a charge build-up in a place that is not movin ...
... Electron flow is a flow of electrons from negative to positive. Conventional current is an imaginary flow of positive charges from positive to negative. 20. Explain the difference between static electricity and current electricity. Static electricity is a charge build-up in a place that is not movin ...