* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electron notes File
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Shockley–Queisser limit wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
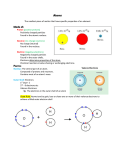
ELECTRONS • Negatively charged particle surrounding the nucleus • Electrons move quickly around the nucleus at a rate of billions of times each second. • In a neutral atom the number of electrons equals the number of protons Location of the electron • Depends on how much energy the electron has • Arranged in energy levels • Lower energy levels are closer to the nucleus Drawing Energy Levels • Start with the lowest energy level • Fill energy level completely before placing electrons in the next energy level Energy levels • 1st energy level can hold 2 electrons • 2nd energy level can hold 8 electrons • 3rd energy level can hold 18 electrons • 4th energy level can hold 32 electrons Energy Sublevels • 1st energy level - S orbital 2 electrons • 2nd energy level - S orbital 2 electrons P orbital 6 electrons • 3rd energy level - S orbital 2 electrons P orbital 6 electrons D orbital 10 electrons • 4th energy level - S orbital 2 electrons P orbital 6 electrons D orbital 10 electrons F orbital 14 electrons Electron Shell Structure • The Octet Rule: • In general, atoms are most stable when they have 8 electrons in their outermost shell. (Octet means 8.) The exception is the first shell which is most stable with TWO electrons. If you know the Atomic Number and Mass Number of an element and the maximum number of electrons in each electron shell you can draw a diagram of the element. Order of Orbital Filling • Electron configuration Electrons and light • When electrons absorb energy they move out to the next energy level • When they lose energy they drop down a level and give off light Colorado - univ of Bolder • Cool site • http://www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/inde x.pl Isotopes • Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons • Round the atomic mass to the nearest whole number to find the number of neutrons in the most common form of the atom • Mass numbers of isotopes differ because the number of neutrons is different