Biol 1406 notes Ch 8 8thed
... Catabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds. ○ A major pathway of catabolism is cellular respiration, in which the sugar glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen to carbon dioxide and water. ○ The energy released by catabolic pathways becomes a ...
... Catabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds. ○ A major pathway of catabolism is cellular respiration, in which the sugar glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen to carbon dioxide and water. ○ The energy released by catabolic pathways becomes a ...
Gluconeogenesis
... A metal ion such as Mn++ is required for the PEP Carboxykinase reaction, in addition to a Mg++ ion that binds with the nucleotide substrate at the active site. Mn++ is thought to promote Pi transfer by interacting simultaneously with the enolate oxygen atom and an oxygen atom of the terminal phospha ...
... A metal ion such as Mn++ is required for the PEP Carboxykinase reaction, in addition to a Mg++ ion that binds with the nucleotide substrate at the active site. Mn++ is thought to promote Pi transfer by interacting simultaneously with the enolate oxygen atom and an oxygen atom of the terminal phospha ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... The quantity E + PV defines a function describing the state of the system and is the heat content or enthalpy. The enthalpy change associated with a transformation is equivalent in magnitude to the heat of the reaction at constant pressure, but with the opposite sign. If a transformation not only ta ...
... The quantity E + PV defines a function describing the state of the system and is the heat content or enthalpy. The enthalpy change associated with a transformation is equivalent in magnitude to the heat of the reaction at constant pressure, but with the opposite sign. If a transformation not only ta ...
Nucleic Acid metabolism De Novo Synthesis of Purine
... dihydroorotase activities are part of a multifunctional protein. • Oxidation of the ring by a complex, poorly understood enzyme produces the free pyrimidine, orotic acid. This enzyme is located on the outer face of the inner mitochondrial membrane, in contrast to the other enzymes which are cytosoli ...
... dihydroorotase activities are part of a multifunctional protein. • Oxidation of the ring by a complex, poorly understood enzyme produces the free pyrimidine, orotic acid. This enzyme is located on the outer face of the inner mitochondrial membrane, in contrast to the other enzymes which are cytosoli ...
K m + [S]
... • The synthesis of certain enzymes may also be specifically inhibited. In a process called repression, the end product of a biochemical pathway may inhibit the synthesis of a key enzyme in the pathway. Both induction and repression involve cis-elements, specific DNA sequences located upstream of ge ...
... • The synthesis of certain enzymes may also be specifically inhibited. In a process called repression, the end product of a biochemical pathway may inhibit the synthesis of a key enzyme in the pathway. Both induction and repression involve cis-elements, specific DNA sequences located upstream of ge ...
Practical Methods for Biocatalysis and Biotransformations 2 Brochure
... Biocatalysts are increasingly used by chemists engaged in fine chemical synthesis within both industry and academia. Today, there exists a huge choice of high–tech enzymes and whole cell biocatalysts, which add enormously to the repertoire of synthetic possibilities. Practical Methods for Biocatalys ...
... Biocatalysts are increasingly used by chemists engaged in fine chemical synthesis within both industry and academia. Today, there exists a huge choice of high–tech enzymes and whole cell biocatalysts, which add enormously to the repertoire of synthetic possibilities. Practical Methods for Biocatalys ...
Energy Systems - Southwest High School
... Creatine (produced in the body as Creatine Phoshate) is naturally produced in the human body from amino acids primarily in the kidney and liver. It is transported in the blood for use by muscles. Approximately 95% of the human body's total Creatine is located in skeletal muscle. Creatine helps to su ...
... Creatine (produced in the body as Creatine Phoshate) is naturally produced in the human body from amino acids primarily in the kidney and liver. It is transported in the blood for use by muscles. Approximately 95% of the human body's total Creatine is located in skeletal muscle. Creatine helps to su ...
Driving natural systems: Chemical energy production and use
... drive natural systems I Now: ODE modelling – physical models for the species concentrations and physical properties of bioenergetic systems (particularly oxidative phosphorylation and the mitochondrion) I Next: FBA (flux balance analysis) – coarse-grained representation of large networks of metaboli ...
... drive natural systems I Now: ODE modelling – physical models for the species concentrations and physical properties of bioenergetic systems (particularly oxidative phosphorylation and the mitochondrion) I Next: FBA (flux balance analysis) – coarse-grained representation of large networks of metaboli ...
Chapter 8 Notes Bio AP
... The release of energy during the hydrolysis of ATP comes from the chemical change to a state of lower free energy, not from the phosphate bonds themselves. Why does the hydrolysis of ATP yield so much energy? o Each of the three phosphate groups has a negative charge. o These three like charges are ...
... The release of energy during the hydrolysis of ATP comes from the chemical change to a state of lower free energy, not from the phosphate bonds themselves. Why does the hydrolysis of ATP yield so much energy? o Each of the three phosphate groups has a negative charge. o These three like charges are ...
Unit 6 - Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... 6. State and explain the chemical equation that summarizes photosynthesis. 7. Define pigment and chlorophyll. 8. Describe the roles of pigments, chlorophyll and light in photosynthesis. Topic 3: Photosynthesis details (8-3) 9. Draw and label a diagram of the chloroplast, including the location and s ...
... 6. State and explain the chemical equation that summarizes photosynthesis. 7. Define pigment and chlorophyll. 8. Describe the roles of pigments, chlorophyll and light in photosynthesis. Topic 3: Photosynthesis details (8-3) 9. Draw and label a diagram of the chloroplast, including the location and s ...
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
... 4. What is a “sticky end”, and how is it created? 5. How are probes used to screen colonies to find the ones that contain the gene of interest? 6. How does gel electrophoresis work? 7. How can gel electrophoresis be used to identify differences between individuals? What is a RFLP? 8. What is a VNTR ...
... 4. What is a “sticky end”, and how is it created? 5. How are probes used to screen colonies to find the ones that contain the gene of interest? 6. How does gel electrophoresis work? 7. How can gel electrophoresis be used to identify differences between individuals? What is a RFLP? 8. What is a VNTR ...
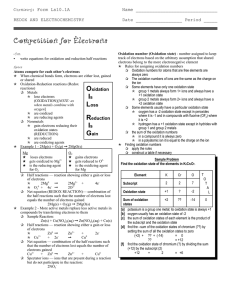
Competition for Electrons
... track of electrons based on the arbitrary assumption that shared electrons belong to the more electronegative element n Rules for assigning oxidation numbers q Oxidation numbers for atoms that are free elements are always zero q The oxidation numbers of ions are the same as the charge on the ion q S ...
... track of electrons based on the arbitrary assumption that shared electrons belong to the more electronegative element n Rules for assigning oxidation numbers q Oxidation numbers for atoms that are free elements are always zero q The oxidation numbers of ions are the same as the charge on the ion q S ...
File
... • Protein RDA is 44 to 60 g/day – Weight in pounds x 0.37 = estimate of RDA of protein – Higher intake recommended under conditions of stress, infection, injury, and pregnancy – Excessive intake overloads the kidneys with nitrogenous waste and can cause kidney damage ...
... • Protein RDA is 44 to 60 g/day – Weight in pounds x 0.37 = estimate of RDA of protein – Higher intake recommended under conditions of stress, infection, injury, and pregnancy – Excessive intake overloads the kidneys with nitrogenous waste and can cause kidney damage ...
Unit 2 Biochemistry Chp 8 Metabolism Notes
... A spontaneous process is one that is energetically favorable. A process that cannot occur on its own is said to be nonspontaneous: it will happen only if energy is added to the system. ○ Water flows downhill spontaneously but moves uphill only with an input of energy, such as when a machine pumps th ...
... A spontaneous process is one that is energetically favorable. A process that cannot occur on its own is said to be nonspontaneous: it will happen only if energy is added to the system. ○ Water flows downhill spontaneously but moves uphill only with an input of energy, such as when a machine pumps th ...
Enzymes - CEA Workshop Teacher Notes.pptx
... to assist enzyme acJvity • A coenzyme will bind to a protein to form an acJve enzyme • Coenzymes osen help by carrying a group of atoms to the acJve site which are then transferred to the su ...
... to assist enzyme acJvity • A coenzyme will bind to a protein to form an acJve enzyme • Coenzymes osen help by carrying a group of atoms to the acJve site which are then transferred to the su ...
Lipid Oxidation - anslab.iastate.edu
... Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) • Not a radical • Important in biological systems because it can pass readily through cell membranes • Superoxide-generating systems produces H2O2 by nonenzymatic or SOD-catalyzed dismutation ...
... Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) • Not a radical • Important in biological systems because it can pass readily through cell membranes • Superoxide-generating systems produces H2O2 by nonenzymatic or SOD-catalyzed dismutation ...
Key Area 8 Respiration
... respiration in the absence of oxygen that takes place in animals. Success Criteria: Be able to name the process of respiration in the absence of oxygen Be able to describe the process of respiration in the absence of oxygen . Be able to name the conditions that an animal would be in to carry out thi ...
... respiration in the absence of oxygen that takes place in animals. Success Criteria: Be able to name the process of respiration in the absence of oxygen Be able to describe the process of respiration in the absence of oxygen . Be able to name the conditions that an animal would be in to carry out thi ...
Coupling of electron and proton movement in
... Photosynthetic oxidation of two water molecules to molecular oxygen and four protons takes place at a manganese containing unit - the water oxidizing complex (WOC) - within the multimeric Photosystem II (PS II) complex that acts as a water-plastoquinone-oxidoreductase. The overall process comprises ...
... Photosynthetic oxidation of two water molecules to molecular oxygen and four protons takes place at a manganese containing unit - the water oxidizing complex (WOC) - within the multimeric Photosystem II (PS II) complex that acts as a water-plastoquinone-oxidoreductase. The overall process comprises ...
Carnosine: can understanding its actions on energy metabolism and
... The metabolic shifts that occur as organisms grow, mature and finally age are complex and incompletely understood. When rapid growth ceases, in the transition to adulthood, the preferred pathway for ATP generation changes from glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation [17]. However, one hallmark of ce ...
... The metabolic shifts that occur as organisms grow, mature and finally age are complex and incompletely understood. When rapid growth ceases, in the transition to adulthood, the preferred pathway for ATP generation changes from glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation [17]. However, one hallmark of ce ...
Chapter 6 "Mechanisms of Enzymes" Reading Assignment: pp. 158
... amino acids within the active site. A. Polar amino acid residues in active sites The active site cavity of an enzyme is generally lined with hydrophobic aa residues. The side chains of the few polar amino acids located in the enzyme active site often participate directly in catalysis. As a result of ...
... amino acids within the active site. A. Polar amino acid residues in active sites The active site cavity of an enzyme is generally lined with hydrophobic aa residues. The side chains of the few polar amino acids located in the enzyme active site often participate directly in catalysis. As a result of ...
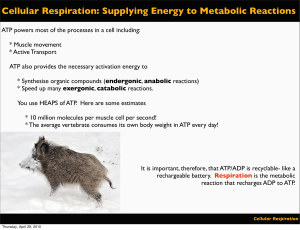
Cellular Respiration: Supplying Energy to Metabolic Reactions
... Many of the most successful organisms in existence are anaerobic and thus only achieve 3% efficiency. Nonetheless it was only after the evolution of the Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain that respiration could achieve a level of efficiency capable of sustaining larger, and more ...
... Many of the most successful organisms in existence are anaerobic and thus only achieve 3% efficiency. Nonetheless it was only after the evolution of the Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain that respiration could achieve a level of efficiency capable of sustaining larger, and more ...
training handout - Science Olympiad
... signaling pathways. o In their negative role, rafts may spatially segregate interacting components to block nonspecific pathway activation, or may directly suppress the activity of signaling proteins present in rafts. Proteins serve different functions ...
... signaling pathways. o In their negative role, rafts may spatially segregate interacting components to block nonspecific pathway activation, or may directly suppress the activity of signaling proteins present in rafts. Proteins serve different functions ...
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation (or OXPHOS in short) is the metabolic pathway in which the mitochondria in cells use their structure, enzymes, and energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to reform ATP. Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, ATP is the molecule that supplies energy to metabolism. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is probably so pervasive because it is a highly efficient way of releasing energy, compared to alternative fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis.During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from electron donors to electron acceptors such as oxygen, in redox reactions. These redox reactions release energy, which is used to form ATP. In eukaryotes, these redox reactions are carried out by a series of protein complexes within the inner membrane of the cell's mitochondria, whereas, in prokaryotes, these proteins are located in the cells' intermembrane space. These linked sets of proteins are called electron transport chains. In eukaryotes, five main protein complexes are involved, whereas in prokaryotes many different enzymes are present, using a variety of electron donors and acceptors.The energy released by electrons flowing through this electron transport chain is used to transport protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, in a process called electron transport. This generates potential energy in the form of a pH gradient and an electrical potential across this membrane. This store of energy is tapped by allowing protons to flow back across the membrane and down this gradient, through a large enzyme called ATP synthase; this process is known as chemiosmosis. This enzyme uses this energy to generate ATP from adenosine diphosphate (ADP), in a phosphorylation reaction. This reaction is driven by the proton flow, which forces the rotation of a part of the enzyme; the ATP synthase is a rotary mechanical motor.Although oxidative phosphorylation is a vital part of metabolism, it produces reactive oxygen species such as superoxide and hydrogen peroxide, which lead to propagation of free radicals, damaging cells and contributing to disease and, possibly, aging (senescence). The enzymes carrying out this metabolic pathway are also the target of many drugs and poisons that inhibit their activities.





![K m + [S]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008289247_1-97eed219b6e242b1a447e591c5c01f05-300x300.png)