Metabolic Adaptation - Washington State University
... versus protein • Amino acids and carbohydrates are at about the same oxidation state – so although the exact pathways may vary from one amino acid to another, the yield of ATP from a gram of amino acid is about the same as the yield from a gram of glucose. • However, as in the example of the fly, am ...
... versus protein • Amino acids and carbohydrates are at about the same oxidation state – so although the exact pathways may vary from one amino acid to another, the yield of ATP from a gram of amino acid is about the same as the yield from a gram of glucose. • However, as in the example of the fly, am ...
ADM: Facts about Fats
... of long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs). As their name implies, LCFAs are long chains of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms attached, as illustrated in the figure below. The most common fatty acids found in feed supplements are 16 and 18 carbons in length (see table). These can be found either combined with ...
... of long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs). As their name implies, LCFAs are long chains of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms attached, as illustrated in the figure below. The most common fatty acids found in feed supplements are 16 and 18 carbons in length (see table). These can be found either combined with ...
First test material Study guide
... b- hormone from specific secreting cells enters blood stream and travels to targets c- involve messengers that act on cells from which secreted, or same cell types d- Acetylcholine is an example of this mechanism e- Involves only tyrosine kinase surface receptor signaling Answer: B… A and D defines ...
... b- hormone from specific secreting cells enters blood stream and travels to targets c- involve messengers that act on cells from which secreted, or same cell types d- Acetylcholine is an example of this mechanism e- Involves only tyrosine kinase surface receptor signaling Answer: B… A and D defines ...
Intro to and Thermodynamics In Metabolism:
... Skip the “Interactions of fat Metabolism pathways” diagram. Understand the fat metabolism in specific tissues but don’t worry about the diagram. Skip the “Export of Acetyl CoA for Fatty Acid Biosynthesis” diagram. Understand how the fatty Acid Synthase works (No structures). Understand esterificatio ...
... Skip the “Interactions of fat Metabolism pathways” diagram. Understand the fat metabolism in specific tissues but don’t worry about the diagram. Skip the “Export of Acetyl CoA for Fatty Acid Biosynthesis” diagram. Understand how the fatty Acid Synthase works (No structures). Understand esterificatio ...
Gluconeogenesis
... ATP with its high energy phoshoanhydride bonds: How does GTP get made from GDP? Directly from a single step in the Krebs cycle AND from the following reaction GDP + ATP → GTP + ADP This is carried out in the cell by an enzyme called Nucleotide diphosphate kinase which carries out the general reactio ...
... ATP with its high energy phoshoanhydride bonds: How does GTP get made from GDP? Directly from a single step in the Krebs cycle AND from the following reaction GDP + ATP → GTP + ADP This is carried out in the cell by an enzyme called Nucleotide diphosphate kinase which carries out the general reactio ...
Step 2: Pyruvate Oxidation
... • Happens in the cytoplasm • Does not require oxygen (anaerobic) • Inefficient (net 2 ATP produced) ...
... • Happens in the cytoplasm • Does not require oxygen (anaerobic) • Inefficient (net 2 ATP produced) ...
citric acid cycle
... cytosol. The mitochondrion contains the enzymes of the citric acid cycle, βoxidation of fatty acids, and of oxidative phosphorylation. The endoplasmic reticulum also contains the enzymes for many other processes, including protein synthesis, glycerolipid formation, and drug metabolism. • Metabolic p ...
... cytosol. The mitochondrion contains the enzymes of the citric acid cycle, βoxidation of fatty acids, and of oxidative phosphorylation. The endoplasmic reticulum also contains the enzymes for many other processes, including protein synthesis, glycerolipid formation, and drug metabolism. • Metabolic p ...
Lipid Synthesis 1. Fatty acid synthesis
... Fatty acids are a more efficient form of energy storage than carbohydrates because they are less hydrated, as result of fewer hydroxyl groups being available for hydrogen bonding. The energy content of fat tissue is 38 kJ/gm compared to 17 kJ/gm for carbohydrates. The processes of fatty acid degrada ...
... Fatty acids are a more efficient form of energy storage than carbohydrates because they are less hydrated, as result of fewer hydroxyl groups being available for hydrogen bonding. The energy content of fat tissue is 38 kJ/gm compared to 17 kJ/gm for carbohydrates. The processes of fatty acid degrada ...
Glucose homeostasis in the blood (2) – un-storing energy
... glucose levels are low Figure 2: Low levels of glucose stimulate the pancreas to make glucagon that signals the liver to un-store glucose. and send the message to storage organs that more glucose is needed in the blood. The pancreas sends this signal in the form of glucagon, a hormone made out of am ...
... glucose levels are low Figure 2: Low levels of glucose stimulate the pancreas to make glucagon that signals the liver to un-store glucose. and send the message to storage organs that more glucose is needed in the blood. The pancreas sends this signal in the form of glucagon, a hormone made out of am ...
UNIT 11. CATABOLISM OF GLUCOSE • Aerobic glycolysis: scheme
... Glycolysis is an oxidative specific pathway by which one mole of glucose is enzymatically split into two moles of pyruvate. It occurs in cytosol of all cells of the body. The principle function of glycolysis is the generation of ATP. Glycolysis also provides precursors for fatty acids biosynthesis, ...
... Glycolysis is an oxidative specific pathway by which one mole of glucose is enzymatically split into two moles of pyruvate. It occurs in cytosol of all cells of the body. The principle function of glycolysis is the generation of ATP. Glycolysis also provides precursors for fatty acids biosynthesis, ...
Chapter 24
... When both glucose and stored glycogen are depleted, glucose can be synthesis by gluconeogenesis. (in liver) ...
... When both glucose and stored glycogen are depleted, glucose can be synthesis by gluconeogenesis. (in liver) ...
chapter 11 - rci.rutgers.edu
... contrast to glycolysis which is anaerobic. The CAC takes place in the mitochondrial matrix of eukaryotic cells – whereas glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm. The immediate products of the CAC are reduced cofactors (NADH and FADH2) which then feed electrons into oxidative phosphorylation, yielding muc ...
... contrast to glycolysis which is anaerobic. The CAC takes place in the mitochondrial matrix of eukaryotic cells – whereas glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm. The immediate products of the CAC are reduced cofactors (NADH and FADH2) which then feed electrons into oxidative phosphorylation, yielding muc ...
Self Assessment Form This is a pre
... o Regulation of metabolic pathways 2) Carbohydrate metabolism – o overview of carbohydrate digestion and absorption: glucose and glycogen o glycolysis, glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis; TCA cycle, electron transfer chain and energy metabolism. 3) Lipid metabolism o overview of digestion and absorp ...
... o Regulation of metabolic pathways 2) Carbohydrate metabolism – o overview of carbohydrate digestion and absorption: glucose and glycogen o glycolysis, glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis; TCA cycle, electron transfer chain and energy metabolism. 3) Lipid metabolism o overview of digestion and absorp ...
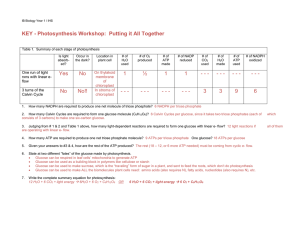
KEY - Photosynthesis Workshop: Putting it All Together
... 3. Judging from # 1 & 2 and Table 1 above, how many light-dependent reactions are required to form one glucose with linear e- flow? 12 light reactions if are operating with linear e- flow. ...
... 3. Judging from # 1 & 2 and Table 1 above, how many light-dependent reactions are required to form one glucose with linear e- flow? 12 light reactions if are operating with linear e- flow. ...
Enzymes Problem Set 1 A) What concentration of the substrate
... DHA kinase catalyzes the conversion of dihydroxyacetone (DHA) to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) using ATP as a co-substrate. The enzyme assay relies on a coupled reaction in which the reaction product, DHAP, is subsequently converted into glycerol 3phosphate by the presence of the enzyme glycerol ...
... DHA kinase catalyzes the conversion of dihydroxyacetone (DHA) to dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) using ATP as a co-substrate. The enzyme assay relies on a coupled reaction in which the reaction product, DHAP, is subsequently converted into glycerol 3phosphate by the presence of the enzyme glycerol ...
Lecture 1 Course overview and intro to enzymes
... glucagons (in liver) increase activity (more phosphorylated GP) hormonal control of GS phosphorylation insulin, glucose increase activity (decrease phosphorylation) glucagon and epinephrine inhibit GS (increase phosporylation) Liver as a glucostat various ways glucose is processed in liver normal bl ...
... glucagons (in liver) increase activity (more phosphorylated GP) hormonal control of GS phosphorylation insulin, glucose increase activity (decrease phosphorylation) glucagon and epinephrine inhibit GS (increase phosporylation) Liver as a glucostat various ways glucose is processed in liver normal bl ...
Energetics and Catabolism
... Glucose is activated by one phosphorylation reaction, and then dehydrogenated to 6phosphogluconate. - Then dehydrated and cleaved to pyruvate and glyceraldedyde-3-P, which enters the EMP pathway to form pyruvate The ED pathway produces 1 ATP, 1 NADH, and 1 NADPH. ...
... Glucose is activated by one phosphorylation reaction, and then dehydrogenated to 6phosphogluconate. - Then dehydrated and cleaved to pyruvate and glyceraldedyde-3-P, which enters the EMP pathway to form pyruvate The ED pathway produces 1 ATP, 1 NADH, and 1 NADPH. ...
WHY DO CARDIOMYOCYTES (HEART MUSCLE CELLS) STORE
... derived from pyruvate, and not from fats. So brain tissue is almost 100% dependent on glucose for its ATP production. All other cells need pyruvate to top up the mitochondrial oxaloacetate, which keeps ...
... derived from pyruvate, and not from fats. So brain tissue is almost 100% dependent on glucose for its ATP production. All other cells need pyruvate to top up the mitochondrial oxaloacetate, which keeps ...
THE METABOLISM OF KETONE BODIES
... the brain. Note the important times at which the brain switches from: • Glucose derived from liver glycogenolysis to glucose derived from gluconeogenesis (~12 hours) • Glucose derived from gluconeogenesis to ketones derived from fatty acids (~1 week) • In the brain, when ketones are metabolized to a ...
... the brain. Note the important times at which the brain switches from: • Glucose derived from liver glycogenolysis to glucose derived from gluconeogenesis (~12 hours) • Glucose derived from gluconeogenesis to ketones derived from fatty acids (~1 week) • In the brain, when ketones are metabolized to a ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.