Preparation of pyruvate for the citric acid cycle Recap 1. We have
... We have already stated what happens to pyruvate: Aerobic conditions 1. Converts to acetyl CoA (by pyruvate dehydrogenase) for use in the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (leads to more ATP production) 2. Converts to oxaloacetate , which can then shuttle into the synthesize glucose (can also b ...
... We have already stated what happens to pyruvate: Aerobic conditions 1. Converts to acetyl CoA (by pyruvate dehydrogenase) for use in the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation (leads to more ATP production) 2. Converts to oxaloacetate , which can then shuttle into the synthesize glucose (can also b ...
Cellular Respiration www.AssignmentPoint.com Cellular respiration
... Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that takes place in the cytosol of cells in all living organisms. This pathway can function with or without the presence of oxygen. In humans, aerobic conditions produce pyruvate and anaerobic conditions produce lactate. In aerobic conditions, the process converts o ...
... Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that takes place in the cytosol of cells in all living organisms. This pathway can function with or without the presence of oxygen. In humans, aerobic conditions produce pyruvate and anaerobic conditions produce lactate. In aerobic conditions, the process converts o ...
glucose, faKy acids, amino acids
... (anaerobic -‐ no O2 needed) 2) Citric Acid (Krebs) cycle (2 ATP) (aerobic -‐ O2 needed) 3) Electron transport chain (32-‐34 ATP) (aerobic) *steps 2 and 3 happen inside mitochondria ...
... (anaerobic -‐ no O2 needed) 2) Citric Acid (Krebs) cycle (2 ATP) (aerobic -‐ O2 needed) 3) Electron transport chain (32-‐34 ATP) (aerobic) *steps 2 and 3 happen inside mitochondria ...
The Central Role of Acetyl-CoA
... • Amino acids, from protein hydrolysis, can be deaminated to form α-ketoacids • Some α-ketoacids can be converted to pyruvate or to other intermediates in the citric acid cycle for glucose synthesis • Others are converted into acetyl-CoA, used in fatty acid synthesis ...
... • Amino acids, from protein hydrolysis, can be deaminated to form α-ketoacids • Some α-ketoacids can be converted to pyruvate or to other intermediates in the citric acid cycle for glucose synthesis • Others are converted into acetyl-CoA, used in fatty acid synthesis ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism
... 2- Isomertzation of glucose-6- phosphate to fructose–6 – phosphate. 3- Phosphorylation of fructose – 6 – phosphate to fructose 1,6 – bis – phosphate : This reaction is phosphorylated by ATP by the enzyme phosphofructokinase – 1 (PFK-1) is the most important control point and the rate – limiting ste ...
... 2- Isomertzation of glucose-6- phosphate to fructose–6 – phosphate. 3- Phosphorylation of fructose – 6 – phosphate to fructose 1,6 – bis – phosphate : This reaction is phosphorylated by ATP by the enzyme phosphofructokinase – 1 (PFK-1) is the most important control point and the rate – limiting ste ...
Repression of Glutaminase I in the rat Retina by
... determination, according to Rudnick and Waelsch.0 Glutamotransferase. This enzyme catalyzes the transfer of the glutamyl radical from glutamine or glutamine peptides to other amine receptors. Here, too, hydroxylamine can be used, and the color of the resultant glutamohydroxamic acid can be utilized ...
... determination, according to Rudnick and Waelsch.0 Glutamotransferase. This enzyme catalyzes the transfer of the glutamyl radical from glutamine or glutamine peptides to other amine receptors. Here, too, hydroxylamine can be used, and the color of the resultant glutamohydroxamic acid can be utilized ...
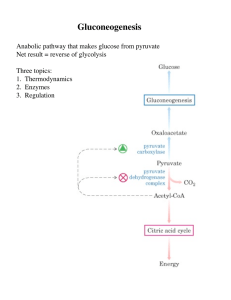
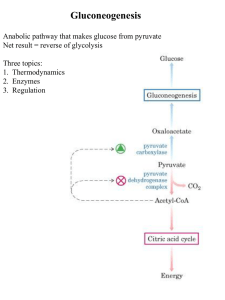
Biochemistry 304 2014 Student Edition Gluconeogenesis Lectures
... Lactate is formed by active skeletal muscle when glycolysis > oxidative metabolism. Lactate is converted by lactate dehydrogenase to pyruvate. Pyruvate (Certain) Amino acids are derived from protein in the diet or from muscle protein catabolism during starvation. Carbon skeletons of most amino acids ...
... Lactate is formed by active skeletal muscle when glycolysis > oxidative metabolism. Lactate is converted by lactate dehydrogenase to pyruvate. Pyruvate (Certain) Amino acids are derived from protein in the diet or from muscle protein catabolism during starvation. Carbon skeletons of most amino acids ...
Exercise Physiology Study Guide-Test 1 History of Exercise
... o ATP-PCr system-quick explosive energy source o Glycolytic system-short, high intensity energy source Anaerobic breakdown of CHO (glucose/glycogen) o Oxidative System-long term aerobic energy production (CHO and fat metabolism) Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, ETC, Beta-Oxidation ATP-PCr System o Can p ...
... o ATP-PCr system-quick explosive energy source o Glycolytic system-short, high intensity energy source Anaerobic breakdown of CHO (glucose/glycogen) o Oxidative System-long term aerobic energy production (CHO and fat metabolism) Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, ETC, Beta-Oxidation ATP-PCr System o Can p ...
Biochemistry 3 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... An enzyme that occurs in the liver but not in the brain or muscle tissue is _________________________. GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATASE The quaternary structure of Hemoglobin refers to the ________________. ASSOCIATION OF ALPHA & BETA SUBUNITS Which of the following Amino Acids have the greatest positive net c ...
... An enzyme that occurs in the liver but not in the brain or muscle tissue is _________________________. GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATASE The quaternary structure of Hemoglobin refers to the ________________. ASSOCIATION OF ALPHA & BETA SUBUNITS Which of the following Amino Acids have the greatest positive net c ...
BrevdueNord.dk Additional Thoughts on Nutrition for Racing Gordon
... incorporated into fatty acids in the liver within three minutes in hungry young pigeons, and that the content of fatty acids in liver reached a plateau in 15 minutes. Significant appearance of fatty acids in blood and fat depots was also first evident at 15 minutes after the injection, and their con ...
... incorporated into fatty acids in the liver within three minutes in hungry young pigeons, and that the content of fatty acids in liver reached a plateau in 15 minutes. Significant appearance of fatty acids in blood and fat depots was also first evident at 15 minutes after the injection, and their con ...
Which of the following is a coenzyme associated with
... The electrons that enter the electron transport system are carried there by _____. A. NADH B. FADH2 C. both A and B ___ ...
... The electrons that enter the electron transport system are carried there by _____. A. NADH B. FADH2 C. both A and B ___ ...
Uncoupling effect of fatty acids on heart muscle
... shown to increase with the increase in the length of hydrocarbon chain of the anion. Thermogenin is absent from tissue other than brown fat, but nevertheless fatty acids can uncouple in these other tissues (for reviw, see [S]). We assumed [2,5] that in these cases the role of the fatty acid anion po ...
... shown to increase with the increase in the length of hydrocarbon chain of the anion. Thermogenin is absent from tissue other than brown fat, but nevertheless fatty acids can uncouple in these other tissues (for reviw, see [S]). We assumed [2,5] that in these cases the role of the fatty acid anion po ...
CHAPTER 6
... buildup of pyruvate and NADH, due to oxygen shortage and the need for more glycolysis • NADH can be reoxidized during the reduction of pyruvate to lactate • Lactate is then returned to the liver, where it can be reoxidized to pyruvate by liver LDH • Liver provides glucose to muscle for exercise and ...
... buildup of pyruvate and NADH, due to oxygen shortage and the need for more glycolysis • NADH can be reoxidized during the reduction of pyruvate to lactate • Lactate is then returned to the liver, where it can be reoxidized to pyruvate by liver LDH • Liver provides glucose to muscle for exercise and ...
Air
... produce: 8 Acetyl-CoA x 12 = 96 ATP (3NADH + 1FADH2 + 1 GTP = 9 + 2 =12) 7 NADH x 3 = 21 ATP 7 FADH2 x 2 = 14 ATP ...
... produce: 8 Acetyl-CoA x 12 = 96 ATP (3NADH + 1FADH2 + 1 GTP = 9 + 2 =12) 7 NADH x 3 = 21 ATP 7 FADH2 x 2 = 14 ATP ...
Stryer An overview of the citric acid cycle
... Origin of mitochondria: the endosymbiont hypothesis The endosymbiont hypothesis suggests that mitochondria have evolved from anaerobic bacteria which were phagocytosed by eukaryote cells at the time oxygen appeared on earth, Similarities between mitochondria and bacteria include the presence of: • ...
... Origin of mitochondria: the endosymbiont hypothesis The endosymbiont hypothesis suggests that mitochondria have evolved from anaerobic bacteria which were phagocytosed by eukaryote cells at the time oxygen appeared on earth, Similarities between mitochondria and bacteria include the presence of: • ...
• Sources of glucose • Phases of glucose homeostasis • Hormones
... Phase I (Well-fed state) - Some glucose is converted to glycogen for storage in the liver (glycogenesis) - Excess glucose is converted to fatty acids and triglycerides in the liver - Which are transported via VLDL to adipose tissue for storage - Gluconeogenesis is inhibited in this phase ( Cori and ...
... Phase I (Well-fed state) - Some glucose is converted to glycogen for storage in the liver (glycogenesis) - Excess glucose is converted to fatty acids and triglycerides in the liver - Which are transported via VLDL to adipose tissue for storage - Gluconeogenesis is inhibited in this phase ( Cori and ...
Xenobiotic
... hypoglycemia especially after fasting ingestion of alcohol (+ usually poor dietary habits in chronic alcoholics) B) Excess of lactate in cytosol increased lactate in blood plasma lactic acidosis C) Excess of acetyl-CoA synthesis of FA +TAG liver steatosis ...
... hypoglycemia especially after fasting ingestion of alcohol (+ usually poor dietary habits in chronic alcoholics) B) Excess of lactate in cytosol increased lactate in blood plasma lactic acidosis C) Excess of acetyl-CoA synthesis of FA +TAG liver steatosis ...
Amino Acid Catabolism - Chemistry Courses: About
... the same as the first step of fatty acid oxidation. The fourth step involves an ATPdependent carboxylation, the fifth step is a hydration, and the last step is a cleavage reaction to give products. Draw the intermediates of leucine degradation. ...
... the same as the first step of fatty acid oxidation. The fourth step involves an ATPdependent carboxylation, the fifth step is a hydration, and the last step is a cleavage reaction to give products. Draw the intermediates of leucine degradation. ...
Amino Acid Catabolism - Chemistry Courses: About
... the same as the first step of fatty acid oxidation. The fourth step involves an ATPdependent carboxylation, the fifth step is a hydration, and the last step is a cleavage reaction to give products. Draw the intermediates of leucine degradation. ...
... the same as the first step of fatty acid oxidation. The fourth step involves an ATPdependent carboxylation, the fifth step is a hydration, and the last step is a cleavage reaction to give products. Draw the intermediates of leucine degradation. ...
Gluconeogenesis - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... When does gluconeogenesis occur? When dietary sources of glc are not available When liver has exhausted its glycogen stores (stored glc) What precursors does gluconeogenesis use? Lactate & pyruvate (glycolysis) TCA intermediates Carbon skeletons of AAs ...
... When does gluconeogenesis occur? When dietary sources of glc are not available When liver has exhausted its glycogen stores (stored glc) What precursors does gluconeogenesis use? Lactate & pyruvate (glycolysis) TCA intermediates Carbon skeletons of AAs ...
No Slide Title
... PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low blood sugar ...
... PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low blood sugar ...
Biochemistry 3(Dr.Kawa) Polysaccharide (Complex Carbohydrates
... the day: 80 to 120mg/dl. But they are higher after meals and usually lowest in the morning Diabetes mellitus: - Disease characterized by insufficient blood levels of active insulin and this deficiency leads to inability of glucose to enter muscle and liver cells with abnormal metabolism of proteins ...
... the day: 80 to 120mg/dl. But they are higher after meals and usually lowest in the morning Diabetes mellitus: - Disease characterized by insufficient blood levels of active insulin and this deficiency leads to inability of glucose to enter muscle and liver cells with abnormal metabolism of proteins ...
Sucrose is used for respiration, storage or construction. Plants
... H+ are transported out of the stroma/matrix by during electron transport and H+ flow back into the stroma/matrix through the ATP synthase and generates ATP in the ...
... H+ are transported out of the stroma/matrix by during electron transport and H+ flow back into the stroma/matrix through the ATP synthase and generates ATP in the ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.