Slide 1
... other mitochondrial uncoupling proteins) which are activated by calcium coming in through the calcium uniporter. Also note that electron carriers can autooxidize directly to oxygen, creating oxygen radicals (Co-Q is the major site of autooxidation) with as much as 5% of resting oxygen use due to thi ...
... other mitochondrial uncoupling proteins) which are activated by calcium coming in through the calcium uniporter. Also note that electron carriers can autooxidize directly to oxygen, creating oxygen radicals (Co-Q is the major site of autooxidation) with as much as 5% of resting oxygen use due to thi ...
Citric acid cycle - Issaquah Connect
... In that case, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produce ATP ...
... In that case, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produce ATP ...
4 Dr. M. Alzaharna 2016 Dr. M. Alzaharna 2016 II. REACTIONS OF
... CYCLE AND PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX ...
... CYCLE AND PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX ...
01 P⁄g. iniciales (Page 1)
... characterized by an unusual nucleotide-binding fold, i.e., the palmate- or ATP-grasp fold. This superfamily includes other ATP-dependent carboxylate-thiol ligases (succinate- and malateCoA ligases), as well as enzymes endowed with carboxylateamine ligase activity (glutathione synthetase, biotin carb ...
... characterized by an unusual nucleotide-binding fold, i.e., the palmate- or ATP-grasp fold. This superfamily includes other ATP-dependent carboxylate-thiol ligases (succinate- and malateCoA ligases), as well as enzymes endowed with carboxylateamine ligase activity (glutathione synthetase, biotin carb ...
Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... Thus, we now start to see a return on our initial investment of two molecules of ATP in stage 1. Going backward in the pathway one step to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, we find the outcomes of the reactions catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoglycerate kinase to be as foll ...
... Thus, we now start to see a return on our initial investment of two molecules of ATP in stage 1. Going backward in the pathway one step to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, we find the outcomes of the reactions catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase and phosphoglycerate kinase to be as foll ...
phospholipids
... Sphingomyelin • Sphingomyelin is present in plasma membranes and in lipoproteins PHOSPHOLIPIDS ...
... Sphingomyelin • Sphingomyelin is present in plasma membranes and in lipoproteins PHOSPHOLIPIDS ...
Plasma Total Amino Acids, Plasma Glutamate
... availability of amino acids for gluconeogenesis. The results of present study with type 2 diabetic subjects clearly establishes an elevated plasma levels of AAN,AL, and GM in type 2 diabetic subjects (refer table 1) which may be due to decreased insulin levels or due to decreased insulin action. Thi ...
... availability of amino acids for gluconeogenesis. The results of present study with type 2 diabetic subjects clearly establishes an elevated plasma levels of AAN,AL, and GM in type 2 diabetic subjects (refer table 1) which may be due to decreased insulin levels or due to decreased insulin action. Thi ...
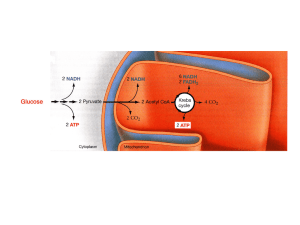
6 Energy and Metabolism
... phosphorylation, or cellular respiration) also takes place in the mitochondria. Here, the NADH molecules from glycolysis and the TCA cycle are oxidized back to NAD so glycolysis can continue. It also generates 3 more ATP. When this system is performing in the presence of oxygen, oxygen is consumed a ...
... phosphorylation, or cellular respiration) also takes place in the mitochondria. Here, the NADH molecules from glycolysis and the TCA cycle are oxidized back to NAD so glycolysis can continue. It also generates 3 more ATP. When this system is performing in the presence of oxygen, oxygen is consumed a ...
Comparative Estimation of Total Protein Content and Enzymatic
... in Duhok abattoirs. With respect to enzymes the activity of the following enzymes were measured namely acid phosphatases (ACP), alcaline phosphatase (ALP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), glutamate oxaloacetate transminase (GOT) and glutamate Pyruvate transminase (GPT) in cysts isolated from both liver ...
... in Duhok abattoirs. With respect to enzymes the activity of the following enzymes were measured namely acid phosphatases (ACP), alcaline phosphatase (ALP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), glutamate oxaloacetate transminase (GOT) and glutamate Pyruvate transminase (GPT) in cysts isolated from both liver ...
The urea cycle
... The two NADH produced can provide energy for the formation of 4 ATP(cytosolic NADH provides only 1.5 ATP due to the glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle who transfers the electrons from cytosolic NADH to FADH2 and that gives 1.5 ATP), a net production of one high-energy phosphate bond for the urea cycle. Ho ...
... The two NADH produced can provide energy for the formation of 4 ATP(cytosolic NADH provides only 1.5 ATP due to the glycerol-3-phosphate shuttle who transfers the electrons from cytosolic NADH to FADH2 and that gives 1.5 ATP), a net production of one high-energy phosphate bond for the urea cycle. Ho ...
Metabolismo dos aminoácidos e proteínas. II. Anabolismo
... of ammonium assimilation and glutamate biosynthesis. A. nidulans mutants disrupted in the gltA encoding GOGAT, were found to be dispensable for growth on ammonium in the presence of NADP-GDH. However, a strain carrying the gltA inactivation together with an NADP-GDH structural gene mutation (gdhA) w ...
... of ammonium assimilation and glutamate biosynthesis. A. nidulans mutants disrupted in the gltA encoding GOGAT, were found to be dispensable for growth on ammonium in the presence of NADP-GDH. However, a strain carrying the gltA inactivation together with an NADP-GDH structural gene mutation (gdhA) w ...
Chapter 4 - Open Science Online
... fruits along with fat and protein from meat. Fructose is phosphorylated to fructose phosphate which depletes the cell of ATP. This inhibits membrane sodium potassium ATPase leading onto increase in intracellular calcium and reduction in intracellular magnesium. This produces glutamate excitotoxicity ...
... fruits along with fat and protein from meat. Fructose is phosphorylated to fructose phosphate which depletes the cell of ATP. This inhibits membrane sodium potassium ATPase leading onto increase in intracellular calcium and reduction in intracellular magnesium. This produces glutamate excitotoxicity ...
All fatty acids are not equal: discrimination in plant membrane lipids
... been described in seed oils1,2, and it has been estimated that thousands more could be present throughout the plant kingdom. The structures of these fatty acids can vary in chain length from 8 to 24 carbons, they can have double bonds in unusual positions, or novel functional groups, such as hydroxy ...
... been described in seed oils1,2, and it has been estimated that thousands more could be present throughout the plant kingdom. The structures of these fatty acids can vary in chain length from 8 to 24 carbons, they can have double bonds in unusual positions, or novel functional groups, such as hydroxy ...
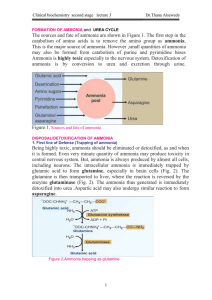
FORMATION OF AMMONIA
... During these reactions, 2 ATPs are used in the1st reaction. Another ATP is converted to AMP +PPi in the 3rd step, which is equivalent to 2 ATPs.The urea cycle consumes 4 high energy phosphatebonds. However, fumarate formed in the4th step may be converted to malate. Malate when oxidised to oxaloaceta ...
... During these reactions, 2 ATPs are used in the1st reaction. Another ATP is converted to AMP +PPi in the 3rd step, which is equivalent to 2 ATPs.The urea cycle consumes 4 high energy phosphatebonds. However, fumarate formed in the4th step may be converted to malate. Malate when oxidised to oxaloaceta ...
Gluconeogenesis, Glycogen Metabolism, and the Pentose
... mitochondria or transported from the cytosol to the mitochondria. Once in the mitochondria the pyruvate is converted to oxaloacetate by the action of Pyruvate Carboxylase. The oxaloacetate generated from pyruvate is then converted to malate by the action of the mitochondrial isoenzyme of Malate Deh ...
... mitochondria or transported from the cytosol to the mitochondria. Once in the mitochondria the pyruvate is converted to oxaloacetate by the action of Pyruvate Carboxylase. The oxaloacetate generated from pyruvate is then converted to malate by the action of the mitochondrial isoenzyme of Malate Deh ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... The transferase transfers 3 glucose residues from a 4-residue limit branch to the end of another branch, reducing the limit branch to a single glucose residue. ...
... The transferase transfers 3 glucose residues from a 4-residue limit branch to the end of another branch, reducing the limit branch to a single glucose residue. ...
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
... 5. Mechanism of arsenic poisoning - As previously described, arsenic can interfere with glycolysis at glyceraldehyde-3P step, thereby decreasing ATP production - “Arsenic poisoning” is, however, due primarily to inhibition of enz’s that require lipoic acid as a cofactor, including pyruvate dehydrog ...
... 5. Mechanism of arsenic poisoning - As previously described, arsenic can interfere with glycolysis at glyceraldehyde-3P step, thereby decreasing ATP production - “Arsenic poisoning” is, however, due primarily to inhibition of enz’s that require lipoic acid as a cofactor, including pyruvate dehydrog ...
The therapeutic implications of ketone bodies
... reduced than pyruvate. One may then ask, why would there not be even more energy released if the heart were to metabolize the fatty acid palmitate, which has even more inherent energy available during combustion than a ketone body. The reasons why the metabolism of fatty acids does not lead to even ...
... reduced than pyruvate. One may then ask, why would there not be even more energy released if the heart were to metabolize the fatty acid palmitate, which has even more inherent energy available during combustion than a ketone body. The reasons why the metabolism of fatty acids does not lead to even ...
Energy Substrate Metabolism in - Journal of Clinical Investigation
... in 24 hr and 7.5% in 48 hr. By comparison with the much greater per cent decreases in the rates of oleic acid-1-'C oxidation after storage of the platelets, the small changes in specific radioactivity of the fatty acid pool were considered negligible. Changes in the specific activity of the fatty ac ...
... in 24 hr and 7.5% in 48 hr. By comparison with the much greater per cent decreases in the rates of oleic acid-1-'C oxidation after storage of the platelets, the small changes in specific radioactivity of the fatty acid pool were considered negligible. Changes in the specific activity of the fatty ac ...
The Puzzle of the Krebs Citric Acid Cycle: Assembling the Pieces of
... sequence shown in Fig. 4 (see also Table 3). In this case the first step of the cycle is a Michael addition of a carbon nucleophile to an enone structure. We note with interest that this class of organic reaction is not used in metabolism of modern cells. The reason for this is not clear but may lie ...
... sequence shown in Fig. 4 (see also Table 3). In this case the first step of the cycle is a Michael addition of a carbon nucleophile to an enone structure. We note with interest that this class of organic reaction is not used in metabolism of modern cells. The reason for this is not clear but may lie ...
Cellular Energy and Mitochondrial ATP Production: A
... Lactic acid fermentation takes place in some fungi and some bacteria like Lactobacillus acidophilus (yogurt). In humans, lactic acid fermentation takes place in the muscles during times of strenuous exercise or great exertion. Under these conditions the oxygen supplied by the lungs and blood system ...
... Lactic acid fermentation takes place in some fungi and some bacteria like Lactobacillus acidophilus (yogurt). In humans, lactic acid fermentation takes place in the muscles during times of strenuous exercise or great exertion. Under these conditions the oxygen supplied by the lungs and blood system ...
Transcriptional Regulation of Metabolism
... their metabolic activity to environmental nutritional changes by modifying the level of expression of specific enzymes and linked modulation of enzymatic activity to the transcriptional control of gene expression for the first time. It is now commonly accepted that metabolic regulation in complex or ...
... their metabolic activity to environmental nutritional changes by modifying the level of expression of specific enzymes and linked modulation of enzymatic activity to the transcriptional control of gene expression for the first time. It is now commonly accepted that metabolic regulation in complex or ...
Lipid Biosynthesis Inhibitors - Plant and Soil Sciences eLibrary
... preparationisolated from leek epidermal cells (1, 4, 83, 84). Microsomes from leek containedtwo acyl-elongases: one that elongated stearoyl-CoA or palmitoyl-CoA to arachidoyl-CoA and the other that elongated arachidoyl-CoA to very longchain homologs (1). In a study conducted with potato tuber slices ...
... preparationisolated from leek epidermal cells (1, 4, 83, 84). Microsomes from leek containedtwo acyl-elongases: one that elongated stearoyl-CoA or palmitoyl-CoA to arachidoyl-CoA and the other that elongated arachidoyl-CoA to very longchain homologs (1). In a study conducted with potato tuber slices ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... Low levels of ADP, Pi, oxygen, and NADH that decrease electron transport activity. ...
... Low levels of ADP, Pi, oxygen, and NADH that decrease electron transport activity. ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.