Presence of Anaplerotic Reactions and Transamination, and the
... Enzymes ofthe TCA cycle. (i) Citrate synthase (EC 4.1.3.7) was assayed by both the methods of Srere (1969) and Stitt (1983~).(ii) Aconitase (EC 4.2.1.3) was assayed by a modification of the method of Goldberg & Ellis (1983). The reaction mixture (1.0 ml) contained 100 mM-HEPES/NaOH (pH 7-4), 1.7 mM- ...
... Enzymes ofthe TCA cycle. (i) Citrate synthase (EC 4.1.3.7) was assayed by both the methods of Srere (1969) and Stitt (1983~).(ii) Aconitase (EC 4.2.1.3) was assayed by a modification of the method of Goldberg & Ellis (1983). The reaction mixture (1.0 ml) contained 100 mM-HEPES/NaOH (pH 7-4), 1.7 mM- ...
Correlation of Hyperglycemia and Succinate dehydrogenase Activity
... Hymenolepis nana, the common intestinal dwarf tapeworm of mouse and man, especially in the tropics and the subtropics[1], is the only known cestode which can be transmitted directly[2-3]. In hymenolepiasis not only the histology of the host gets traumatized[4], but marked alterations in the tissue s ...
... Hymenolepis nana, the common intestinal dwarf tapeworm of mouse and man, especially in the tropics and the subtropics[1], is the only known cestode which can be transmitted directly[2-3]. In hymenolepiasis not only the histology of the host gets traumatized[4], but marked alterations in the tissue s ...
Full Text - Harvard University
... isoleucine, lactate, and pyridoxate were blunted in those with insulin resistance. Our findings demonstrate changes in 91 metabolites representing distinct biological pathways that are perturbed in response to an OGTT. We also identify metabolite responses that distinguish individuals with and withou ...
... isoleucine, lactate, and pyridoxate were blunted in those with insulin resistance. Our findings demonstrate changes in 91 metabolites representing distinct biological pathways that are perturbed in response to an OGTT. We also identify metabolite responses that distinguish individuals with and withou ...
"Fermentation Pathways". In: Microbial Physiology (Fourth Edition)
... The fermentation products formed by yeast can also be altered drastically through metabolic engineering. For example, introduction of a lactate dehydrogenase gene from bovine muscle (LDH-A) into S. cerevisiae engenders the production of lactic acid at levels rivaling those achieved by lactic acid ba ...
... The fermentation products formed by yeast can also be altered drastically through metabolic engineering. For example, introduction of a lactate dehydrogenase gene from bovine muscle (LDH-A) into S. cerevisiae engenders the production of lactic acid at levels rivaling those achieved by lactic acid ba ...
MedBiochem Exam 1, 1998
... two moles of NAD. B. one mole of ribose 5-phosphate, one mole of carbon dioxide and two moles of NADP. C. one mole of xylulose 5-phosphate, one mole of carbon dioxide and two moles of NADPH. D. one mole of ribulose 5-phosphate, one mole of carbon dioxide and two moles of NADPH. E. one mole of fructo ...
... two moles of NAD. B. one mole of ribose 5-phosphate, one mole of carbon dioxide and two moles of NADP. C. one mole of xylulose 5-phosphate, one mole of carbon dioxide and two moles of NADPH. D. one mole of ribulose 5-phosphate, one mole of carbon dioxide and two moles of NADPH. E. one mole of fructo ...
α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Activity Colorimetric Assay Kit
... α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (α-KGDH) (EC 1.2.4.2) is a key enzyme in the citric acid cycle. It forms an enzyme complex with dihydrolipoamide succinyl transferase (E2) and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (E3). α-KGDH converts α-ketoglutarate into succinylCoA in the presence of NAD and CoA. It is hig ...
... α-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (α-KGDH) (EC 1.2.4.2) is a key enzyme in the citric acid cycle. It forms an enzyme complex with dihydrolipoamide succinyl transferase (E2) and dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (E3). α-KGDH converts α-ketoglutarate into succinylCoA in the presence of NAD and CoA. It is hig ...
Muscle as the Primary Site of Urea Cycle Enzyme Activity in an
... localized (Table I). In addition, the GSase in liver is localized in the cytosol (Table II), analogous to largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) where the liver mitochondrial glutamine-dependent CPSase III appears to have little or no function (13). Since GSase biosynthetic activity is '5% of the t ...
... localized (Table I). In addition, the GSase in liver is localized in the cytosol (Table II), analogous to largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) where the liver mitochondrial glutamine-dependent CPSase III appears to have little or no function (13). Since GSase biosynthetic activity is '5% of the t ...
Control of Fatty-Acid Biosynthesis by Long
... between membrane and acetyl-CoA carboxylase is reversible.) Thus the inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by palmitoyl-CoA is directly correlated to the level of occupation of the membrane. Interestingly, a level of palmitoyl-CoA causing 80% inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase does not affect the e ...
... between membrane and acetyl-CoA carboxylase is reversible.) Thus the inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase by palmitoyl-CoA is directly correlated to the level of occupation of the membrane. Interestingly, a level of palmitoyl-CoA causing 80% inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase does not affect the e ...
1958 Shorland: RECENT WORK ON ANIMAL FATS
... Though fats are usunlIy 95% or more digestible, higher fatty acids of high melting point are selectively excreted, unsaturated acids of which the best known as are certain The fats are example is erucic acid present in rape seed oil. l~yclrolysecl in the intestinal lumen giving free fatty acids, as ...
... Though fats are usunlIy 95% or more digestible, higher fatty acids of high melting point are selectively excreted, unsaturated acids of which the best known as are certain The fats are example is erucic acid present in rape seed oil. l~yclrolysecl in the intestinal lumen giving free fatty acids, as ...
Events of The Krebs Cycle
... down fatty acids two carbon units at a time. The two carbon units become acetyl groups that are converted into acetyl COA. An acetyl COA is then used in the Krebs Cycle to make one ATP , 3 NADH2 and 1 FADH2. If a fatty acid has 18 carbon units, then 9 acetyl COA units would be made. Think how much e ...
... down fatty acids two carbon units at a time. The two carbon units become acetyl groups that are converted into acetyl COA. An acetyl COA is then used in the Krebs Cycle to make one ATP , 3 NADH2 and 1 FADH2. If a fatty acid has 18 carbon units, then 9 acetyl COA units would be made. Think how much e ...
14e8d39db06b481
... threshold" and glucose appears in the urine. When the "renal threshold" for glucose (a blood glucose level of about 180 mg/dL), is exceeded for a significant portion of the day, the patient will have the classic symptoms of hyperglycemia: excessive urination (polyuria) with consequent thirst and nee ...
... threshold" and glucose appears in the urine. When the "renal threshold" for glucose (a blood glucose level of about 180 mg/dL), is exceeded for a significant portion of the day, the patient will have the classic symptoms of hyperglycemia: excessive urination (polyuria) with consequent thirst and nee ...
video slide
... funnel electrons into cellular respiration wide range of carbohydrates amino groups can feed glycolysis or the citric acid cycle fats -- glycerol (used in glycolysis) and fatty acids (used in generating acetyl CoA) ...
... funnel electrons into cellular respiration wide range of carbohydrates amino groups can feed glycolysis or the citric acid cycle fats -- glycerol (used in glycolysis) and fatty acids (used in generating acetyl CoA) ...
Metabolism of Selenoamino Acids and Contribution of Selenium
... is metabolized by reduced glutathione (GSH) and/or glutathione reductase to hydrogen selenide (H2Se) via selenocysteine-glutathione selenenyl sulfide (CySeSG). The H2Se is a key intermediate in the methylation process of inorganic and organic selenium compounds. Accumulation of H2Se resulting from i ...
... is metabolized by reduced glutathione (GSH) and/or glutathione reductase to hydrogen selenide (H2Se) via selenocysteine-glutathione selenenyl sulfide (CySeSG). The H2Se is a key intermediate in the methylation process of inorganic and organic selenium compounds. Accumulation of H2Se resulting from i ...
Metabolism
... from the air combines with water (H2O) from the earth to form a carbohydrate, usually glucose (C6H12O6), and oxygen (O2). Plants store glucose as starch and release oxygen into the atmosphere. Plants such as corn, peas, squash, turnips, potatoes, and rice store especially high amounts of starch in t ...
... from the air combines with water (H2O) from the earth to form a carbohydrate, usually glucose (C6H12O6), and oxygen (O2). Plants store glucose as starch and release oxygen into the atmosphere. Plants such as corn, peas, squash, turnips, potatoes, and rice store especially high amounts of starch in t ...
Hormonal Control of Glucose Metabolism
... The rate-limiting step in hepatic glycogenolysis is catalyzed by phosphorylase. This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of 1,4 linkages of glycogen to yield glucose-1phosphate. In liver, phosphorylase exists in both an active and an inactive form (Fig. 1). Active phosphorylase (phosphorylase a) is phos ...
... The rate-limiting step in hepatic glycogenolysis is catalyzed by phosphorylase. This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of 1,4 linkages of glycogen to yield glucose-1phosphate. In liver, phosphorylase exists in both an active and an inactive form (Fig. 1). Active phosphorylase (phosphorylase a) is phos ...
Masterclass 1
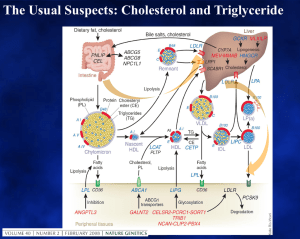
... How could you obtain an LDL-C result? The case for “d”, but “c” is misleading Lab Tests Online: “Direct LDL-C is ordered whenever calculation of LDL cholesterol will not be accurate because the person's triglyceridesare significantly elevated. It may be ordered by a doctor when prior test results h ...
... How could you obtain an LDL-C result? The case for “d”, but “c” is misleading Lab Tests Online: “Direct LDL-C is ordered whenever calculation of LDL cholesterol will not be accurate because the person's triglyceridesare significantly elevated. It may be ordered by a doctor when prior test results h ...
glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and the pentose phosphate pathway
... reactions. A bacterium such as Escherichia coli can obtain from glucose the carbon skeletons for every amino acid, nucleotide, coenzyme, fatty acid, or other metabolic intermediate it needs for growth. A comprehensive study of the metabolic fates of glucose would encompass hundreds or thousands of t ...
... reactions. A bacterium such as Escherichia coli can obtain from glucose the carbon skeletons for every amino acid, nucleotide, coenzyme, fatty acid, or other metabolic intermediate it needs for growth. A comprehensive study of the metabolic fates of glucose would encompass hundreds or thousands of t ...
Lecture 24
... Lecture 24 – Quiz Mon. on Pentose Phosphate Pathway – Glycogen regulation – Quiz next Fri. on TCA cycle ...
... Lecture 24 – Quiz Mon. on Pentose Phosphate Pathway – Glycogen regulation – Quiz next Fri. on TCA cycle ...
Slides
... §Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the Crabtree effect §S. cerevisiae is the only yeast that can produce ethanol and CO2 in such large quantities §S. cerevisiae ferments carbohydrates efficiently and dominates its environment due to the Crabtree effect §Unlike most fermenting organisms S. cerevisiae can ...
... §Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the Crabtree effect §S. cerevisiae is the only yeast that can produce ethanol and CO2 in such large quantities §S. cerevisiae ferments carbohydrates efficiently and dominates its environment due to the Crabtree effect §Unlike most fermenting organisms S. cerevisiae can ...
View Full Text-PDF
... media. Glucose isomerase (EC. 5.3.1.5) catalyzes the reversible isomerization of glucose to fructose and that of xylose to xylulose. It is an important enzyme used in the industrial production of high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS). Glucose isomerase was purified from Bacillus thuringiensis. The final p ...
... media. Glucose isomerase (EC. 5.3.1.5) catalyzes the reversible isomerization of glucose to fructose and that of xylose to xylulose. It is an important enzyme used in the industrial production of high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS). Glucose isomerase was purified from Bacillus thuringiensis. The final p ...
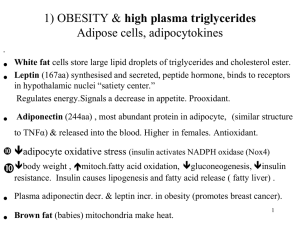
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.