Chem*3560 Lecture 16: Reciprocal regulation of glycolysis and
... Negative effectors: ATP and acetyl CoA indicate that energy status is being satisfied by other pathways. Alanine indicates that starting substrate for gluconeogenesis is available. Positive effector: Presence of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate indicates that phosphofructokinase 1 is passing substrate into ...
... Negative effectors: ATP and acetyl CoA indicate that energy status is being satisfied by other pathways. Alanine indicates that starting substrate for gluconeogenesis is available. Positive effector: Presence of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate indicates that phosphofructokinase 1 is passing substrate into ...
Chap 5
... (1) under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate may be converted to lactic acid, ethanol, acetone, butanol, and acetic acid (2) under aerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to CO2 and NADH through TCA cycle (3) the overall glycolysis rxn: glucose+2ADP+2NAD++2Pi→2pyruvate+2ATP+2(NADH+H+) (4) pyruvate pro ...
... (1) under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate may be converted to lactic acid, ethanol, acetone, butanol, and acetic acid (2) under aerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to CO2 and NADH through TCA cycle (3) the overall glycolysis rxn: glucose+2ADP+2NAD++2Pi→2pyruvate+2ATP+2(NADH+H+) (4) pyruvate pro ...
Metabolism at Skeletal muscle in the well-fed state
... - Fatty acid synthesis is favored by availability of substrates (acetylCoA,NADPH derived from glucose metabolism). This activate acetyl-CoA carboxylase which mediates the rate limiting reaction. 2) Increasing of triglyceride synthesis: a) TG synthesis is favored because fatty acyl-CoA is available ...
... - Fatty acid synthesis is favored by availability of substrates (acetylCoA,NADPH derived from glucose metabolism). This activate acetyl-CoA carboxylase which mediates the rate limiting reaction. 2) Increasing of triglyceride synthesis: a) TG synthesis is favored because fatty acyl-CoA is available ...
(i)
... (a) The frozen layer cuts off the atmospheric oxygen from dissolving into the pond water. The dissolved oxygen in the pond water is used up by the aquatic lives. (b) The goldfish carries out anaerobic respiration The amount of energy produced from anaerobic respiration of glucose is one-nineteenth o ...
... (a) The frozen layer cuts off the atmospheric oxygen from dissolving into the pond water. The dissolved oxygen in the pond water is used up by the aquatic lives. (b) The goldfish carries out anaerobic respiration The amount of energy produced from anaerobic respiration of glucose is one-nineteenth o ...
CHAPTERS 23-25
... A process coupled with the electron transport chain whereby ADP is converted to ATP ATP is synthesized at three sites within the electron transport chain The entire catabolic pathway generates 10 ATP molecules for every 1 acetyl CoA Read pages 724-730 will be on test ...
... A process coupled with the electron transport chain whereby ADP is converted to ATP ATP is synthesized at three sites within the electron transport chain The entire catabolic pathway generates 10 ATP molecules for every 1 acetyl CoA Read pages 724-730 will be on test ...
review-examIII-2011
... Q26. What distinguishes eicosanoids from other potent biological signaling molecules such as ...
... Q26. What distinguishes eicosanoids from other potent biological signaling molecules such as ...
Document
... (A) Glucose Catabolism Begins with glycolysis – 12 steps divides glucose into two pyruvates. Generates 2 ATPS. Usually followed by: -1- cellular respiration – in mitochondria. Produces an additional ~34 ATPs/ glucose. Requires oxygen = aerobic. a. Krebs Cycle: generates reduced coenzymes, which are ...
... (A) Glucose Catabolism Begins with glycolysis – 12 steps divides glucose into two pyruvates. Generates 2 ATPS. Usually followed by: -1- cellular respiration – in mitochondria. Produces an additional ~34 ATPs/ glucose. Requires oxygen = aerobic. a. Krebs Cycle: generates reduced coenzymes, which are ...
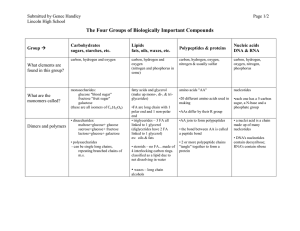
The Four Groups of Biologically Important Compounds
... sucrose=glucose+ fructose lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
... sucrose=glucose+ fructose lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
Fatty Acid Metabolism
... Clinical significances of impairment of β-oxidation: 1. acquired and genetic deficiency of carnitine substance. 2.genetic deficiency of one or more of enzymes of pathway. Hypoglycemia, muscle weakness , cardiomyopathway, coma and death ...
... Clinical significances of impairment of β-oxidation: 1. acquired and genetic deficiency of carnitine substance. 2.genetic deficiency of one or more of enzymes of pathway. Hypoglycemia, muscle weakness , cardiomyopathway, coma and death ...
Triacylglycerol Metabolism Gone Bad: A major cause of disease
... • Transport into the mitochondria is the primary rate limiting step of fatty acid oxidation. • The maximum rate of fatty acid oxidation is transcriptionally regulated by PPARα. – Unsaturated fatty acids increase PPARα activity – Fibrates, a class of triacylglycerol lowering drugs, increase PPARα ...
... • Transport into the mitochondria is the primary rate limiting step of fatty acid oxidation. • The maximum rate of fatty acid oxidation is transcriptionally regulated by PPARα. – Unsaturated fatty acids increase PPARα activity – Fibrates, a class of triacylglycerol lowering drugs, increase PPARα ...
Bios 302 FINAL FOR 1999.
... converted to urea for nitrogen excretion and how the carbons are returned to muscle (specific reactions not required but major pathway precursors and products (names or structures) are necessary, transport should be indicated). i.e. you do not have to show the complete pathways, just where they star ...
... converted to urea for nitrogen excretion and how the carbons are returned to muscle (specific reactions not required but major pathway precursors and products (names or structures) are necessary, transport should be indicated). i.e. you do not have to show the complete pathways, just where they star ...
glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids
... The shift from glucose to ketones as the major fuel diminishes the amount of protein that must be degraded to support gluconeogenesis. There is no "energystorage form" for protein because each protein has a specific function in the cell. Therefore, the shift from using glucose to ketones during star ...
... The shift from glucose to ketones as the major fuel diminishes the amount of protein that must be degraded to support gluconeogenesis. There is no "energystorage form" for protein because each protein has a specific function in the cell. Therefore, the shift from using glucose to ketones during star ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... V. Answer any five questions, each in not more than 350 words (5X8=40) 21. What are the ten steps of glycolysis, its regulation and energetics? 22. Write about Glucose-Alanine cycle and Glutamate cycle. 23. Explain the molecular models for structure elucidation with emphasis to ball and stick and sp ...
... V. Answer any five questions, each in not more than 350 words (5X8=40) 21. What are the ten steps of glycolysis, its regulation and energetics? 22. Write about Glucose-Alanine cycle and Glutamate cycle. 23. Explain the molecular models for structure elucidation with emphasis to ball and stick and sp ...
Outline06 Metabolism - Napa Valley College
... > 2X more energy yield per gram than carbohydrates 2. Lipid Synthesis - fatty acids are synthesized from 2C units of acetyl CoA - fatty acids are combined with glycerol to form triglycerides and phospholipids 3. Tissue Utilization of Fatty Acids - triglycerides are stored mostly in adipose tissue - ...
... > 2X more energy yield per gram than carbohydrates 2. Lipid Synthesis - fatty acids are synthesized from 2C units of acetyl CoA - fatty acids are combined with glycerol to form triglycerides and phospholipids 3. Tissue Utilization of Fatty Acids - triglycerides are stored mostly in adipose tissue - ...
Fractose and galactose Metabolism
... mental retardation, failure to walk or talk, hyperactivity and failure to grow occurs. PKU is treated by restriction of Phe in diet. The complete neuralgic damage can be prevented. ...
... mental retardation, failure to walk or talk, hyperactivity and failure to grow occurs. PKU is treated by restriction of Phe in diet. The complete neuralgic damage can be prevented. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 14. Describe the mechanism of prokaryotic translation process. 15. Explain the role of bicarbonate buffers in regulating blood pH. Derive the relationship of pH andpKa through Henderson Hassalbach equation. The values of pKa is 6.4, partial pressure of bicarbonate ions is 24 and carbonic acid is 1.3 ...
... 14. Describe the mechanism of prokaryotic translation process. 15. Explain the role of bicarbonate buffers in regulating blood pH. Derive the relationship of pH andpKa through Henderson Hassalbach equation. The values of pKa is 6.4, partial pressure of bicarbonate ions is 24 and carbonic acid is 1.3 ...
This is Most of an Old Exam
... Cellular oxidation of food fuels is the immediate source of electrons for oxidative phosphorylation. B. In oxidative phosphorylation, both the electron transport proteins and the ATP synthase molecules are in the same membrane. C. NAD+ and FAD+ are hydrogen carrier molecules. NAD+ can carry one hydr ...
... Cellular oxidation of food fuels is the immediate source of electrons for oxidative phosphorylation. B. In oxidative phosphorylation, both the electron transport proteins and the ATP synthase molecules are in the same membrane. C. NAD+ and FAD+ are hydrogen carrier molecules. NAD+ can carry one hydr ...
L20_StvnWAT
... • In starvation we want PDH to be off – PDH kinase >> PDH phosphatase – PDH kinase is stimulated by acetyl-CoA – PDH is inactive when phosphorylated – Prevents wasteful oxidation of pyruvate – Pyruvate only made into lactate • FA released from WAT (from lipolysis), causes [FA]blood to increase and t ...
... • In starvation we want PDH to be off – PDH kinase >> PDH phosphatase – PDH kinase is stimulated by acetyl-CoA – PDH is inactive when phosphorylated – Prevents wasteful oxidation of pyruvate – Pyruvate only made into lactate • FA released from WAT (from lipolysis), causes [FA]blood to increase and t ...
Chemistry of Life Review Sheet Key
... 10. Explain the difference between amylose and amylopectin. Both are types of starch, amylose is straight chains of glucose, amylopectin in branched chains of glucose. 11. What is glycogen? A string of 15-24 glucose formed in a muscle or liver cell. Why is it referred to as animal starch? Plants sto ...
... 10. Explain the difference between amylose and amylopectin. Both are types of starch, amylose is straight chains of glucose, amylopectin in branched chains of glucose. 11. What is glycogen? A string of 15-24 glucose formed in a muscle or liver cell. Why is it referred to as animal starch? Plants sto ...
Slide 1
... Types of fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenases • Long chain fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase (LCAD) • Medium chain fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) ...
... Types of fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenases • Long chain fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase (LCAD) • Medium chain fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.