PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY
... The hexose monophosphate pathway has several names just to confuse you. It’s called the hexose monophosphate shunt or pathway (HMP shunt or pathway), or the pentose phosphate pathway, or the phosphogluconate pathway (Fig. 15-1). The pathway in its full form is complicated and has complicated stoichi ...
... The hexose monophosphate pathway has several names just to confuse you. It’s called the hexose monophosphate shunt or pathway (HMP shunt or pathway), or the pentose phosphate pathway, or the phosphogluconate pathway (Fig. 15-1). The pathway in its full form is complicated and has complicated stoichi ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... Problems with the AMPK activation theory Some of the enzyme activities modulated through changed gene expression (e.g. fatty acid synthetase and liver pyruvate kinase) or direct phosphorylation (acetyl CoA carboxylase) are in the opposite direction to insulin. Many experiments have been performed a ...
... Problems with the AMPK activation theory Some of the enzyme activities modulated through changed gene expression (e.g. fatty acid synthetase and liver pyruvate kinase) or direct phosphorylation (acetyl CoA carboxylase) are in the opposite direction to insulin. Many experiments have been performed a ...
PL05_Glucdisp
... • The stimulation of glycogen synthesis by insulin creates an ‘energy demand’ – Glycogenesis is anabolic – The activation of glucose prior to incorporation into glycogen requires ATP – This drops the cellular [ATP] and increases the [ADP] & [AMP] ...
... • The stimulation of glycogen synthesis by insulin creates an ‘energy demand’ – Glycogenesis is anabolic – The activation of glucose prior to incorporation into glycogen requires ATP – This drops the cellular [ATP] and increases the [ADP] & [AMP] ...
Role of IDH2 in the brown adipose tissue Abstract
... Role of IDH2 in the brown adipose tissue Abstract Brown adipose tissue (BAT) plays a key role in controlling energy expenditure and thermogenesis by fatty acid oxidation (FAO) in mitochondria. Accumulation of oxidative stress in adipose tissue is one of the early events in the development of metabol ...
... Role of IDH2 in the brown adipose tissue Abstract Brown adipose tissue (BAT) plays a key role in controlling energy expenditure and thermogenesis by fatty acid oxidation (FAO) in mitochondria. Accumulation of oxidative stress in adipose tissue is one of the early events in the development of metabol ...
Alcohol Metabolism - Jessica Leary Nutrition Portfolio
... What is Alcohol? Ethyl alcohol, or ethanol, is the common alcohol that will make one intoxicated when ingested. This is the chemical this is found in beer, wine, and liquor. ...
... What is Alcohol? Ethyl alcohol, or ethanol, is the common alcohol that will make one intoxicated when ingested. This is the chemical this is found in beer, wine, and liquor. ...
Chapter 25: Metabolism
... • HDLs (high-density lipoproteins) – “Good” cholesterol – Transport excess cholesterol from peripheral tissues back to liver for storage or excretion in bile – Do not cause circulatory problems ...
... • HDLs (high-density lipoproteins) – “Good” cholesterol – Transport excess cholesterol from peripheral tissues back to liver for storage or excretion in bile – Do not cause circulatory problems ...
Organic Molecules: The Molecules of Life
... into glucose which we burn to make ATP. Glycogen- storage of carbs in animals. Excess sugar is stored in the liver. This molecule has many side branches. Glycogen is broken down into glucose when blood sugar is low. ...
... into glucose which we burn to make ATP. Glycogen- storage of carbs in animals. Excess sugar is stored in the liver. This molecule has many side branches. Glycogen is broken down into glucose when blood sugar is low. ...
All 3 fates of pyruvate from glycolysis provide for the regeneration of
... discovery of the enzyme that starts the conversion of glycogen to glucose. ...
... discovery of the enzyme that starts the conversion of glycogen to glucose. ...
Pancreatic enzymes basics
... Similar to secretin and gastrin GIP and VIP Synthesis is from a preprohormone as well. Prohormone is split releasing it to the blood Very little in blood – short ½ life ½ removed in first pass through the liver. ...
... Similar to secretin and gastrin GIP and VIP Synthesis is from a preprohormone as well. Prohormone is split releasing it to the blood Very little in blood – short ½ life ½ removed in first pass through the liver. ...
Metabolism
... • May be catabolized (including deamination) to produce ATP, used to synthesize a variety of proteins, or converted to other types of molecules (e.g. glucose, fatty acids) • Of the 20 amino acids, 10 cannot be synthesized - essential amino acids Protein Anabolism • Formation of peptide bonds between ...
... • May be catabolized (including deamination) to produce ATP, used to synthesize a variety of proteins, or converted to other types of molecules (e.g. glucose, fatty acids) • Of the 20 amino acids, 10 cannot be synthesized - essential amino acids Protein Anabolism • Formation of peptide bonds between ...
5 Lipid and Protein Metabolism
... that is being produced • Formed by joining together 2 acetates • There are 2 ketone bodies used by the body 1. Acetoacetic acid (4C) • Converted to acetyl-CoA – Acetone (3C) • Waste product • Fasting • Ketogenic diet ...
... that is being produced • Formed by joining together 2 acetates • There are 2 ketone bodies used by the body 1. Acetoacetic acid (4C) • Converted to acetyl-CoA – Acetone (3C) • Waste product • Fasting • Ketogenic diet ...
Topic 3.2: Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Proteins
... in animals, and of fructose, sucrose, and cellulose in plants • 3.2.5: Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides • 3.2.6: S ...
... in animals, and of fructose, sucrose, and cellulose in plants • 3.2.5: Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides • 3.2.6: S ...
3. GLYCOLYSIS
... up into mitochondria, and after conversion to acety-CoA is oxidized to CO2 by the citric acid cycle. • The reducing equivalents from the NADH+H+ formed in glycolysis are taken up into mitochontria for oxidation. ...
... up into mitochondria, and after conversion to acety-CoA is oxidized to CO2 by the citric acid cycle. • The reducing equivalents from the NADH+H+ formed in glycolysis are taken up into mitochontria for oxidation. ...
Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism:
... by release of glucose from the liver (glycogen) • As we run out of glycogen we maintain the blood glucose level by making glucose from amino acids (protein) and other compounds • The energy to make glucose comes from burning fatty acids, which also generates ketones that are used as an alternative ...
... by release of glucose from the liver (glycogen) • As we run out of glycogen we maintain the blood glucose level by making glucose from amino acids (protein) and other compounds • The energy to make glucose comes from burning fatty acids, which also generates ketones that are used as an alternative ...
this lecture as PDF here
... Lipids are anhydrous due to non-polar nature and represent more energy than carbohydrates which are heavily hydrated due to polar nature. The presence of lipids in diet contributes considerably to palatability. Lipids contribute palatability in two ways. They induce olfactory responses, namely ...
... Lipids are anhydrous due to non-polar nature and represent more energy than carbohydrates which are heavily hydrated due to polar nature. The presence of lipids in diet contributes considerably to palatability. Lipids contribute palatability in two ways. They induce olfactory responses, namely ...
Learning Objectives
... Six principles – name them and describe something about them (an example, etc.) Glycolysis - know ALL the details for the QUIZ, including net reaction, ATP/NAD used and made Know importance of phosphorylated intermediates What are the three nonequilibrium steps? How are each regulated? Hexokinase Ph ...
... Six principles – name them and describe something about them (an example, etc.) Glycolysis - know ALL the details for the QUIZ, including net reaction, ATP/NAD used and made Know importance of phosphorylated intermediates What are the three nonequilibrium steps? How are each regulated? Hexokinase Ph ...
Malonyl-CoA: the regulator of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation
... published a study in the JCI noting the surprising realization that malonylCoA, the substrate of fatty acid synthesis, was also an inhibitor of fatty acid oxidation. Subsequent experiments have borne out this finding and furthered our understanding of molecular metabolism. Ketogenesis, the productio ...
... published a study in the JCI noting the surprising realization that malonylCoA, the substrate of fatty acid synthesis, was also an inhibitor of fatty acid oxidation. Subsequent experiments have borne out this finding and furthered our understanding of molecular metabolism. Ketogenesis, the productio ...
ANSWERS - Unit 1 Review File
... amino groups, bases release glycerol d) acids release hydroxide ions, bases release hydrogen ions. 31. The process that joins amino acids together to make enzymes is: a)oxidation b) hydrolysis c)denaturation d) dehydration synthesis 32. Which of the following is an amino (amine) group? a)NH2 b)OH-1 ...
... amino groups, bases release glycerol d) acids release hydroxide ions, bases release hydrogen ions. 31. The process that joins amino acids together to make enzymes is: a)oxidation b) hydrolysis c)denaturation d) dehydration synthesis 32. Which of the following is an amino (amine) group? a)NH2 b)OH-1 ...
Fatty Acids - National Lipid Association
... Acyl groups are derived from hydrolyzed fatty acids (which are carboxylic acids or -COOH). When an acyl group is attached to an -OH on a glycerol, the process is called esterification. Esterification of glycerol will produce TG or PL. Glycerol with one acyl group is a monoacylglycerol (MAG), those w ...
... Acyl groups are derived from hydrolyzed fatty acids (which are carboxylic acids or -COOH). When an acyl group is attached to an -OH on a glycerol, the process is called esterification. Esterification of glycerol will produce TG or PL. Glycerol with one acyl group is a monoacylglycerol (MAG), those w ...
Synthesis of Triacylglycerols and Glycerophospholipids
... activity--> cholesterol synthesis ceases when ATP levels are low If enzyme is dephosphorylated via insulin pathway --> increased activity ...
... activity--> cholesterol synthesis ceases when ATP levels are low If enzyme is dephosphorylated via insulin pathway --> increased activity ...
Integration and regulation of fuel metabolism in maintaining
... Throughout evolution, humans and animals have evolved redundant mechanisms promoting the accumulation of fat during periods of feast to survive during periods of famine. However, what was an asset during evolution has become a liability in the current ‘pathoenvironment’ or ‘obesogenic’ environment [ ...
... Throughout evolution, humans and animals have evolved redundant mechanisms promoting the accumulation of fat during periods of feast to survive during periods of famine. However, what was an asset during evolution has become a liability in the current ‘pathoenvironment’ or ‘obesogenic’ environment [ ...
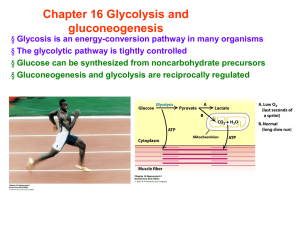
Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis § Glycosis is an energy-conversion pathway in many organisms § The glycolytic pathway is tightly controlled § Glucose can be synthesized from noncarbohydrate precursors § Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are reciprocally regulated ...
... Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis § Glycosis is an energy-conversion pathway in many organisms § The glycolytic pathway is tightly controlled § Glucose can be synthesized from noncarbohydrate precursors § Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are reciprocally regulated ...
Lipid Biosynthesis - Chemistry Courses: About: Department
... Are those which are required for cell survival. Are required for synthesis of cholesterol. Must be acquired by diet because they contain an odd number of carbon atoms. Cannot be synthesized by humans because we lack enzymes necessary to make ...
... Are those which are required for cell survival. Are required for synthesis of cholesterol. Must be acquired by diet because they contain an odd number of carbon atoms. Cannot be synthesized by humans because we lack enzymes necessary to make ...
1. Lactose is a disaccharide found in milk. In the small intestine, it is
... By what mechanism would amino acids leave the epithelial cell at point Z? ...
... By what mechanism would amino acids leave the epithelial cell at point Z? ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.