Quantum Mechanical Model
... sublevel - division of an energy level. Number of sublevel = value of n Ex: n = 3 # of sublevels equals 3 n = 4 # of sublevels equals 4 ...
... sublevel - division of an energy level. Number of sublevel = value of n Ex: n = 3 # of sublevels equals 3 n = 4 # of sublevels equals 4 ...
First Semester Honors Chemistry Exam Review (2011
... 48. What is the horizontal row of blocks in the periodic table called? 49. What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom called? 50. What is the trend of electronegativity on the periodic table? 51. What is a positive ion? A negative ion? 52. What are Valence electrons? 53. How many ...
... 48. What is the horizontal row of blocks in the periodic table called? 49. What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom called? 50. What is the trend of electronegativity on the periodic table? 51. What is a positive ion? A negative ion? 52. What are Valence electrons? 53. How many ...
Quantum Mechanical Model - Elmwood Park Memorial Middle School
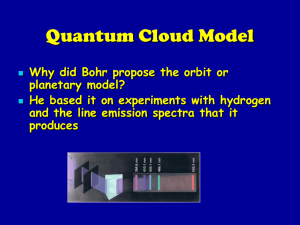
... • From Heisenberg’s principle we know that we can’t exactly locate electrons • We can determine probable locations… general areas • Schrodinger created an equation for solving these locations, but it has only been completely solved for hydrogen Why hydrogen? The modern model of the atom is ...
... • From Heisenberg’s principle we know that we can’t exactly locate electrons • We can determine probable locations… general areas • Schrodinger created an equation for solving these locations, but it has only been completely solved for hydrogen Why hydrogen? The modern model of the atom is ...
Quantum Numbers Primer The quantum numbers
... When n = 2, l can be 0 or 1. When l = 0, ml = 0. Because ml has only one value (the value 0), there is only one 2s orbital. The label 2s comes from n = 2 and l = 0. When l = 1, ml = -1, 0, +1. Because ml has three values (the values –1, 0, and +1), there are three 2p orbitals. These three 2p orbital ...
... When n = 2, l can be 0 or 1. When l = 0, ml = 0. Because ml has only one value (the value 0), there is only one 2s orbital. The label 2s comes from n = 2 and l = 0. When l = 1, ml = -1, 0, +1. Because ml has three values (the values –1, 0, and +1), there are three 2p orbitals. These three 2p orbital ...
Quantum Numbers and Electron Configurations Worksheet
... What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that can have these quantum numbers? ...
... What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that can have these quantum numbers? ...
Superconcepts
... xv. S orbitals are spherical. P orbitals are dumbbell shaped and occur in threes. D orbitals are four-bladed propeller shaped and occur in fives. xvi. Not all principle energy levels have all orbitals: 1 = s; 2 = s, p; 3 = s,p,d; 4 = s,p,d,f. xvii.The order of orbital filling (aufbau) is not as expe ...
... xv. S orbitals are spherical. P orbitals are dumbbell shaped and occur in threes. D orbitals are four-bladed propeller shaped and occur in fives. xvi. Not all principle energy levels have all orbitals: 1 = s; 2 = s, p; 3 = s,p,d; 4 = s,p,d,f. xvii.The order of orbital filling (aufbau) is not as expe ...
Bohr Model, Quantum Mechanical Model
... b. energy is involved in moving an electron from one level to another. 4. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle- It is impossible to know the momentum (mass of electron times velocity) of an electron and its position in space at the same time. One or the other. 5. Quantum Mechanical Model- a mathematical ...
... b. energy is involved in moving an electron from one level to another. 4. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle- It is impossible to know the momentum (mass of electron times velocity) of an electron and its position in space at the same time. One or the other. 5. Quantum Mechanical Model- a mathematical ...
Chem 1a Midterm Review
... Look at pictures of the hydrogen orbitals at http://www.shef.ac.uk/chemistry/orbitron/ . Note particularly the shape, nodes and sign of the orbitals. Note that the s and d orbitals are symmetric to inversion through the origin while the p is anti-symmetric toward inversions. Orbital energy: one ele ...
... Look at pictures of the hydrogen orbitals at http://www.shef.ac.uk/chemistry/orbitron/ . Note particularly the shape, nodes and sign of the orbitals. Note that the s and d orbitals are symmetric to inversion through the origin while the p is anti-symmetric toward inversions. Orbital energy: one ele ...
NAME PERIOD ______ DATE Chapter 5 Sec. 2
... 10. How many orientations are possible for the orbitals related to each of the following sublevels? a. s b. p c. d d. f ...
... 10. How many orientations are possible for the orbitals related to each of the following sublevels? a. s b. p c. d d. f ...
Steve Hansen`s second test - Kwantlen Polytechnic University
... The transition of an electron in a He+ ion from the n=5 level to a lower energy level produced a photon having a wavelength of 1.01 x 10-6 m. Determine the value of "n" for this lower level. (5) ...
... The transition of an electron in a He+ ion from the n=5 level to a lower energy level produced a photon having a wavelength of 1.01 x 10-6 m. Determine the value of "n" for this lower level. (5) ...
Chemistry I Midterm Exam
... In solving the Schrödinger equation for a particle constrained in a box of size L (x = 0 to L), the allowed wavefunctions have the form (x) = A sin kx + B cos kx. (a) What are the boundary conditions and normalization that can be used to find A, B, and k?? (b) Sketch the wavefunction for the 1st-ex ...
... In solving the Schrödinger equation for a particle constrained in a box of size L (x = 0 to L), the allowed wavefunctions have the form (x) = A sin kx + B cos kx. (a) What are the boundary conditions and normalization that can be used to find A, B, and k?? (b) Sketch the wavefunction for the 1st-ex ...
Honors Chemistry Name_________________________________
... neutral atom in long form and short form. Write the electron configuration of an ion in long and short form. Relate the position of an atom on the periodic table and its predicted electron configuration. Identify the number of valence electrons in a given atom or ion. Explain the similaritie ...
... neutral atom in long form and short form. Write the electron configuration of an ion in long and short form. Relate the position of an atom on the periodic table and its predicted electron configuration. Identify the number of valence electrons in a given atom or ion. Explain the similaritie ...
Atomic Theory Study Guide - Reading Community Schools
... 4. Calculate the energy of absorption and emission spectral lines of the hydrogen atom, and identify the electron transitions that caused the lines. 5. Describe the concept of wave-particle duality, and relate the DeBroglie wavelength of a wave or particle to its momentum. 6. Describe the photoelect ...
... 4. Calculate the energy of absorption and emission spectral lines of the hydrogen atom, and identify the electron transitions that caused the lines. 5. Describe the concept of wave-particle duality, and relate the DeBroglie wavelength of a wave or particle to its momentum. 6. Describe the photoelect ...
mp2b-16 honors
... Be able to write electron configurations and orbital filling diagrams a. What are the two types of electrons in an atom? Where are they? How do we define the outer electrons? a. Core style – short form b. Full style c. Orbital filling diagrams [show the arrows] d. Remember the exceptions in the firs ...
... Be able to write electron configurations and orbital filling diagrams a. What are the two types of electrons in an atom? Where are they? How do we define the outer electrons? a. Core style – short form b. Full style c. Orbital filling diagrams [show the arrows] d. Remember the exceptions in the firs ...
Quantum Numbers and Atomic Structure Honors
... D) weighted average mass of all the naturally occurring isotopes of Ti 5. The atomic mass of element A is 63.6 atomic mass units. The only naturally occurring isotopes of element A are A -63 and A-65. The percent abundances in a naturally occurring sample of element A are closest to A) B) C) D) ...
... D) weighted average mass of all the naturally occurring isotopes of Ti 5. The atomic mass of element A is 63.6 atomic mass units. The only naturally occurring isotopes of element A are A -63 and A-65. The percent abundances in a naturally occurring sample of element A are closest to A) B) C) D) ...
The Atom
... ground state quantumanumber De Broglie equation Heisenberg uncertainty principle quantum mechanical model of the atom atomic orbital principal quantum number principal energy level energy sublevel electron configuration Aufbau principle Hund’s Rule ...
... ground state quantumanumber De Broglie equation Heisenberg uncertainty principle quantum mechanical model of the atom atomic orbital principal quantum number principal energy level energy sublevel electron configuration Aufbau principle Hund’s Rule ...
CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 4 – QUANTUM MECHANICS
... 7. Explain how the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and the Schrödinger wave equation led to the idea of atomic orbitals. 8. List the four quantum numbers and describe their significance. 9. Relate the number of sublevels corresponding to each of an atom’s main energy levels, the number of orbitals ...
... 7. Explain how the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and the Schrödinger wave equation led to the idea of atomic orbitals. 8. List the four quantum numbers and describe their significance. 9. Relate the number of sublevels corresponding to each of an atom’s main energy levels, the number of orbitals ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.