* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download mp2b-16 honors
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Hartree–Fock method wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
James Franck wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
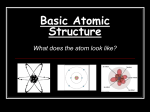
X Planck A. What is a quantum? B. What was different about Planck's description of light compared to the previous theory of light? C. Know how to use the two equations of light - know the metric system! E=hx C=x D. What are the frequency, wavelength, and amplitude of a light wave? Be able to diagram. What happens when each is changed? XI Bohr – Planetary model A. What is Bohr's model for the atom? B. What does it look like? C. Where are the electons?! D. What was Bohr's explanation for what happens in a gas discharge tube? E. What are the good points about Bohr's atom? F. What is its weak point? XII. Moseley – discovered the proton A. What did he study? B. What was the structure of the nucleus to account for all the mass? C. What old problem did discovery of the proton solve? XIII. DeBroglie - matter waves A. What experiment did DeBroglie do? B. What are the implications of wave-particle duality? C. How did he change Bohr’s model of the atom? D. Where are the electrons?! XIV. Schrödinger's model - the modern atom - quantum mechanical atom A. Where are the electrons? 1. What are orbitals? 2. What does the Heisenberg Uncertainty principle say? 3. How does Heisenberg effect electrons in orbitals? 4. What does Uncertainty Principle say about Bohr’s model of the atom? B. What are the four types of quantum numbers? 1. what are the symbols 2. What are the names 3. What does each one do? C. Know the different types of orbitals 1. know the names 2. know the shapes - draw and describe 3. how many of each type 4. given one of the above, be able to provide the other two D. Pauli Exclusion Principle - what does it mean? E. Orbital filling diagrams and electron configurations 1. Hund's Rule a. What is it? (English translation) b. how does it work? Effect when putting electrons into orbitals 2. F. Be able to write electron configurations and orbital filling diagrams a. What are the two types of electrons in an atom? Where are they? How do we define the outer electrons? a. Core style – short form b. Full style c. Orbital filling diagrams [show the arrows] d. Remember the exceptions in the first row transition metals and why they occur. Neutron 1. Who discovered it? 2. Isotopes – know the notation for isotopes and what each number means. PERIODICITY I. Ion formation A. B. C. II. How do we make Cations? How do we make Anions? Octet Rule – Who? What? Know the various groups and regions in the periodic table alkali metals, halogens, etc.