N - University of St Andrews
... Bad news: too complicated, even for only 2 electrons. We can’t calculate the eigenvalues and functions exactly ...
... Bad news: too complicated, even for only 2 electrons. We can’t calculate the eigenvalues and functions exactly ...
Chapter 5 Review “Electrons in Atoms”
... series: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? In Bohr’s model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located? What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram? How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? ...
... series: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? In Bohr’s model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located? What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram? How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? ...
Chapter 5 Review “Electrons in Atoms”
... series: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? In Bohr’s model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located? What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram? How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? ...
... series: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? In Bohr’s model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located? What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram? How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? ...
Chapter 3
... finding an electron at various locations around the nucleus of. An atomic orbitals is represented pictorially as a region of space in which there is a high probably of finding an electron. ...
... finding an electron at various locations around the nucleus of. An atomic orbitals is represented pictorially as a region of space in which there is a high probably of finding an electron. ...
Chapter 4
... Think of orbitals as sort of a "border” for spaces around the nucleus inside which electrons are allowed. No more than 2 electrons can ever be in 1 orbital. The orbital just defines an “area” where you can find an electron. ...
... Think of orbitals as sort of a "border” for spaces around the nucleus inside which electrons are allowed. No more than 2 electrons can ever be in 1 orbital. The orbital just defines an “area” where you can find an electron. ...
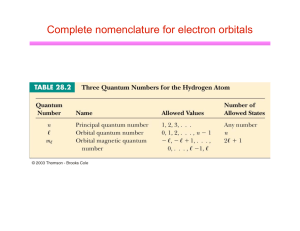
Complete nomenclature for electron orbitals
... What happens? Some of the electrons can accelerate and gain energy. This is possible because the conduction band is close in energy to the valence band and there are empty energy states to jump into. This can’t happen with insulators where there is too large of an energy gap between. ...
... What happens? Some of the electrons can accelerate and gain energy. This is possible because the conduction band is close in energy to the valence band and there are empty energy states to jump into. This can’t happen with insulators where there is too large of an energy gap between. ...
Ch. 5.1 Models of the Atom
... an electron can have, and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus. ...
... an electron can have, and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations around the nucleus. ...
Schrodinger models of the atom
... Quantum mechanics places the electrons in orbitals, not fixed orbits. Orbitals are regions of space. The electrons are like a cloud of negative charge within that orbital. The electron shells proposed by Bohr are still used, but the electrons in each shell are not all equal in energy. The shell has ...
... Quantum mechanics places the electrons in orbitals, not fixed orbits. Orbitals are regions of space. The electrons are like a cloud of negative charge within that orbital. The electron shells proposed by Bohr are still used, but the electrons in each shell are not all equal in energy. The shell has ...
WS on obj. 1-11
... 15. _____ (T/F) All the alkaline earth elements (Group 2A) will need to lose two electrons to obtain a noble gas electron configuration. 16. _____ (T/F) All the elements of the oxygen group (Group 6A) will need to gain two electrons to obtain the electron configuration of a noble gas. 17. _____ (T/F ...
... 15. _____ (T/F) All the alkaline earth elements (Group 2A) will need to lose two electrons to obtain a noble gas electron configuration. 16. _____ (T/F) All the elements of the oxygen group (Group 6A) will need to gain two electrons to obtain the electron configuration of a noble gas. 17. _____ (T/F ...
Electron Configuration Notes File
... Steps to Writing Electron Configuration 1. Determine the # of electrons 2. Use the redesigned PT to get the configuration 3. Superscripts will equal the electrons ...
... Steps to Writing Electron Configuration 1. Determine the # of electrons 2. Use the redesigned PT to get the configuration 3. Superscripts will equal the electrons ...
Quantum Model Worksheet
... PART A – WAVES & QUANTUM MECHANICS 1. What experimental evidence supported de Broglie’s idea that electrons have wave-like properties? ...
... PART A – WAVES & QUANTUM MECHANICS 1. What experimental evidence supported de Broglie’s idea that electrons have wave-like properties? ...
WS on obj. 1-11
... 23. _____ (T/F) Cations are formed by the gain of protons. 24. ____________________________ ions are the ions of the halogens and have a 1- charge, 25. _____________________________________ compounds are composed of positive and negative ions. 26. _____ (T/F) A formula unit shows the smallest whole- ...
... 23. _____ (T/F) Cations are formed by the gain of protons. 24. ____________________________ ions are the ions of the halogens and have a 1- charge, 25. _____________________________________ compounds are composed of positive and negative ions. 26. _____ (T/F) A formula unit shows the smallest whole- ...
The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this
... The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this year is the Periodic Table and its power of predicting the existence and properties of elements yet to be discovered. Dimitri Mendeleev placed the 65 known elements of his time into a grid table and observed gaps in the table. Based on ...
... The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this year is the Periodic Table and its power of predicting the existence and properties of elements yet to be discovered. Dimitri Mendeleev placed the 65 known elements of his time into a grid table and observed gaps in the table. Based on ...
Chem 400 Chem 150 REVIEW SHEET Amanda R
... o Elements in groups 1,2,13 and 14 form cations (positively charged ion) o Elements in groups 15, 16 and 17 form anions (negatively charged ions) o Most transition metals form cations of various charge Trends in Periodic Table – trends of elements to predict formation of bonds o Counting valence ele ...
... o Elements in groups 1,2,13 and 14 form cations (positively charged ion) o Elements in groups 15, 16 and 17 form anions (negatively charged ions) o Most transition metals form cations of various charge Trends in Periodic Table – trends of elements to predict formation of bonds o Counting valence ele ...
Exam on Matter through Bonding
... atom, the orbitals are regions of the most probable location of (1) protons (3) electrons (2) neutrons (4) positrons 5. Which type of bond is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another? (1) covalent (3) hydrogen (2) ionic (4) metallic 6. Which substance can not be decomposed by a ...
... atom, the orbitals are regions of the most probable location of (1) protons (3) electrons (2) neutrons (4) positrons 5. Which type of bond is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another? (1) covalent (3) hydrogen (2) ionic (4) metallic 6. Which substance can not be decomposed by a ...
Tutorial 3 - answers • Complete the following table, giving either the
... Copper enzymes are involved in electron transport systems due to the ability of copper to change its oxidation state. ...
... Copper enzymes are involved in electron transport systems due to the ability of copper to change its oxidation state. ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.