* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BLOOD GROUP GENOTYPING: THE FUTURE IS NOW
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
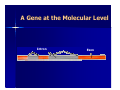
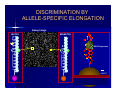
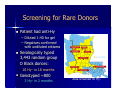
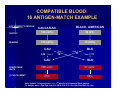
BLOOD GROUP GENOTYPING: THE FUTURE IS NOW Joann M. Moulds PhD, MT(ASCP)SBB Director, Clinical Immunogenetics LifeShare Blood Centers, Shreveport, LA. BASIC TERMINOLOGY “…a gene had been defined as a region of the genome that segregates as a single unit during meiosis and gives rise to a definable phenotypic trait”. “…a gene became identified as that stretch of DNA that was transcribed into the RNA coding for a single polypeptide chain” Alberts B, et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell A Gene at the Molecular Level Intron Exon mRNA is Transcribed Into a Gene Product DNA Intron Splicing mRNA Exon Typing for Blood Group Genes Traditionally has been done by phenotyping using serological methods Can now be done by genotyping (DNA) – – – – – PCR-RFLP PCR-SSP or AS-PCR Real-time PCR Sequencing Microarray Molecular Typing Terminology PCR- polymerase chain reaction = amplification of a gene a million-fold Primers- a string of ~20 nucleotides that are complementary to the gene being amplified Multiplex PCR- amplification of more than one gene in a single reaction SNP- single nucleotide polymorphism Thermal Cycler for PCR Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Restriction enzymes: named after the bacteria in which they are found – Hind III, Eco RI PCR product is digested with enzymes Fragments are separated by gel electrophoresis Allele Specific PCR Primer is designed only to detect one allele of a gene Must set up multiple PCR reactions to detect 2 or more alleles as well as a DNA control M H L C H L C H L C DNA Sequencing Knb 1st do a PCR with primers for the gene of interest “clean-up” PCR product Set-up sequencing reaction and run gel (automated) Good if several SNPs are in the same region Microarray Genotyping – Oligonucleotide probes on glass slides – ABO, Rh (Cc, D, Ee) – Kell, Jk, Fy, Di, Do, Co, MNSs Bead-Chip Microarray Type for: C/c, E/e, K1/K2, MNSs, JKA/JKB, FYA/FYB, DIA/DIB, COA/COB LWA/LWB, SC1/SC2, DOA/DOB, HY, JO, LUA/LUB, Hgb S Cost is competitive due to saving of tech time MAKING BEADCHIPS … Bead Functionalization 0.3 mm 4,000 ENCODED BEADS Pooling Bead Synthesis & Encoding Array Assembly BeadChip™ Wafer DNA ANALYSIS BY BEAD CHIP DNA Extraction m’plex PCR post-PCR Processing BeadChipTM Analysis 96 sample results x 28 antigens DISCRIMINATION BY ALLELE-SPECIFIC ELONGATION Assay Image MATCH T A G C C G T A A T G C T A T A C G T A A T G MISMATCH A C G X A C G T T C T A DNA Polymerase T C A A G A T G eMAP™ RECORDING & DECODING ARRAY IMAGES Decoding Image Automated “Snapshot” Array Imaging Assay Image ANALYZING DATA Chip Analysis Bar Chart DNA Analysis\ ∆ Chart (for each probe pair) SNP = FY-GATA ( FY -33T>C ) AA "AB "BB” C e E K k Fya Fyb Jka Jkb M N S s Lua Lub Doa Dob Jo(a) Hy LWa LWb Dia Dib Coa Cob Sc1 Sc2 HgbS Silencing FY HEA04961_1 A1 + - + - + + - + - + + + - + - + + + + + + - - + + - + - - 1 No HEA04961_2 A2 + - + - - + + + + - + + - + - + + + + + + - - + + - + - - No No HEA04961_3 A3 + - + - - + + - + + + - - + - + - + + + + - - + + - + - - 1 No HEA04961_4 A4 + - + - - + - - + + + - - + - + - + + + + - - + + - + - + 2 HEA04961_5 A5 + - + - - + - - + + - + + + + + - + + + + - - + + - + - - 2 No HEA04961_6 A6 - + + - - + + - + + - + - + - + + + + + + - - + + - + - HEA04961_7 A7 - + + - - + + - + + - + - + - + + + + + + - - + + - + - - No No HEA04961_8 A8 - + + - - + - - + - + - - + - + + + + + + - - + + - + - + 2 No ChipName Sample WarnMsg Fyx[Fy(b+w) c PHENOTYPE REPORT 1 ++ 1 No Cmmnt Why do DNA Typing? To identify at risk fetus & paternal zygosity To determine antigen status in problem cases – Recently transfused patient – Patient with positive DAT – Multiply transfused patients, eg. SCD To screen for antigen negative donors – When reagents or licensed antisera are unavailable for mass screening DNA Typing Commercial Donors Antigen type when suitable antisera is unavailable eg. Dob, Jsa, V/VS To confirm homozygosity – 3 RhD samples were heterozygous Dd Confirm weak antigens – 1 Fy(a+b-) sample was FY*A/FY*X (Fy b weak) So Now Let’s Peek Into Your Genes Some LifeShare experiences….. Evaluation & Validation of the Bead-Chip Microarray Tested 84 rare or null phenotypes: e-, k-, Jk-3, Fy(a-b-), U-, Lu(b-), Di(b-), Co(a-), Hy-, Jo(a-), LW(a-), Sc-1 Tested 40 Black donors in duplicate: – In house for precision – Another BAS user for accuracy Concurrent testing of 200 random Blacks: – by serology for C/c, E/e, MNSs, Fy, Jk, Kell – by DNA for 28 antigens Screening for Rare Donors Patient had anti-Hy – Diluted 1:40 for gel – Negatives confirmed with undiluted antisera Serologically typed 3,443 random group O Black donors: 10 Hy- in 18 months Genotyped ~800 3 Hy- in 2 months Area screened for Hy- In the First 500 Blacks We Also Found…….. Rares 10 R2R2 (e neg) 7 U neg 4 Co(a-b+) 4 Hy3 Jo(a-) 1 Sc -1,2 Unusual 14 Co(a+b+) 17 Lu(a+b+) 6 Sc 1,2 1 Di(a+) Screening for Phenotype Matched Donors 450 units supplied to ARDP in 2006 97% were phenotype matched for Rh, Kell, Duffy, Kidd, MNSs NIH recommendation for transfusion of SCD patients: – Minimum of C/c, E/e, K1 matched – If possible do Fy, Jk, MNSs Can we match even better? COMPATIBLE BLOOD: 16 ANTIGEN-MATCH EXAMPLE NYC ETHNICITY PROFILE CAUCASIAN BLACK- AMERICAN SUPPLY 720 (96%) 30 (4%) DEMAND 775 (90%) 75 (10%) CAU 549 COMPATIBLE UNITS % FULFILLMENT Step 3 Step 1 39 Step 4 9 BLK Step 2 12 CAU BLK 558 units 51 units 83% 68% Note: optimal “firing sequence”: i.e., 1ST priority in all cases to Black patients 16 Antigen base = Fya /Fyb /Lua /Lub /M /N /S /s /K /k /Jka /Jkb /Doa /Dob /Hy /Joa Other Uses for Genotyping Recently transfused patients who develop alloantibodies Patients with strongly positive DAT DAT = 3 to 4+ Unable to remove with chloroquine or EGA Strong serum antibody, unable to absorb Perform genotype and give matched units Reagent red cells (home grown) Duffy Typing Discrepancy Unit labeled on the shelf as Fy(a-b-) Genotyping by bead-chip microarray Homozygous FY*B gene but – heterozygous for -33 (GATA) SNP – “ “ 265 SNP – FY*FY/FY*X or Fy(a-b+w) Summary Technology is now available for blood group genotyping – On an individual case – For high through-put typing We now can provide the best product for our repeat customers