* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heredity and Genetics Vocabulary (Part 2) 1. Traits: A
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
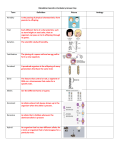
Heredity and Genetics Vocabulary (Part 2) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Traits: A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes. Heredity: The passing of genes from parents to offspring: the genes are expressed in the traits of the offspring. Inheritance: receiving genetic qualities that are passed from parent to offspring. Genetics: The scientific study of heredity. Allele: A form of a gene for a specific trait. Offspring: The new organisms produced by one or two parent organisms. Punnett square: A chart used to show all the ways genes from two parents can combine and be passed to offspring; used to predict all genotypes that are possible. Punnett square example using R to represent the alleles. 8. 9. 10. 11. Dominant: Describes the allele that determines the phenotype of an individual organism when two different copies are present in the genotype. Recessive: A term that describes an allele that in not expressed (masked or hidden) when combined with a dominant form of the gene. Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism: all the genes that an organism has. Phenotype: The observable characteristics or traits of an organism. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Homozygous: Having two identical alleles for a trait. Example: TT Heterozygous: Having two different alleles for a trait. Example: Tt Homozygous Dominant: Having two dominant alleles for a trait. Example: TT Homozygous Recessive: Having two recessive alleles for a trait. Example: tt Purebred: An organism that always produces offspring with the same form of a trait as the parent. Hybrid: An organism that has two different alleles for a trait; an organism that is heterozygous for a particular trait. Pedigree: A chart that shows family relationships, including two or more generations. Sample pedigree chart: