* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11.2 (Pg. 313-318): Applying Mendel*s Principles
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Life history theory wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
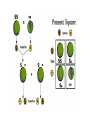
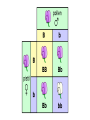
Chapter 11.2 (Pg. 313-318): Applying Mendel’s Principles Genetics Vocabulary - Genotype - An organism’s genetic makeup - Phenotype - An organism’s physical traits - Homozygous - An organism has two of the same allele for a trait - Heterozygous - An organism has two different alleles for a trait Probability and Genetics - Probability is the likelihood an event will occur - Can be predicted in genetics through segregation - Assumes that each gamete has a ½ chance of carrying an allele Punnett Squares - Are named for their creator, Reginald Punnett - Are a simple matrix to calculate the probability of inheritance outcomes - Show the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring The Principle of Independent Assortment - Genes for different traits can segregate independently during formation of gametes - Traits that segregate independently do not influence each other’s inheritance - The gene that determines seed shape does not affect gene for seed color Two-Factor Crosses - Show how the alleles for one trait are inherited independently of another trait - Two dominant alleles don’t always stay together - Trick is to show the correct combinations of alleles in the parents