* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes The Work of Gregor Mendel Mendel studied 7 different pea
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
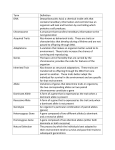
Notes The Work of Gregor Mendel Mendel studied 7 different pea plant traits. A trait is a characteristic that varies from one individual to the next, i.e. plant height. Each trait had 2 contrasting forms, i.e. tall or short. Today, scientists call the chemical factors that determine traits genes. The different forms of the gene are called alleles. 1. The Principle of Dominance: states that some alleles are dominant and others are recessive. If an organism carries a single dominant allele, it will exhibit the trait. In order for the organism to show a recessive trait, the organism must have 2 copies of this allele. 2. The Principle of Segregation: states that alleles are segregated (separated) from each other so that each gamete carries only a single copy of each gene. 3. The Principle of Independent Assortment: states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes.