* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Technology Review (Cambridge, Mass
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
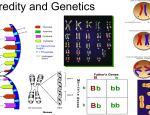
Website for Rost et al/Plant Biology 2e, ISBN: 0534495958 Objectives Chapter #16 Chapter 16 Genetics OBJECTIVES After reading this chapter, you should be able to: ■ Describe how genes work, how they are expressed, and how they are inherited. Show the correlation between the chemical structure of a gene and its function. Discuss ways in which the location of a gene along a chromosome can be determined. Explain how alleles (which are variable forms of a gene) can arise and how they may be expressed. ■ Describe the basic principles of inheritance discovered by Gregor Mendel, including the concepts of dominant and recessive traits, segregation, and independent assortment. Show how these concepts together with the principles of mathematical probability make it possible to predict ratios of observable traits expected in offspring. Solve simple genetics problems using Mendel’s principles and the laws of probability. Use a Punnett square in solving genetic problems. ■ Distinguish between the terms “homozygous” and “heterozygous.” Explain why the phenotype (observed traits) may not reveal the genotype (actual genetic makeup) of an individual. Describe a test cross, and discuss when such a cross would be useful. ■ Explain why predicted results are not always observed. Show how it has become necessary to expand Mendel’s basic concepts to include the presence of multiple alleles, linked alleles, continuous traits, and multiple genes. ■ Define the terms “polyploidy” and “hybrid vigor.” Explain the significance of these phenomena in agriculture. ■ Define all boldface terms. Page 1 of 1