* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11.2 (Pg. 313-318): Applying Mendel*s Principles
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
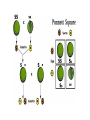
Chapter 11.2 (Pg. 313-318): Applying Mendel’s Principles Genetics Vocabulary - Genotype - An organism’s genetic makeup - Phenotype - An organism’s physical traits - Homozygous - An organism has two of the same allele for a trait - Heterozygous - An organism has two different alleles for a trait Probability and Genetics - Probability is the likelihood an event will occur - Can be predicted in genetics through segregation - Assumes that each gamete has a ½ chance of carrying an allele Punnett Squares - Are named for their creator, Reginald Punnett - Are a simple matrix to calculate the probability of inheritance outcomes - Show the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring Sickle Cell Anemia Homozygous Dominant Alleles (SS) Normal red blood cells Homozygous Recessive Alleles (ss) Sickled red blood cells The Principle of Independent Assortment - Genes for different traits can segregate independently during formation of gametes - Traits that segregate independently do not influence each other’s inheritance - The gene that determines seed shape does not affect gene for seed color Two-Factor Crosses - Show how the alleles for one trait are inherited independently of another trait - Two dominant alleles don’t always stay together - Trick is to show the correct combinations of alleles in the parents