* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2016 Final review level
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Taxonomy (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terms of location wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
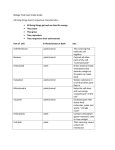
Biology Final Exam Review Sheet - 2016 Evolution 1.During his voyage on the Beagle, Charles Darwin made most his observations on the ______________Islands. 2. The species of birds that Darwin is famous for studying on these islands were called ___________. During his observations, Charles Darwin found these birds displayed different structural ________________. One of these adaptations that Darwin noted was the shape of the birds ___________. An adaptation is an inherited characteristic that can be ____________ or behavioral. Darwin also studied fossils during his voyage on the Beagle. He viewed the fossil records as a record of change ______ _______. After his voyage, he returned home to ______________ where he examined his findings and developed his Theory of ___________________. This theory is his explanations of the process where modern organisms have descended from accent organisms. During the development of organisms, ____________ occur over time, which has helped this organism survive its environment. Define the following: Artificial selection Survival of the fittest Evolution Adaptation 2. Describe the three types of natural selection that can occur within a population and explain what is happening to the gene pool in each of the following graphs. Directional, Disruptive, and Stabilizing selection: pg 398-399/notes 4. List the three main circumstances that causes speciation within and existing population and give an example of what would cause each to occur. (hint: types of isolation) Pg 404-405/Notes 5. If a mutation introduces a new skin color in a lizard population, which factor might determine whether the frequency of the new allele will increase? Pg 397 (look at figure 16-5 on this page) 6. They were once working organs or body parts that are now unused structures. An example would be a pelvic bone in some species of whale is a good example. Pg. 384/notes Taxonomy, Bacteria, Protist, Fungus, and Virus: 7. Fill in the blanks in the chart below. Auto/Heterotrophic/Both Multi/Unicellular Eu/Prokaryotic Cell Wall? Kingdom Archaebacteria Eubacteria Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia 8. Aristotle classified organisms into two groups: ___________ and _____________. 9. What taxonomic levels does Linnaeus classify organisms into (most general to most specific? 10. What is a binomial nomenclature? (Also, write a human’s binomial nomenclature in the correct form.) 11. Protists are classified by how they ___________. 12. An amoeba moves by _____________. 13. A Euglena moves by _____________. 14. A Paramecium moves by ________________. 15. Label the diagram to the right: Label numbers 1, 3, 4, 5, and 6 only. Words: Food vacuole, Cell membrane, Pseudopodia, Nucleus, Vacuole 16. Label the diagram below. Only label 2 and 7. Words: Oral groove and cilia. 17. Label the below diagram. Only label 1, 5, 6, and 9. Words: Chloroplast, cell membrane, flagellum and vacuole. 18. Match the Bacteria Shapes by drawing a line to the one that matches. Three Shapes 1. Spirillum: spiral shaped 2. Coccus: round 3. Bacillus: rod-shaped 19. Tell which disease is caused by a bacteria and which one is by a virus: A. Pneumonia B. HIV C. Common cold D. TB (tuberculosis) E. Flu F. Strep throat G. Herpes simplex 20. Give examples of a virus that goes through the lytic cycle and what are the lytic cycle stages. 21. Name a virus that is a retrovirus and what does that mean. 22. Name 2 viruses that go through the lysogenic cycle. 23. What is this structure in diagram A? 24. What type of organism does this virus infect? 25. Label parts A-D on the virus picture given on the last page. 26. Give three examples of fungus. 27. Where do we find fungus, bacteria, and protist? 28. How does fungus reproduce? Bacteria? Protist? 29. What is a chain of bacteria that is rod shaped called? _________________A grape like cluster of round bacteria called? ______________________ 30. What is used to streak a petri dish with bacteria? ____________________(lab equipment). 31. Bacteria grows on a ___________ ____________ and feeds off of nutrient ____________. 32. What does ZOI (Zone of inhibition) mean? 33. The bigger the ZOI (Zone of inhibition), the ____________ ______________ the antibiotic. 34. __________________—break down animal waste and organic matter. 35. Name two infections caused by fungus. 36. What two things destroy (attack) a virus? 37. What does autotrophic and heterotrophic mean? 38. What does eukaryotic and prokaryotic mean? Plants: Roots & Stems: 39. List 3 functions of roots: 40. List 3 functions of stems. 41. Identify the 2 types of roots below and give two examples of each type. (fibrous, taproot) 42. What do nonvascular plants need for reproduction? 43. Describe the mutualistic relationship between bacteria and plants. 44. State the functions of the internal leaf parts listed below: a. b. c. Chloroplasts: Xylem: Phloem: 45. Identify the following parts of the internal leaf diagram using the terms below: Next to each term, state its function. Cuticle: Upper epidermis: Lower epidermis: Palisade cells: Spongy cells: Stomata: Guard cells: Vein: 46. a. Photosynthesis: Write the formula for photosynthesis. b. What are the two reactants in photosynthesis? c. What are the two products of photosynthesis? d. What tissue brings water from the roots to the leaf? e. In what organelle does photosynthesis occur? f. Which pigment is required for photosynthesis? 47. What is a tropism? 48. What is the difference between positive and negative tropisms? 49. What part of the plant shows positive phototropism? 50. What part of the plant shows negative phototropism? 51. What part of the plant shows positive gravitropism? 52. What part of the plant shows negative gravitropism? 53. Ivy growing up a fence is an example of (positive/negative) thigmotropism. 54. The stem of a plant growing upward towards the sun (positive/negative) gravitropism. Angiosperms (Flowers): 55. Label the parts of the flower below using the following terms: Next to each term, state its function. Sepal: Petal: Pistil: Stigma: Style: Ovary: Ovule: Stamen: Filament: Anther: 56. What is the function of the flower? 57. What part of the flower becomes the fruit? 58. In angiosperms reproduction takes place in ________________. In Gymnosperms reproduction takes place in _______________. Digestive system: 59. Which organ makes insulin and breaks down blood sugar (letter)? 60. Which organ produces bile (letter)? 61. Which organ stores bile (letter)? 62. Label the digestive system AND give function of each: A. G. B. H. C. D. E. F. Respiratory System: 63. Which gas is exiting the blood and which gas is entering the blood via the lungs? 64. Label parts A-F of the respiratory system and list functions using the following diagram word bank: bronchioles, larynx, pharynx, trachea, alveoli, bronchi, diaphragm Part: Function: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. 65. Excretory system: main function 66. Fill in the chart below on the excretory system and list functions. Word bank: kidneys, urethra, ureter, bladder Skeletal System: 67. List 3 functions of the skeletal system. 68. Put the levels of organization in order from smallest (1) to largest (4). _____ organs _____ cells _____ organ systems _____ tissues _____ organism 69. List 3 functions of the skeletal system. 70. Explain the functions of red & yellow bone marrow. 71. Define the following terms: a. Ligamentb. Tendonc. Cartilage 72. Label the skeletal system Circulatory System: 73. What is the function of the circulatory system? 74. Which vessels carry oxygenated blood? Arteries or Veins 75. Which vessels carry deoxygenated blood? Arteries or Veins 76. Is the heart muscle voluntary or involuntary? 77. Which side of the heart (right or left) carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs? 78. Which side of the heart (right or left) pumps blood to the systemic circulation (whole body)? 79. Name the largest artery in the body that pumps blood out to the rest of the body. 80. Label the parts of the heart and draw arrows showing the flow of blood. Right Atria Left Atria Right Ventricle Left Ventricle Superior Vena Cava Septum Aorta Pulmonary Vein Pulmonary Artery Inferior Vena Cava Body System Interactions and Homeostasis 81. How do the circulatory and respiratory system interact to maintain homeostasis in your body? Explain. 82. Humans sweat when they are in the hot sun. How does sweating help humans maintain a constant body temperature? 83. Which three body systems function together to move and control body parts? (Think) 84. Explain how the circulatory and respiratory systems interact with one another. 85. How do the reproductive and endocrine systems work together in developing adolescents? Ecology 86. Define ecology87. Compare biotic and abiotic factors. 88. Fill in the missing Levels of Organization: Organism, ____________, Community, ____________, _____________, Biosphere. 89. Compare niche and habitat90. What do the following niche’s consume? Carnivores: _____________ Omnivores:___________ Herbivores:____________Scavengers___________Decomposer __________ 91. Define the following terms and give an example of each: ProducerConsumerPrimary consumerSecondary consumerTertiary consumerDecomposerTrophic levelFood chainFood web- 92. In the food chain below, do the following 3 things: label the niche of each organism, identify each trophic level, and state the amount of energy available at each level. 93. If there is a sudden population explosion of small fishes, what will happen to the population of zooplankton? Squid? Algae? 94. Directions: Match the terms on the left with the definitions on the right. _____ Organism a. all biotic and abiotic factors in an area _____ Population b. all of the biomes _____ Community c. geographical area that has a certain amount of rainfall, temperature, plants and animals _____ Ecosystem d. all of the living organisms in an area _____ Biomes e. a group of organisms of the same species _____ Biosphere f. one member of a species Use the food web to answer questions 92-94. 95. List four producers shown in the food web. 96. List four primary consumers shown in the web. 97. List five secondary consumers shown in the food web. 98. List two tertiary (third-level) consumers shown in the food web above. 99. What is the niche of the wolf when he eats a rabbit? 100. Using the diagram below, which organisms should have the greatest amount of stored energy? _________________Which has the least? __________ 101. What is the energy level of the Bass? _________kcal 102. In a well-balanced ecosystem, which organism should have the greatest population size? ________________ Which would have the least?____________ 103. Which population should have the greatest biomass?_______ Least? _______ 104. Create a food chain using the organisms from the Diagram 1 below. (add Bacteria) _________ _________ ________ ? kcal ________ ______ Use word bank for matching below: A. Commensalism B. Symbiosis C. Parasitism D. Competition E. Mutualism F. Predation ____Close permanent relationships ____When two species compete over the same resource. ____When both species benefit. ____When one species benefits and the other is harmed. ____When one species is hunted and eaten. ____When one species benefits but the other is neither helped or harmed. Biochemical Cycles Review the following cycles: (carbon, nitrogen, water) (Book pages 404-410) 102. Which cycle is shown in the diagram below? 103. Which cycle involves the processes of cellular respiration and photosynthesis? 104. Which cycle involves lightning and bacteria in the soil? 105. Certain bacteria that live in the soil and in the roots of plants are able to take N 2 gas from the air and change it into ________________ that is then used by plants to make proteins. This process is called ___________ ___________.