* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download fall final exam review ws #1
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
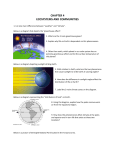
FALL FINAL REVIEW WORKSHEET #1 Below is a diagram representing Francesco Redi’s 1668 experiment. 1. What was the question that Redi was attempting to answer with this experiment? 2. What was his hypothesis? 3. What was Redi’s independent variable (manipulated variable)? 4. What was Redi’s dependent variable (responding variable)? 5. Give an example of “quantitative data” from Redi’s experiment. 6. Give an example of “qualitative data” from Redi’s experiment. 7. What was Redi’s conclusion? 8. Explain how the following diagram represents 2 characteristics of living things. 9. Below is a hierarchy of life collage starting with smallest level and leading to the largest level. Label the missing levels (according to your textbook) and sketch an example of each missing level. 10. Scientists use the metric system when collecting data and performing experiments. Fill in the missing unit prefixes and the amount that each prefix represents. ____(___) Hecta (100) Deka (10) Base (1) deci (0.1) _____(___) _____(___) Below is a graph representing a specific biological experiment. 11.What type of graph is this (line or bar)? 12.What is the independent variable? 13.What is the dependent variable? 14.What was being studied in this experiment? 15.What is the overall conclusion for this experiment? Below is a diagram representing the “ecological levels of organization”. 16. Which level includes the interaction of multiple species? 17. Which level is the first to include “abiotic” factors? 18. What makes one biome different from another? Below is a diagram representing a “food chain”. 19. Which organism is a “producer”? 20. Which organism is the second “consumer”? 21. Where does the initial energy source for the producer originate? Below is a diagram representing a “food web”. 22. What is the role of decomposers in the food web? 23. Which organisms are in the first trophic level (producers)? 24. Which organisms are primary consumers (“herbivores”)? 25. Which 2 organisms are tertiary consumers (they eat secondary consumers which eat primary consumers)? Below is a diagram representing an “ecological pyramid”. 26. The diagram shows the kcal declining as the pyramid moves up toward the apex. How much does it decline for each trophic level? Why does it decline by this amount? 27. Which trophic level would have the most biomass? Below is a diagram representing a “pyramid of numbers”. 28. This type of pyramid is the only ecological pyramid that can be inverted (apex broader than the base). Explain this anomaly. 29. What are the 4 “biogeochemical cycles”? Below is a diagram of the “carbon cycle”. 30. Why is the carbon cycle important to organisms? 31. This diagram depicts two methods in which carbon is released into the atmosphere. What is a third method not depicted in this diagram? 32. What is the biological process called that takes the carbon from the atmosphere and makes it available to consumers? Below is a diagram of the “nitrogen cycle”. 33. Why is the nitrogen cycle important to organisms? 34. What organisms take the nitrogen directly from the atmosphere? 35. Consumers get nitrogen from producers. However, producers cannot directly take nitrogen from the atmosphere. How do the producers obtain nitrogen? Below is a picture of Serengeti National Park located in the Tanzania area. 36. List 4 biotic factors found in this picture. 37. From the picture, infer 3 abiotic factors of this ecosystem. Below is a picture of a Western Diamondback rattlesnake eating a rat. 38. Choose either the snake or rat and describe its niche. Below is a diagram of “niche partitioning” or what is also known as the “competitive exclusion principle”. This concept allows one Spruce tree to support 5 different species of Warblers. 39. Using the concept of this principle, explain how the Spruce tree can support 5 different species of birds. 40.Below are three pictures representing the three forms of “symbiosis”. Below each picture, describe the form of symbiosis represented and how the picture depicts this type of symbiosis. Below is a diagram representing “ecological succession”. 41. What type of succession does this diagram represent? 42. What is the “pioneer species”? 43. For this diagram to represent the other type of succession, what would have to be different? Below is a diagram representing the “major terrestrial biomes” of Earth. 44. What differentiates one biome from another? Below is a graph representing “population growth”. 45. Label the exponential growth phase on the graph. 46. What is the carrying capacity for this population? 47. Under what type of conditions would a population grow exponentially? Below is a graph illustrating how “limiting factors” can affect population growth. 48. Of the two types of limiting factors, which does this illustrate? 49. What type of community interaction does this represent? 50. Analyze the graph with an emphasis on the correlation between the Snowshoe hare and Lynx population growth pattern. 51. How do “density-independent factors” differ from “density-dependent factors”? Below is a diagram representing a wetland ecosystem. 52. Would this hypothetical ecosystem demonstrate high biodiversity? Why or why not? 53. Describe how humans have altered habitats such as the one depicted here. Below is a diagram representing the “biological magnification” of a pesticide known as DDT. 54. Analyze this diagram in reference to the correlation between trophic level and concentration of DDT. Below is a picture of two “introduced” and “invasive species” to this area: the Nutria and Water Hyacinth. 55. How do invasive species impact the biodiversity of the ecosystems in which they have been introduced?