* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Lab CCR Notes Chapter 3 The Biosphere
Survey
Document related concepts
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Ecological economics wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
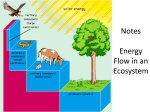
Biology Lab CCR Notes: Chapter 3 The Biosphere The branch of biology dealing with interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment is called ecology. The following is a correct description about the organization of an ecosystem: species make up populations, which make up communities. The simplest grouping of more than one kind of organism in the biosphere is a community. The lowest level of environmental complexity that includes living and nonliving factors is the ecosystem. Experimenting, modeling, and observing are basic methods used by ecologists to study the living world but animal training is NOT. The ecological inquiry method that an ecologist is using when he or she sets up a greenhouse and measures the effects of different levels of carbon dioxide on an endangered plant species is experimenting. A mathematical formula designed to predict population fluctuations in a community could be called an ecological model. Plants are primary producers. Most primary producers make their own food by using light energy to make carbohydrates. Compared to land, the open oceans are nutrient-poor environments. Plants in a sunny mountain meadow and sulfur bacteria in a deep-sea volcanic vent because they both produce carbohydrates and oxygen. Corn planted in a field that has been previously planted with legumes and then plowed under is likely to be more productive because bacteria living on the roots of legumes fix nitrogen in the soil. Herbivores and carnivores are alike because they both obtain energy by consuming other organisms. The total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level is called biomass. A model of the complex feeding interactions among organisms in a community from producers to decomposers is called a food web. Omnivores are animals that eat both producers and consumers. Trophic level is the term for each step in the transfer of energy and matter within a food web. A bird stalks, kills, and then eats an insect. Based on its behavior, the pair of ecological terms that describe the bird are carnivore and consumer. Energy, biomass, and numbers are the three kinds of ecological pyramids. Only 10 percent of the energy stored in an organism can be passed on to the next trophic level. Of the remaining energy, some is used for the organism’s life processes, and the rest is eliminated as heat.