* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bio Ch3 Ecology 2013
Biosphere 2 wikipedia , lookup
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
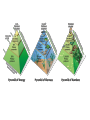
ECOLOGY The SHORT version Biology Ch 3 Levels of Ecological Organization Biosphere – combined portions of Earth that include & interacts with living organisms Biome – group of ecosystems with same climate & similar dominant communities Ecosystem – collection of all organisms in one place & abiotic factors Community – populations that live together in one place Population – groups of individuals that live together in same area Species – individuals in same are that can produce fertile offspring Ecological Methods Computer Modeling Observation Experimentation Energy Flow PRODUCERS Autotrophs Photosynthesis Chemosynthesis Consumers Heterotrophs Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores Detritivores Decomposers Food Chain Energy relationship between organisms in ecosystem Food Web Trophic Levels Trophic Levels Specific level (relationship) that an organism occupies in a food chain Ecological Pyramids • Energy • Biomass • Pyramid of numbers Energy Pyramid Shows relative amount of energy available at each trophic level Only 10% of available energy transferred from one trophic level to the next Biomass Pyramid Represents amount of living organic matter at each level 10% transferred between levels Pyramid of Numbers Relative number of organisms at each trophic level Only about 10% transferred between levels Pyramid of Numbers for oak tree community Biogeochemical Cycles Biological, geological, & chemical matter recycled through ecosystems WATER CYCLE Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Biological processes (photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition) take up & release carbon Geochemical processes (erosion, volcanic activity) release CO2 into the atmosphere Mixed processes (burial & decomposition of dead organisms converting to petroleum) store carbon underground Human activities (mining, forestation, burning fossil fuels) release CO2 into atmosphere Used in forming DNA/RNA Not in atmosphere, just soil and water Nitrogen Cycle All organisms require nitrogen to build proteins N2 is in atmosphere Nitrogen fixation – bacteria convert N2 to NH3 in soil, used as nutrients for producers Denitrification – bacteria convert NH3 to N2 in atmosphere Limiting Factors Primary productivity Rate at which organic matter is created by producers Limiting factors Abiotic - ??? Biotic - ??? OVERVIEW