* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nutrition
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Fluorescent glucose biosensor wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biomolecular engineering wikipedia , lookup
Puppy nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
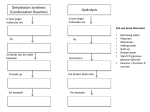
Nutrition (Chapter 3) Need for food: Food is required for energy, for the growth and repair of cells and to make chemicals for metabolic reactions occurring in the body. The 6 common elements found in food are: The 5 elements present in dissolved salts are: Carbon (C) Hydrogen (h) Nitrogen (N) Oxygen (O) Phosphorus (P) Sulfur (S) Sodium (Na) Magnesium (Mg) Chlorine (Cl) Potassium (K) Calcium (Ca) The 3 trace elements (only found in small amounts in organisms) are: Iron (Fe) Copper (Cu) Zinc (Zn Biomolecules Biomolecules are chemicals that are made inside a living thing. The 4 main types of biomolecules found in food are: Carbohydrates, Lipids (fats, oils), Proteins, Vitamins When elements are combined in certain ratios, they form simple biomolecular units. The ratio for all carbohydrates = Cx(H2O)y Example: Formula for glucose = C6H12O6 (x = 6, y = 6) Carbohydrates Elements in carbohydrates: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen 3 main types of carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides Monosaccharides Monosaccharide: a carbohydrate made up of a single sugar unit. Examples: glucose (fruit, sweets, soft drinks), fructose (fruit) Disaccharides Disaccharide: a carbohydrate made up of two sugar units. Examples: sucrose = glucose + fructose (table sugar) Maltose = glucose + fructose (in germinating seeds) Lactose = glucose + galactose (milk) Monosaccharide (glucose) Disaccharide (maltose) Polysaccharide (starch) Polysaccharides Polysaccharide: a carbohydrate made up of many sugar units Examples: starch, cellulose, glycogen Starch = many glucose molecules joined together (rice, potatoes, bread, pasta) Function of starch: to provide energy Starch is a carbohydrate stored by plants Cellulose = many glucose molecules joined together (plants) Function: Important structural function in plants - it is a component of plant cell walls. Glycogen = many glucose molecules Function: stored by animals (many in liver and muscles) and can be used for energy Metabolic Function of Carbohydrates: to provide a source of energy for metabolic activity Structural function: Cellulose is an important component of plant cell walls Lipids Elements in lipids: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (no simple ratio, like carbs) Fats & Oils: Fats: are lipids that are solid at room temperature. Oils: are lipids that are liquid at room temperature Sources: butter, olive/sunflower oil, cream, margarine Structure of Lipids: Lipids are composed of glycerol molecules attached to fatty acid molecules. The smallest lipid, a triglyceride, contains one glycerol molecule attached to 3 fatty acids. Phospholipids: Phospholipids are lipid-like substances, where one of the fatty acids is replaced by a phosphate group or has a phosphate group attached. Structure of a Phospholipid Phosphate Metabolic function of lipids: to provide a source of energy for metabolic activity Structural Function: component of cell membranes Proteins Elements in Proteins: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen (also sometimes contain small amounts of sulfur, phosphorous) no simple ratio Structure: Proteins are composed of small units called amino acids. Peptide = small chain of up to 20 amino acids Polypeptide = chain of more than 20 amino acids Protein = long polypeptide Primary structure of a protein aa aa aa aa aa aa peptide bonds Sources: lean meat, fish, eggs, nuts, peas, beans The function of protein is very dependent on their 3D shape and the way in which they are folded. Fibrous proteins: show little or no folding. e.g. keratin, myosin Globular proteins: show lots of folding. e.g. albumen, enzymes Metabolic Functions: Proteins are used to make enzymes, which control metabolic reactions. (Enzymes are proteins which speed up chemical reactions) Hormones are also proteins. Like enzymes, they regulate metabolic activity. Structural function: fibrous proteins have a structural function for example: keratin is a component of hair and skin & myosin is a component of muscles Vitamins Some vitamins are water-soluble and some are fat-soluble. Water soluble – Example: Vitamin C Function: tissue growth, cell production and to maintain good health Sources: citrus fruits, such as oranges and lemons Deficiency disease: Scurvy (soft gums and loose teeth) Fat soluble – Example: Vitamin D Function: tissue growth, cell production and to maintain good health Sources: cod liver oil, egg yolk, dairy products Deficiency disease: Rickets (bones do not form properly) Minerals Minerals are needed by plants and animals in small amounts. Plants: Calcium – helps bind cell walls together (absorbs from soil) Magnesium – part of the structure of chlorophyll (absorbs from soil) Animals: Calcium – forms bones and teeth (dairy products) Iron – required for healthy red blood cells, forms haemoglobin (red meat, green veg) Water The human body is about 60% water. Water is very important for living organisms for a number of reasons: (1) Water has an important structural function, it is a component of cytoplasm and body fluids. (2) Water is a good solvent. Many substances in the body can dissolve in water, so it provides a medium for chemical reactions to take place in. (3) Water can easily move through membranes in the body and helps to transport many chemicals around the body. (4) It plays a direct role in many chemical reactions. Examples: respiration, photosynthesis (5) It is a good heat absorber. This helps maintain fairly constant body temperature. Metabolism Anabolic Reaction: a reaction in which simple molecules are built up into more complex molecules. Energy is required for anabolic reactions. Example: Photosynthesis Carbon dioxide 6CO2 + Water 6H2O Sunlight Energy Glucose C6H12O6 + + Oxygen 6O2 Catabolic Reaction: a reaction in which a complex molecule is broken down into simpler molecules. Energy is released during a catabolic reaction. Example: Respiration Glucose C6H12O6 + Oxygen 6O2 Carbon dioxide 6CO2 + Water 6H2O + Energy