* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint Presentation - The Human Digestive
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
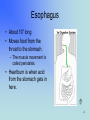
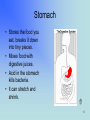
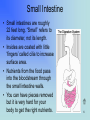
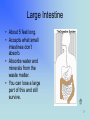
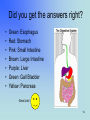
By Rebecca K. Fraker 1 The Digestive System What has happened to the food you ate today? • • • • • • • Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Liver Gall Bladder Pancreas 2 In the Mouth • Digestion actually begins in the mouth. • The teeth break the food into smaller pieces, and the tongue moves the pieces around so that saliva can be mixed with them. • This begins the digestion. • Then swallow, and the journey begins! 3 Esophagus • About 10” long • Moves food from the throat to the stomach. – The muscle movement is called peristalsis. • Heartburn is when acid from the stomach gets in here. 4 Stomach • Stores the food you eat, breaks it down into tiny pieces. • Mixes food with digestive juices. • Acid in the stomach kills bacteria. • It can stretch and shrink. 5 Small Intestine • Small intestines are roughly 22 feet long. “Small” refers to its diameter, not its length. • Insides are coated with little ‘fingers’ called cilia to increase surface area. • Nutrients from the food pass into the bloodstream through the small intestine walls. • You can have pieces removed but it is very hard for your body to get the right nutrients. 6 Large Intestine • About 5 feet long. • Accepts what small intestines don’t absorb. • Absorbs water and minerals from the waste matter. • You can lose a large part of this and still survive. 7 Liver • Directly affects digestion by producing bile. – Bile helps digest fat. • Processes nutrients in the blood, filters out toxins and waste. • Is often called the body’s energy factory. • You cannot live without a liver, although you can live with a part of one. • Drinking alcohol damages the liver. 8 Gall Bladder • Stores bile from the liver. • Delivers bile when food is digested. • Fatty diets can cause gallstones. • You can live without a gallbladder. 9 Pancreas • Produces compounds to digest fats and proteins. • Neutralizes acids that enter small intestine. • Regulates blood sugar by producing insulin. • If it doesn’t work right you get diabetes. 10 Fun Facts • HOW LONG ARE YOUR INTESTINES? At least 25 feet in an adult. Be glad you're not a full-grown horse -- their coiled-up intestines are 89 feet long! • Food drying up and hanging out in the large intestine can last 18 hours to 2 days! • In your lifetime, your digestive system may handle about 50 tons!! 11 12 On a sheet of paper, write the name of each colored organ: • • • • • • • Green: Red: Pink: Brown: Purple: Green: Yellow: 13 Did you get the answers right? • • • • • • • Green: Esophagus Red: Stomach Pink: Small Intestine Brown: Large Intestine Purple: Liver Green: Gall Bladder Yellow: Pancreas Great Job! 14 References and Links • Your Digestive System and How It Works: http://digestive.niddk.nih.gov/ddiseases/pubs/yrdd/Your_Digestive_Sys.pdf – Digestive system diagram comes from this site • The Real Deal on the Digestive System http://kidshealth.org/kid/body/digest_SW_p2.html • Pancreas: Introduction and Index http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/digestion/pancreas/i ndex.html • Your Gross and Cool Body – Digestive System http://yucky.discovery.com/flash/body/pg000126.html 15