* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Severe combined immune deficiency syndrome
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
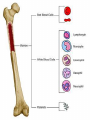
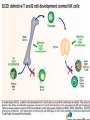
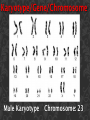
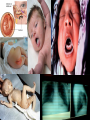
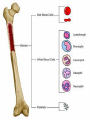
SEVERE COMBINED IMMUNE DEFICIENCY SYNDROME (SCID, SCIDS, XSCID) SUDHA KOLLA HISTORY • • • • • • • • • • • • “Bubbly boy disease” Known and discovered in 1970’s and 80’s David Vetter X – linked syndrome Wore a plastic germ free bubble for 12 years Born without a working immune system Gene mutation Bubble = protect from outside environment David Vetter’s brother had same disease Bone Marrow Transplant = Victor = death Bone Marrow Transplant was to help Victor gain strength to fight infection Died in 1984 How It Occurs • • Gene mutation Lymphocytes (type of white cells) Thymus Gland T-cells kill antigens B-cells (killer of antigens) attack healthy cells (healthy antigens) weak immune system • Genetic = defect in the “X” chromosome Can it passed? Karyotype/Gene/Chromosome Male Karyotype Chromosome: 23 Symptoms of SCIDS 1. pneumonia - infection of the lungs. 2. meningitis - infection of the brain. 3. sepsis - infection in the bloodstream. 4. yeast infections in the mouth and diaper area 5. Diarrhea 6. infection of the liver 7. Eight or more ear infections 8. Infections that do not resolve with antibiotic treatment for two or more months 9. Failure to gain weight or grow normally 10. Infections that require intravenous antibiotic treatment 11. Deep-seated infections, such as pneumonia that affects an entire lung or an abscess in the liver 12. Persistent thrush in the mouth or throat 13. A family history of immune deficiency or infant deaths due to infections Diagnose SCIDS • DNA Family mutation • T & B cells function • Blood tests • Automated Screening Cure SCIDS • Transplantation of blood-forming stem cells bone marrow • Tissue matching from relative = ¼ • Anonymous donor = very common • HLA = Human Leucocyte Antigen • HLA = bone marrow transplantation type = cheotheraphy = bone marrow rescue Bibliography (ON THE SEPARATE PAPER)