* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Handout: Naming Organic Compounds Substituents Longest carbon
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
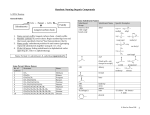
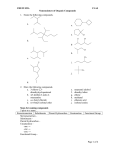
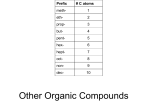
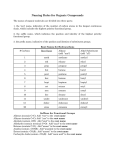
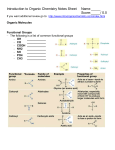
Handout:NamingOrganicCompounds A.IUPACNaming GeneralRules: Prefix+Parent+Suffix Family Substituents Longestcarbonchain SomeSubstituentNames Substituent Substituent Group Name Hydrocarbon alkyl withsingle bondsonly 1. Nameparent+suffix:longestcarbonchain+familysuffix. 2. Numbercarbonsinparentchain:Beginnumberingfromend thatmeetsspecifiedcriteria(*SeeNomenclatureChart). 3. Nameprefix:substituentposition#sandnames(group repeatedsubstituentstogetherusingdi-,tri-,etc). 4. Writefullname,listingsubstituentsinalphabeticalorder (ignoredi-,tetra-inalphabetizing). H 3C C H H 3C C H CH 3 H 3C C H H2 C H2 C CH 3 sec-butyl C CH 3 –OR O HC O tert-butyl O acyl O C C H 3C C (Endswith–oyl, H 3C H2 exceptfor acetylpropanoyl acetyl) H2 alkoxy H 3C C H 3C O C Methane Ethane Propane Butane Pentane Hexane Heptane Octane Nonane Decane CH 3 H 3C R Name H 3C C methylethyl CH 3 SomeParentAlkaneNames No.of Structure Carbons 1 CH4 2 CH3CH3 3 CH3CH2CH3 4 CH3CH2CH2CH3 5 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 6 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 7 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 8 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 9 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 10 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 H2 H 3C isopropylisobutyl NameFormat:#–substituent–#–substituentparentsuffix SpecificExamples formyl methoxyethoxy keto hydroxy nitro amino halo -Clchloro-Brbromo -Iiodo C –OH -NO2 –NH2 -X(halogen) phenyl H.KimforChem30B 1 B.CommonNames Frequently-UsedCommonNames Compound CommonName CH2=CH2 ethylene CH3CH=CH2 propylene HC CH acetylene O acetone C CH 3 H 3C O CH2 O CH H 3C O HC OH O H 3C C OH O H 3C C H2 C OH O H 3C H2 C C H2 C OH IUPACName 1-ethene 1-propene 1-ethyne 2-propanone formaldehyde methanal acetaldehyde ethanal formicacid methanoicacid aceticacid ethanoicacid propionicacid propanoicacid butyricacid butanoicacid H.KimforChem30B 2 NomenclatureChartforOrganicCompounds(FromHIGHESTTOLOWESTnamingpriority) FAMILY Carboxylicacid PARENT SUFFIX NUMBERING Parentislongest carbonchain containingcarboxylic acid.Derivename fromparentalkane. –oicacid (-dioicacid fordicarboxylicacid; -enoicacid forunsaturatedacid) BeginatcarbonylC. Commonnamesareoftenused (CnexttoCOOHgroupis designatedas“α”). [Salts:cation+namederived fromparentacid,replacing–ic acidwith–ate] NOTES EXAMPLES O H C H 3C C OH Cl 2-chloropropanoicacidor α-chloropropionicacid(common) O HO O H2 C C OH C propanedioicacid Ester NameofalkylgroupR’ –ate in-COOR’+Nameof acylgroup(derived fromparentacid, replacing–icacidwith –ate) Amides Derivenamefrom parentcarboxylicacid, replacing–oicacid with–amide. Derivenamefrom parentalkane.Parent alkaneislongestCchaincontaining carbonyl. Derivenamefrom parentalkane.Parent alkaneislongestCchaincontaining carbonyl.Parentname startswithposition# ofcarbonylC. Parentislongest carbonchain containingOH.Parent namestartswith position#oftheC withOH. Aldehydes Ketones Alcohol –amide –al –one –ol (-diol, -triol,etc.) Numberalkyl groupR’andacyl groupseparately. ForR’,begin numberingatend nearertocarbonyl C.Forparent,begin numberingat carbonylC. BeginatcarbonylC. O Commonnamesareoftenused: H2 H2 H2 nameofalkylgroupthat H 3C C C C O C CH 3 replaced-Hin-COOH+name ethylbutanoateor derivedfromcommonnameof ethylbutyrate(common) parentacid,replacing–icacid with–ate Alkylsubstituentsonnitrogen startwith“N-.” H 3C Beginatendnearer Commonnamesareoftenused tocarbonylC. forsimpleketones:namesof twoalkylgroups+“ketone.” Beginatendnearer Cyclicalcohols:Parentname toOHgroup. beginswith“cyclo”(noneedto startparentnamewith“1”). BeginnumberingatCwithOH, andnumbertogive substituentslowestnumbers. CH 3 C N CH 3 N,N-dimethylacetamide BeginatcarbonylC. Commonnamesareoftenused forsimplestaldehydes,ending with“–aldehyde.” O CH 3 H 3C C H O H2 C C H 3-methylbutanalor β-methylbutyraldehyde(common) O H2 C H2 C H 3C C CH 3 2-pentanoneor methylpropylketone(common) CH 3 H 3C C H OH H2 C C H H2 C 5-methyl-3-hexanol CH 3 H.KimforChem30B 3 OH CH 3 2-methylcyclohexanol OH H 3C FAMILY Thiols PARENT SUFFIX NUMBERING NOTES –thiol Amines –amine Nameinsamewayasalcohols, exceptendwith“-thiol.” 1°amines,and2°,3°amines withsameRgroupsonN:Treat alkylgroupsattachedto nitrogenassubstituents.For samesubstituents,use“di”and “tri.” 2°,3°amineswithdifferentR groupsonN:Parentamineis theonewithlargestRgroup; nameothergroupsas substituents,startingwithN-. [Ionsderivedfromamines: Replace–aminewith –ammonium.] Cyclicalkenes:Parentname beginswith“cyclo”(noneedto startparentnamewith“1”). Numbermultiplebonds1and 2,indirectiontogivefirst substituentthenextsmaller possiblenumber. Alkenes Alkynes Alkanes Parentislongest carbonchain containingthedouble ortriplebond.Parent namestartswith positionnumberof multiplebond. Mayneedcis/trans designation. –ene –yne (-diene, -triene,etc.) Parentislongest carbonchain. –ane Beginatendcloser tomultiplebond. (Ifmultiplebonds areequidistant, givesmaller numbertofirst branchpoint). Thengivesmallest numberspossible tosubstituents. Beginatendnearer tobranchpoint. Thengivesmallest numberspossible tosubstituents. H2 C C H H2 C OH 1,3-butanediol EXAMPLES Cyclicalkanes:Parentname beginswith“cyclo.”Give smallestnumbertosubstituent thatcomesfirstinalphabetical order.Numberindirectionto givesecondsubstituentthe smallerpossiblenumber.(If singlesubstituent,don’tneed “1-.”) H 3C H2 C SH H2 C H 3C ethanethiol H2 C NH 2 (1°) propylamine H 3C H2 C H2 C N H 2C CH 3 CH 3 triethylamine (3°withsameR groups) H2 C H 3C H2 C H N (2°with diff’tRgroups) N-methylpropanamine H 3C H2 C CH 3 CH2CH2CH 3 C C H CH 3 cis-4-methyl-3-heptene H 3C H2 C H2 C H2 C C C H2 C H C H2 C CH 3 CH 3 2-heptyne CH 3 4-methylcyclohexene CH 3 H 3C C H H 2C CH 3 4-ethyl-2-methylhexane H 3C H2 C CH 3 1-ethyl-3-methylcyclohexane H.KimforChem30B 4 FAMILY Ethers PARENT SUFFIX NUMBERING NOTES EXAMPLES Thealkoxygroup–OR istreatedasthe substituent(Alkaneor anotherfunctional groupistheparent). Commonnamesareoftenused forsimpleethers:twoRgroups +“ether.” Commonnamesareusedfor cyclicethercompounds. CH 3 1-ethoxypropaneor ethylpropylether(common) H 3C H2 C O H 3C H2 C O H2 C H2 C H2 H2 H2 C C C OH 3-ethoxypropanol Haloalkanes(or AlkylHalides) Halogenatomis treatedassubstituent (Alkaneoranother functionalgroupisthe parent). Commonnamesareoftenused forsimplehaloalkanes,in format“alkylhalide.” H 3C H2 C Br 1-bromoethaneor ethylbromide(common) AromaticNomenclature FAMILY Aromatic (Benzenecontaining) PARENT “benzene”orcommon nameforsubstituted benzene SUFFIX NUMBERING NOTES Fordi-substituted Commonnamesformonobenzenes:o,m,p substitutedbenzenesareoften systemistypically used: O O used,with substituentslisted C OH CH inalphabetical order.(Ifusing numbering, BenzoicAcidBenzaldehyde numberby alphabetical NH 2 OH priorityof substituents.) PhenolAniline o- CH 3 Toluene m- Ifcommonnameofmonsub’d benzeneisusedasparentand thereare>2substituents,the carbonbearingthefunctional p- groupoftheparentisnumbered 1,thennumberindirectionto givesubstituentslowestnumbers possible. EXAMPLES NO 2 nitrobenzene NO 2 Cl m-chloronitrobenzeneor 1-chloro-3-nitrobenzene(IUPAC) OH O2N p-nitrophenolor 1-hydroxy-4-nitrobenzene(IUPAC) NO 2 Cl OH 2-chloro-4-nitrophenol H.KimforChem30B 5