* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download problem set 5b assigned
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
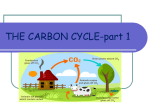
Problem Set 5b ________ OF POINTS Name _____________________________ ____ Honors A. Bonding Compare and contrast ionic and covalent bonding. Use examples. B. Molecules of Life Here is the structure of a generic amino acid. R means any group of atoms. 1. What is the chemical formula for an amino acid? 2. Here is the structure of guanine (a base in DNA). A. Label the elements on the picture on the right. 4. What is the chemical formula for guanine? B Molecular Workbench Activity Center: Choose molecular geometry Do Day 1: 1-5; Answer all questions and sketch all snapshots OR print out report C. Stoichiometry. Please use a separate page to do these. 1. Cellular Respiration is a process that happens in the dark. In it plants combust glucose (C6H12O6) and then use the resulting energy to fuel cellular activity. If a plant begins with 5.00 g of glucose and 5.00 g of oxygen, what will the limiting reactant be? How much carbon dioxide will result? 2. Photosynthesis is a reaction that is the direct opposite of cellular respiration: plants use the sun's energy to combine carbon dioxide into glucose and has leftover oxygen. If a plant begins with 110.0 kg of carbon dioxide and 210.0 kg of water, what will the limiting reactant be? How much glucose can be made? 3. Ethanol is combusted. How much ethanol will be needed to produce 24.5 g of carbon dioxide? 4. Pentane is combined with bromine to produce 3-bromo pentane. If 79.05 g of pentane is used, how much bromine is needed? 5. Acetic acid (hydrogen acetate) and sodium are combined in a single replacement reaction. If 1.67 x 10-4 g of acetic acid are used, how much sodium is needed to use all of the acid? D Draw the structure of these hydrocarbon molecules and name each one. formula name structure C6H12 C5H12 C5H10 C5H8 HONORS (Omit all but 2 problems from part C and 9 or 10 of part E) 1. A student combines 5.00 mL 1 M MgCl2 a 2.00 mL of 0.5 M NaOH. Which is the limiting reactant? Show how you know. Write the net ionic reaction for the precipitate (magnesium hydroxide) produced. 2. Another student combines 20.0 mL of 6M Al2(SO4)3 and 5.00 ml of 18 M BaCl2. How much of the precipitate (barium sulfate) will be produced? What is the net ionic reaction? A net ionic reaction is discussed in your problem solving textbook and in Crash Course Chemistry #9 on youtube as well as on https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vbx5nfAiBlM.