* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download molecule building organic
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
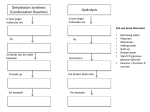
NAME ________________________ INTRODUCTION TO BIOCHEMISTRY HONORS BIOLOGY The cell with the aid of enzymes combines small molecules into large complex molecules. This process makes cell organelles and substances necessary for cell activity. This is the way that starch is formed from glucose molecules and proteins are formed from amino acids. The monomers are linked together by the REMOVAL of a water molecule from the site of the new bond. This process is called dehydration synthesis (dehydration=removal of water, synthesis=joining together. Dehydration synthesis is an important building process in the cell and requires energy. This energy is stored in the chemical bonds. Hydrolysis is the reverse of this process and will break monomers apart by adding water in the presence of the specific enzyme. Directions: Each group is to use the set of molecular models. The black=carbon, red=oxygen, white=hydrogen, and blue =nitrogen. Make a model of the different structures. Have them approved by your teacher before continuing. PROTEINS 1. 2. 3. 4. What elements are in all proteins? What is the shape of proteins? The name of the subunits of a protein are called________________________. Name 4 foods that are rich in proteins. 5. What is a functional group? 6. Name the two functional groups in an amino acid. Write their molecular and structural formulas below Make a model of the two functional groups. 7. model________ Write the molecular and structural formulas for an amino acid. What does the R represent? Make a model of a general amino acid. model________ 1 8. Write the structural formula for the amino acid, glycine. The abbreviation for glycine is __________. How does glycine differ from the general formula? Make a model of glycine. 9. model_______ Write the structural formula for alanine. The abbreviation for alanine is __________. How does alanine differ from glycine? Make a model of alanine. model_______ 10. Diagram the structural formula for the dipeptide combining alanine and glycine. model________ What atoms were eliminated from the combination? These atoms formed the new molecule called __________. The new bond is called a ____________________. The process is called ______________________________________. The process needs an _______________ to lower the activation energy of the reaction. A single long chain of amino acids is called a ________________________. 11. Describe and diagram the four levels of structure of a protein molecule. 12. Name 3 functions of a protein molecule in your body. 2 NAME ________________________ CARBOHYDRATES 1. 2. What 3 elements are always found in carbohydrates? Name 3 properties of a sugar molecule. 3. Name 3 properties of a starch molecule. 4. Name 4 foods which are rich in carbohydrates. Indicate if it is in the category of a starch or a sugar. 5. Name 3 functions of carbohydrates in your body. 6. Write the molecular and structural formula for glucose. Make a model. 7. model________ Write the molecular formula for fructose. How does the molecular formula of fructose compare to glucose? Write the structural formula for fructose. Make a model of fructose. model________ 8. Fructose and glucose are isomers of each other. Define isomer. 9. Glucose and fructose are both monosaccharides. Define monosaccharide. 10. Glucose + Glucose ---------------> Maltose + Water The name of the process shown above is ___________________________. The reactants in the reaction are __________________________________. The products in the reaction are___________________________________. The type of saccharide formed is a _________________________________. 3 11. Diagram the reaction shown in question 10. Make a model of the reactants and show how they combine. model________ 12. Glucose + Fructose -----------------------> Sucrose + Water Sucrose is a _____saccharide. What protein molecule is necessary for this reaction to occur? How does sucrose differ from maltose? Diagram the reaction described above. Make a model of the reactants and show how they combine. model________ 13. Starch is a ________saccharide. What does this mean? 14. Starch molecules are made of __________________. The starch molecule is built from single units by the process called ____________________________________. The breakdown of a starch molecule is called _______________________. Both reactions require a protein molecule called an __________________. Why is this protein molecule needed? 15. For each of these carbohydrates, state where they are found and what their function is. starch: cellulose: glycogen: 16. Most carbohydrates end with the chemical suffix -____________. 4 NAME______________________________ LIPIDS 1. What chemical elements compose a lipid molecule? 2. Which elements are abundant in a lipid molecule? Which element is scarce in a lipid molecule? 3. The main characteristic of a lipid molecule is____________________________. 4. Name 3 different categories of lipid molecules. 5. Describe 3 major functions of lipid molecules. 6. Name the 2 major subunits that make up the lipid molecule, triglyceride. Diagram and label the structural formulas of these molecules. Make a model. 7. model________ Diagram the formation of a triglyceride. Make a model of the reactants and show how they combine. model________ 5 8. The functional group in a fatty acid is ___________. The functional group in the glycerol is ______________. The difference between a fatty acid and a lipid is: 9. A fatty acid can be saturated or unsaturated. A saturated fatty acid has _____ single bonds. An unsaturated fatty acid has ________ and ___________ bonds. Diagram and label a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid. Where do you find saturated fatty acids? Where do you find unsaturated fatty acids? 10. Most molecules are water soluble. Lipids are not soluble in water. Cell membranes are made of lipids. Explain why lipids make a good membrane. 11. Soap isolates the fatty acids in a lipid molecule. This makes soap an emulsifier. The lipid is separated into its soluble and nonsoluble parts. This separation creates a condition which allows lipids to be soluble in water. ***MICELLE O O O O O O O O Label the fatty acids and the glycerol. Label the part which is hydrophillic and the part which is hydrophobic. Define emulsifier. What do you need to add to make lipids soluble in water? *** This structure is called a micelle. It is formed to make lipids soluble. The outside of the micelle is negatively charged. This is attracted to the positive charges in the soap. Label the negative charges on the micelle. 6