* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Photosynthesis means synthesis in presence of light
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
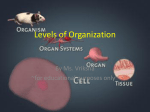
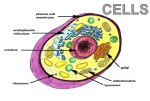
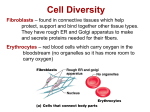
Photosynthesis means synthesis in presence of light. In this process carbon dioxide is absorbed from the atmosphere and water is taken from soil in presence of sunlight and chlorophyll to synthesize the simplest carbohydrate C6H12O6 according to the following chemical reaction: 6CO2 + 6H2O Sunligh, Chlorophyl l C6H12O6 + 6O2 As we can see in this reaction chlorophyll, which is a Mg (II) compound absorbs sunlight in the form of light photons, which are nothing but the energy particles, and sunlight is converted into chemical energy in the form of glucose. Although this process looks simple it undergoes a series of complex steps of bond breaking and bond forming accompanied by energy changes. The overall energy change remains same to preserve the law of conservation of energy. During respiration complex molecules like carbohydrates, proteins etc are broken into simpler molecules CO2 and H2O according to the following reaction: C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O So the respiration reaction is opposite of photosynthetic reaction and both occur as paired processes. Both run hand in glove with each other. During respiration adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules which are the powerhouse of energy are generated which give us energy to do our day-to-day functions. These ATPs and ADPs (adenosine diphosphates) are the phosphates, which are characterized by their curly phosphate bonds, which the chemists and biochemists have characterized as the high-energy bonds. Once again, like the photosynthetic process, respiration is also a complex chemical process involving bond breaking and bond forming with energy transformation. The overall energy again remains constant to obey the law of conservation of energy. Photosynthesis takes place in leaves (stomata) respiration takes place in lungs, which is accomplished in the presence of blood, which is Fe (II) heme compound. Blood in organisms performs two main functions 1) storage of oxygen 2) transport of oxygen. Although the term oxidation is commonly used for these reactions actually it oxygenation not oxidation since blood is oxygenated not oxidized. So simple basic coordination chemistry tells us that on oxygenation, hemoglobin is converted to oxyhemoglobin and it is this oxygen, which is transported through our circulatory system. This brings out the process of respiration resulting into breaking of glucose and other complex molecules into CO2 and H2O. There are 9 basic Human Organ Systems 1) Respiratory System – The main role of this system is to provide gas exchange between the environment and human’s blood stream. Basically, oxygen is inhaled from the air into the lungs; Carbon Dioxide is expelled out of the lungs. Major organs include nose, lungs and trachea 2) Circulatory System – The main role of this system is to circulate (transport) nutrients, hormones, gases like O2 and CO2, wastes throughout the body. Main organs include heart, blood, and blood vessels. 3) Skeletal System – This system provides support to the body, protects vital delicate organs, and provides attachment site for many of the organs. Main organs are bones, tendons, cartilage and ligaments 4) Muscular System – This system provides movement to the body. Muscles together to move limbs and provide the organism with mobility. They also control the movement of nutrients and other materials through the muscles present in organs, like stomach and intestine, and the heart and circulatory system. Main organs include various types of muscles, for example Skeletal and smooth muscles 5) Nervous System – Major function of this system is to send out and receive electric signals throughout the body. It is also responsible for the directing movement and behavior and working with the endocrine system it also controls some of the physiological systems like digestion, blood and nutrient circulation, etc. Main organs are brain, peripheral nerves, and the spinal cord. 6) Digestive System – Major role is to break down and absorb nutrients that control the healthy operation and maintenance of the human body. Main organs are small intestine, mouth, large intestine, esophagus, and stomach. 7) Endocrine System – As supposed to the nervous system where electrical signals are involved, this system is responsible for transmitting and accepting chemical signals throughout the body. Infact, this system works with the nervous system to carry out important processes like nutrient absorption, growth, etc. Main organs of this system are many glands, some of which are thyroid, pituitary, hypothalamus glands 8) Reproductive System – The major role is to produce cells responsible for reproduction. In males, sperm is produced to work with the egg cells in the females body to produce a fetus. This system has different organs for males, which are testes, penis and, seminal vesicles. Females have ovaries, oviducts, vagina, mammary glands, and uterus. 9) Excretory System – This system’s major function is to filter out cellular waste and excess water, toxins and nutrients from the blood stream. Major organs are 2 kidneys, urethra, ureters, and bladder. Animal Cells structure and Functions Animal cell can be identified with these characteristics; first of all, unlike plant and fungi cells, they do not have any cell wall. This lack of cell wall allowed animals to more diverse in terms of cell types, tissues, and organs. An animal cell does have a plasma membrane and membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Some of the organelles and their functions are as follows: 1) Centrioles – they are self-replicating consisting of 9 bundles of microtubules. Main function is to help in organizing cell division but is not completely responsible for it. 2) Cilia and Flagella – in single celled organism, these are responsible for their movement in multicellular organisms they move fluid and other materials. 3) Endoplasmic Reticulum - is an organization of sacs that process, manufacture, and transport chemical compounds to be used inside and outside the cells 4) Golgi apparatus – This is where the distribution and shipment of modified protein and fats which are built in the endoplasmic reticulum takes place. Then these proteins and fats are exported outside the cell. 5) Lysosomes - The main function of this organelle is digestion. The break down of cellular waste products and debris from outside the cell happens here. 6) Mitochondria – Oblong shaped organelles, found in the cytoplasm. These are the power generators in an animal cell, which convert oxygen and nutrients into energy. 7) Nucleus – This is a very complex organelle, which basically along with many other smaller functions works as the administrative and information centre of the cell. 8) Peroxisomes – These kind-of spherical bodies are a diverse group of organelles, again found in the cytoplasm, and bound by a single membrane. 9) Plasma Membrane - All living cells have a plasma membrane in which all of the above organelles reside. In plants and fungi, this membrane is an inner layer of protection surrounded by the rigid cell wall. In animals, this membrane’s only function is to contain and protect the organelles in the cell. 10) Ribosome – these are tiny organelles made up of 60% Ribose Nucleic Acid (RNA) and 40 percent protein. Plant Cell Structure and Functions A plant cell has all of the same organelles as in an animal cell, and they have same functions too, but all plant cells have 3 more organelles which an animal cell doesn’t have, namely cell wall, chloroplast, and a vacuole. Functions:1) Cell Wall - Plant cell walls reinforces structures containing cellulose and lignin to make them rigid. 2) Chloroplast – this is where energy for a plant is produced because chloroplast contains chlorophyll, which drives the photosynthesis process. 3) Vacuole – This is a very large organelle whose main function is just to store organics acids, salts, minerals, etc. Chemistry and Characteristics of living things. To be considered living, all of the following are required. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) requirement of a physical substance Some kind of organization process Ability of reproduce Ability to obtain energy Ability to use that energy Some of the chemical processes occur in a living organisms body are these will be reactions such as oxidation-reduction reactions, photosynthesis and respiration explained earlier. This reaction is also known as electron transfer reactions. Some more processes that identify living things are dehydration, hydrolysis, acid-base reactions, addition, polymerization, etc Dehydration – This term is used in biology to signify the loss of water, which can cause life-threatening condition. Similarly, enough, in chemistry, dehydration refers to a type of elimination reaction that involves the loss of water from a molecule. Hydrolysis – This is a chemical reaction or process in which a molecule is split into two parts when it reacts with water. One of the parts gets an OH- and the other part gets an H+ from the H2O water molecule. The relationship of this process with living things is the hydrolysis of amide links. In this process, hydrolysis of an amide link into a carboxylic acid and an amine product, only the carboxylic acid product has a hydroxyl group derived from the water. A more specific biological case of hydrolysis of an amide link is hydrolyzation of the peptide links of amino acids. Acid – Base Reactions: - Acids and bases have real-life significance. The human body functions properly only at acid-base equilibrium. Crops grow best in soil with the proper pH, which is a result of the balance between acids and bases. Addition/Polymerization – it is a process of reacting monomers together in a chemical reaction to form three-dimensional networks or polymer chains. This process is involved in a very important process in an eukaryptic cell, Actin polymerization. Actin is a globular structural protein that polymerizes in a helical fashion to form an actin filament. They form the cytoskeleton - a three-dimensional network inside plant and fungi cells. These filaments mechanically support the cell, wich determines cell shape, enable cell movements. In muscle cells, these actins play an essential role of muscle contraction.