* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Renaissance Art - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Northern Mannerism wikipedia , lookup
Waddesdon Bequest wikipedia , lookup
Spanish Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Brancacci Chapel wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
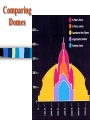
Renaissance Art Italian Early and High Renaissance Art Medieval Art Characteristics of Renaissance Art Realism & Expression Expulsion from the Garden Masaccio, 1427 First nudes since classical times. Perspective The Ideal City Piero della Francesca, 1470 Classicism • Greco-Roman influence • Secularism • Humanism • Individualism • Free standing figures • Contrapposto • Symmetry/Balance Medici “Venus” Emphasis on Individualism Batista Sforza & Federico de Montefeltro: The Duke & Dutchess of Urbino Piero della Francesca, 1465-1466 Light & Shadowing/Softening Sfumato Chiaroscuro Geometrical Arrangement of Figures The Dreyfus Madonna with the Pomegranate Leonardo da Vinci, 1469 Early Renaissance Filippo Brunelleschi 1377-1446 Commissioned to create the dome for Cuppolo of St. Maria del Fiore Also known as “Il Duomo” Comparing Domes Other Famous Domes Il Duomo (Florence) St. Peter’s (Rome) St. Paul’s (London) US capital (Washington) A Contest to Decorate the Cathedral: Sacrifice of Isaac Panels Brunelleschi Ghiberti Ghiberti – Gates of Paradise Baptistry Door, Florence – 1425 - 1452 The High Renaissance 1490-1530 Italy starts to lose political and economic vitality due to internal and external (Spain, French) threats Supported by the Papacy - Leo X; Julius II Pope as heir to revival of Classical Rome New trend: Mannerism – Distortion and restlessness emphasized – Reaction against Early Renaissance focus on classical perfection (perspective, shading, etc)