* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics - Partners4results
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Sagnac effect wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Moment of inertia wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Rotational spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
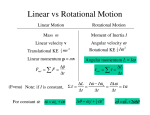
Honors Physics ___________________ Rotational Mechanics Test Version name HONORS Multiple Choice. 1. The number of radians in a revolution is ____. A. 4 radians B. 2 radians C. radians D. not given 2. A red reflector is attached to the spoke of a wheel 10 inches from the center. A blue reflector is attached to the same wheel 5 inches from the center. As the wheel spins, the tangential velocity of the blue reflector is ____ as that of the red reflector. A. half as much B. the same C. twice as much D. not given 3. The centripetal force on an object is always directed ____. A. against the direction of the moving object as it takes a circular path B. tangent to the object’s circular path of motion C. toward the center of the object’s circular path of motion D. not given 4. An amusement park ride has a large rotating platform. Someone who wants a smaller angular velocity would have to stand ____. A. as close to the middle as possible B. as far from the middle as possible C. it does not matter where on the platform he stands D. not given 5. A drum in a clothes dryer goes from 1.8 rev/s to a stop in 6 seconds. The angular acceleration of the drum is ____. (hint: angular acceleration is ) A. -37.7 rad/s2 B. -11.3 rad/s2 C. -1.88 rad/s2 D. not given 6. Torque is a ____. A. rate at which something turns B. rate of change of angular velocity C. measure of how much an object weighs D. not given 7. Angular acceleration is a ____. A. rate of change of angular velocity B. rate at which something turns C. measure of how much an object weighs D. not given 8. An object’s resistance to change in rotational motion is ____. A. torque B. centripetal force C. rotational inertia D. angular acceleration 9. Among the following, the largest torque is the one provided by ____. A. 12 N at 10 meters from the axis of rotation B. 12 N at 5 meters from the axis of rotation C. 6 N at 10 meters from the axis of rotation D. 6 N at 5 meters from the axis of rotation 10. Suppose an ice-skater spins at 3 revs/second. She then changes her body position so that her rotational inertia doubles. Her new angular velocity will be____. A. 4.15 rad/s B. 9.42 rad/s C. 18.85 rad/s D. 37.70 rad/s 11. The rotational inertia of an object generally ____ if more mass is distributed farther from an axis of rotation. A. increases B. decreases C. may increase or decrease D. stays the same 12. A CD changes its angular velocity to provide a constant tangential velocity past the play head. As the play head moves from the edge toward the center of a spinning CD, the angular velocity must ____ to maintain a constant tangential velocity past the play head. A. decrease B. increase C. increase, decrease, then increase again D. stay the same 13. A 1300 kg car moving at 13 m/s takes a turn whose radius is 30 m. What is the size of the centripetal force needed to keep the car on the road? A. 6,591,000 N B. 507,000 N C. 7323 N D. 563 N 14. A condition of “rotational equilibrium” is achieved when ____. A. momentum is conserved B. radius is constant C. torques are balanced D. rotational inertia remains unchanged 15. While moving along, the front wheel of a bicycle makes 1.75 revs/s. If the radius of the wheel is .30 m, then what is the speed of the bicycle? A. 3.3 m/s B. 1.6 m/s C. 1.75 m/s D. 5.8 m/s 16. The angular velocity of the bicycle wheel in problem #15 is ____. A. 11.0 rad/s B. 10.1 rad/s C. 36.4 rad/s D. 3.3 rad/s 17. A ring and a cylinder each have the same mass and radius. Each is allowed to rotate about its normal axis. The ____, has the greater rotational inertia; the ____ would undergo a greater angular acceleration if the same torque was applied to each. A. ring ; cylinder B. cylinder; ring C. ring ; ring D. cylinder ; cylinder 18. In order to “weigh” a fish, a lightweight board is placed across a fulcrum thus balancing the board from the middle. A fish is suspended at a position 60 cm from the middle of the board. A 3 pound tackle box is placed 12 cm from the fulcrum on the side opposite the fish thus balancing the board. What is the weight of the fish? A. 15 lb B. 5 lb C. 1.67 lb D. 0.6 lb 19. The units of angular velocity, torque, centripetal force, and angular acceleration in that order are ____. A. rad/s2 N mN rad/s B. rad/s N mN rad/s2 2 C. rad/s mN N rad/s D. rad/s mN N rad/s2 20. While camping, someone forgets to strap a boat securely to the roof of a car. While taking a turn as the car left the campground, the boat comes off. The boat is most likely to ____ as it comes off the roof of the car. A. continue to follow a curved path of motion B. be pushed out C. be pulled inward D. go in the direction it is moving 21. Newton’s Second Law applied to rotational mechanics may read A. the torque on a body is directly proportional to the angular acceleration, but inversely proportional to the rotational inertia of that body. B. the angular acceleration of a body is directly proportional to the force on the body but inversely proportional to the mass of the body. C. the angular acceleration of a body is directly proportional to the torque on the body but inversely proportional to the rotational inertia of the body. D. the angular momentum of the body is directly proportional to the angular velocity of the body and inversely proportional to the rotational inertia of the body. 22. The rotational inertia of an object depends on _______. A. the mass of the object B. the axis about which the object is rotated C. the mass and the distribution of mass about the axis of rotation D. the mass and the unbalanced torque on the object 23. Two identical meter sticks each have two masses attached to them. Stick A has a 100 gram mass at 10 cm and 90 cm. Stick B has a 100 g mass at 60 cm and 40 cm. If both sticks are rotated about their centers of gravity, the stick with the smaller rotational inertia is________. A. stick A B. stick B C. stick A and stick B have the same rotational inertia D. not enough information 24. A figure skater is spinning about her axis of rotation with her arms spread out. She then draws hem in and her motion changes. Based on the concept of the conservation of angular momentum, the figure skater ________. A. decreased her rotational inertia and increased her angular velocity B. increased her rotational inertia and increased her angular velocity C. decreased her rotational inertia and decreased her angular velocity D. increased her rotational inertia and decreased her angular velocity 25. Suppose someone is pushing on a heavy door with 3 N of force, 0.57 m away from the door’s hinge, at a 40° angle to the door. What torque is this person providing? A. 0 mN B. 1.1 mN C. 1.7 mN D. 1.3 mN Equation Bank: =/t = ( f - i ) / t vt = r vt = C = rF Li = Lf Fc = mvt2 / r or Iii= Iff