Chapter 10
... 25. The linear speed of a point on Earth’s surface depends on its distance from the axis of rotation. To solve for the linear speed, we use v = r, where r is the radius of its orbit. A point on Earth at a latitude of 40° moves along a circular path of radius r = R cos 40°, where R is the radius of ...
... 25. The linear speed of a point on Earth’s surface depends on its distance from the axis of rotation. To solve for the linear speed, we use v = r, where r is the radius of its orbit. A point on Earth at a latitude of 40° moves along a circular path of radius r = R cos 40°, where R is the radius of ...
Slide 1
... The comfortable 1 g we experience at Earth’s surface is due to gravity. Inside a rotating spaceship the acceleration experienced is the centripetal/centrifugal acceleration due to rotation. The magnitude of this acceleration is directly proportional to the radial distance and the square of the rotat ...
... The comfortable 1 g we experience at Earth’s surface is due to gravity. Inside a rotating spaceship the acceleration experienced is the centripetal/centrifugal acceleration due to rotation. The magnitude of this acceleration is directly proportional to the radial distance and the square of the rotat ...
ROTATIONAL VECTORS AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM
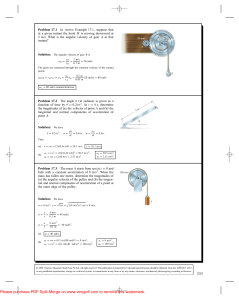
... INTERPRET This problem involves calculating the magnitude of the average acceleration given the initial and final angular velocities, and the time interval between the two. We are also asked to find the angle that the average angular acceleration vector makes with the horizontal. DEVELOP Let the x a ...
... INTERPRET This problem involves calculating the magnitude of the average acceleration given the initial and final angular velocities, and the time interval between the two. We are also asked to find the angle that the average angular acceleration vector makes with the horizontal. DEVELOP Let the x a ...
Giancoli Ch 8.Word
... orbit /t = (2π rad)/(1 yr)(3.16 107 s/yr) = 1.99 10–7 rad/s. (b) The Earth rotates one revolution in one day, so we have rotation /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/day)(3600 s/h) = 7.27 10–5 rad/s. 15. All points will have the angular speed of the Earth: = /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/ ...
... orbit /t = (2π rad)/(1 yr)(3.16 107 s/yr) = 1.99 10–7 rad/s. (b) The Earth rotates one revolution in one day, so we have rotation /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/day)(3600 s/h) = 7.27 10–5 rad/s. 15. All points will have the angular speed of the Earth: = /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/ ...
CHAPTER 8
... orbit /t = (2π rad)/(1 yr)(3.16 107 s/yr) = 1.99 10–7 rad/s. (b) The Earth rotates one revolution in one day, so we have rotation /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/day)(3600 s/h) = 7.27 10–5 rad/s. 15. All points will have the angular speed of the Earth: = /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/ ...
... orbit /t = (2π rad)/(1 yr)(3.16 107 s/yr) = 1.99 10–7 rad/s. (b) The Earth rotates one revolution in one day, so we have rotation /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/day)(3600 s/h) = 7.27 10–5 rad/s. 15. All points will have the angular speed of the Earth: = /t = (2π rad)/(1 day)(24 h/ ...
Momentum
... Newton's second law as discussed in an earlier unit. Newton's second law (Fnet=m*a) stated that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting upon the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. When combined with the definition of acceleration (a=ch ...
... Newton's second law as discussed in an earlier unit. Newton's second law (Fnet=m*a) stated that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting upon the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. When combined with the definition of acceleration (a=ch ...
final exam - PHYSICS57
... 1. At the instant when the traffic light turns green, an automobile starts with a constant acceleration of 1.8 m/s2. At the same instant a truck travelling with a constant speed of 8.5 m/s overtakes and passes the automobile. (a) How far beyond the starting point will the automobile overtake the tru ...
... 1. At the instant when the traffic light turns green, an automobile starts with a constant acceleration of 1.8 m/s2. At the same instant a truck travelling with a constant speed of 8.5 m/s overtakes and passes the automobile. (a) How far beyond the starting point will the automobile overtake the tru ...
Phys11U_Unit 2_Ch4_CE_ms_for_Questions
... You can measure the force of friction acting on a stationary object by pulling on it with a spring scale or a force meter. If you measure the largest force required to move the object, you will determine the maximum amount of friction the surface exerts on the object just before it starts to move. I ...
... You can measure the force of friction acting on a stationary object by pulling on it with a spring scale or a force meter. If you measure the largest force required to move the object, you will determine the maximum amount of friction the surface exerts on the object just before it starts to move. I ...
Physics Review
... c. an electrical conductor b. wood d. an electrical insulator Resistance is affected by a material’s a. thickness. c. temperature. b. length. d. all of the above Which of the following would reduce the resistance of a metal wire? a. increasing its thickness c. increasing its length b. increasing its ...
... c. an electrical conductor b. wood d. an electrical insulator Resistance is affected by a material’s a. thickness. c. temperature. b. length. d. all of the above Which of the following would reduce the resistance of a metal wire? a. increasing its thickness c. increasing its length b. increasing its ...
ROTATIONAL MOTION
... The sun-earth system is similar to this except that the sun’s mass is so much greater than the earth’s that the center of mass (called the barycenter for astronomical objects orbiting each other) is only 450 km from the center of the sun. Q7.12. Reason: When the mass is distributed close to the axis ...
... The sun-earth system is similar to this except that the sun’s mass is so much greater than the earth’s that the center of mass (called the barycenter for astronomical objects orbiting each other) is only 450 km from the center of the sun. Q7.12. Reason: When the mass is distributed close to the axis ...
Gr 12 Physics Exam - Sample for Review
... ____ 10. When forces acting on an object are in equilibrium, the object can still be moving. _________________________ ____ 11. A car accelerates from rest when a traffic light turns green. A cup of coffee that was sitting on the dashboard of the car falls into the driver’s lap. The driver could rig ...
... ____ 10. When forces acting on an object are in equilibrium, the object can still be moving. _________________________ ____ 11. A car accelerates from rest when a traffic light turns green. A cup of coffee that was sitting on the dashboard of the car falls into the driver’s lap. The driver could rig ...
NCFE Review
... a. FALSE - Distance is the scalar and displacement is the vector. Know this one! b. TRUE - Displacement is the change in position of an object. An object which finishes where it started is not displaced; it is at the same place as it started and as such has a zero displacement. On the other hand, th ...
... a. FALSE - Distance is the scalar and displacement is the vector. Know this one! b. TRUE - Displacement is the change in position of an object. An object which finishes where it started is not displaced; it is at the same place as it started and as such has a zero displacement. On the other hand, th ...